Charger for 12-volt batteries, 4,5 Ah. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
If the battery output voltage drops below 11,5 Volts (this parameter can be configured), then the device starts charging it. When the battery output voltage rises to 12,5 Volts (this parameter can be configured), the device will automatically stop charging.
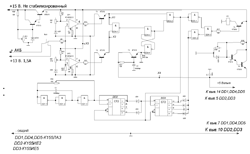
For the operation of the device, a constant voltage of 15 Volts (not stabilized, can be taken from a diode bridge), with a power of 0,5 A. And a constant voltage of 13 Volts, with a power of 2 A (depending on the technical characteristics of the battery) is required.
(click to enlarge)
The device consists of comparators assembled on K140UD12 operational amplifiers. Timer assembled on DD1,DD2,DD3 chips and match node on DD4,DD5 chips.
When the device is turned on, it measures the voltage on the battery and compares it with the threshold (for example, 11,5 V) if the voltage at the battery output is less than the threshold, then the device starts charging the battery (while the voltage at the battery output is not measured), after 7 minutes of charging, the device stops charging battery and check its voltage. If the battery output voltage is less than 12,5 Volts, then the device starts charging the battery again. And so on until the voltage at the battery output becomes higher than 12,5 volts.
For convenience in setting up the device, I built in control points there (X1, X2, X3, X4). At point X3 there should be +15 Volts. At point X4 there should be a voltage of +5 Volts, it can be adjusted using a variable resistor R19. The voltage at point X1 is the threshold for turning off battery charging. It can be adjusted using a variable resistor R2 (I set the voltage to 12,5 volts there). The voltage at point X2 is the threshold for starting battery charging. It can be adjusted using a variable resistor R10 (I set a voltage of 11,5 volts there). To adjust the thresholds for the device, you can use a low-power PSU with an adjustable output voltage of 10-14 volts. You need to put a diode on its output and connect it instead of the battery.
The device uses microcircuits from the K155 series and operational amplifiers K140UD12. The RES22 relay, transistors from the KT315 and KT815 series are used. Resistors and diodes - any low-power.
Author: Giorgi Gulabyan; Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Glasses clean themselves
22.11.2002
Pilkington engineers have created so-called self-cleaning glasses that do not require any human care at all.
The new glasses are based on a special titanium dioxide coating with a thickness of only 0,04 microns, which has two very important properties.
Firstly, thanks to it, under the influence of ultraviolet radiation, organic substances that fall on the glass are split. Secondly, the coating does not allow rainwater to collect in drops: the water flows off it in a continuous stream, washing away the accumulated dust and dirt.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Developed the finest ion sieve
▪ Novelties in electronic technology and fashion for clothes
▪ Facial similarity increases trust between people of the same sex
▪ Water battery for electric vehicles
▪ Eco-friendly steam generator for desalination and water treatment
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Metal detectors. Article selection
▪ article Legal aspects of self-defense. Basics of safe life
▪ article Under what conditions can ice wool appear on trees? Detailed answer
▪ article Hellebore reddish. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Watering the machine. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Guess the time. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: