Charger-machine with control of inclusion and charge. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The proposed version of the charger is automatically disconnected from the AC mains at the end of charging and does not contain scale instruments. The control of the inclusion and flow of the charging current is carried out using two indicator lights.
The device works as follows (Fig. 1). When the AC mains is turned on, the neon lamp HL1 lights up. The primary winding of the transformer T1 is disconnected from the mains by open contacts K1.1. When connected to the output of the battery device, thanks to normally closed contacts K2.1, relay K1 is activated, connecting the charger to the network. In the secondary circuit, the charging current begins to flow, and the HL2 lamp lights up.
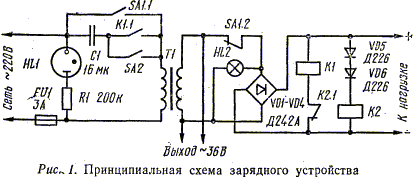
Upon reaching the voltage, which is typical for a charged battery, relay K2 is activated, which, with its contacts K2.1, breaks the winding circuit K1. The device is then disconnected from the network. The winding of relay K2 draws very little current compared to normal discharge, so the battery can be in this state for a long time, waiting for disconnection.
If a fully discharged battery is connected to the device, which is not able to turn on relay K 1, then charging can be started with the SA2 "Start" button, connected in parallel with contacts K1.1. If the batteries are supposed to be charged frequently, then it is more convenient to use the "Start" toggle switch. In the event of an accidental break in the battery circuit, relay K1 turns off at the first passage of the pulsating voltage of the secondary winding of the transformer through zero, which leads to the disconnection of the device from the network.
From the description of the operation of the device, it follows that the glow of the HL2 lamp indicates the flow of the charging current. For this reason, it was possible to exclude the scale instrument.
The device can use transformers with an output voltage of 25 to 40 V with a power of about 150 watts. The secondary winding must have a wire diameter of at least 2 mm. In this design, a transformer TOS-250 with an output voltage of 36 V is used. Relay K2 RES-9, passport RS4.524.200 or RS4.524.201 is used. This relay is selected from the condition of reliable operation at a voltage of 15,8 ... 16,2 V, i.e., when the battery with a nominal voltage of 13,2 V reaches the final charging voltage. The selection is easier to carry out, including in series with the relay K2 from one to three diodes D226 in the forward direction. Relay K1 is any relay that operates at a voltage of 8 ... 9 V and allows switching alternating current with a power of at least 2 A at a voltage of 220 V, for example, MKU-48. Lamp HL1 - any neon, you can even use a faulty thyratron MTX-90. Lamp HL2 - LN-13,6. To clearly distinguish the lamps, the HL2 cap must be a different color, such as green. Diodes VD1 - VD4 should be selected from the D242-D247 series. They must be installed on duralumin plates or other radiators with a surface area of about 100 cm2. Button SA2 - KU-1, allowing switching current of at least 3 A.
A certain convenience is the possibility of using the charger as a source of alternating voltage 36 V. For this purpose, a dual toggle switch SA1 ТЗ has been introduced.
Capacitor C1 - MBGO, MBGP for a voltage of at least 600 V. Its capacitance depends on the impedance of the transformer, it is selected according to the strength of the required charging current. In this design, to obtain a current of 5,5 A, C1 with a capacity of 15 ... 16 μF is selected. If necessary, you can enter a forced or other charging mode by switching various capacitors.
The described charger has been in operation for several years, having proven itself to be very convenient and reliable.
Author: V. Sosnitsky; Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Transplanting a beak to a vulture
13.06.2023
As a result of a unique operation performed by veterinarians, the beak was successfully transplanted to the vulture. This white-backed vulture suffered serious damage when it was hit by a car in northwest South Africa. The accident caused the bird to lose one eye and break off its beak, which posed a serious threat to its survival as it could no longer feed. In the natural environment, she would be doomed to starvation.
However, the vulture was taken to the veterinary department of the University of Pretoria, where a team of experts took on the daunting task. The first two attempts to attach an artificial acrylic beak to a bird were unsuccessful, as they did not have sufficient strength and broke when eating. The doctors decided to take a different approach and turned to the beak of another vulture.
The world premiere of transplanting a beak to a vulture took only 30 minutes. The beak was attached to the damaged vulture with six screws. Currently, the bird feels good and shows positive results.
Experts predict that in a few years the vulture will grow a new beak again, and doctors will be able to remove the prosthesis. This successful operation opens up new prospects for restoring beak functionality in affected birds, which is essential for their survival and adaptation to the wild.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Chinese unnamed smartphones fell in price
▪ RBC Waltz
▪ Lenovo F20 iCoke
▪ Automation against pirates
▪ Microwave oven that chooses how to cook food
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the Radio Control website. Article selection
▪ article Stability of the functioning of economic objects and technical systems in emergency situations. Basics of safe life
▪ article What are the circumstances of victory at the Olympics entrenched in the Australian idiom? Detailed answer
▪ Article Incense tree. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Module of electronic hat and adder of drum signals. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Rubbing knots. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: