Nickel-cadmium batteries. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Nickel-cadmium batteries, commonly referred to as nickel-cadmium cells, are somewhat different from most dry cells, such as the manganese-zinc battery commonly used in flashlights. As the battery discharges, it loses some of its voltage. This effect is manifested in the brightness of the flashlight bulb. As the battery drains, the glow becomes more and more dimmer until it stops altogether.
In contrast, nickel-cadmium cells hold the voltage quite stable during the discharge. This can be seen from the constancy of the glow up to a deep charge. After the element is discharged, the voltage on it quickly drops and the glow stops. On fig. 1 for comparison shows the dependence of the voltage on the degree of discharge of the elements of the two mentioned types.
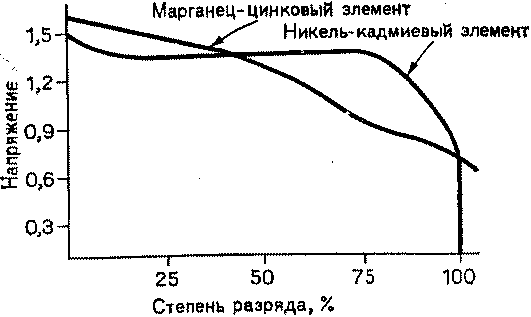
As you can see, to determine the remaining life of a manganese-zinc cell, you simply need to measure the voltage across it. For a nickel-cadmium element, this is not so easy to do. An 80% discharged cell produces the same voltage as a freshly charged cell. Thus, when recharging a nickel-cadmium cell, some difficulty arises. Until the element is completely discharged, we cannot judge its condition. In addition, nickel-cadmium cells are very sensitive to overcharging, which can damage them. So a partially discharged cell poses a really tricky question: how much charge can it take on?
Recharging nickel-cadmium cells
To better understand the principle of operation of the charger, you must first familiarize yourself with the operation of the nickel-cadmium cell itself. You can start consideration with a completely discharged element. To charge it, you need to pass current through it.
Due to its design, the nickel-cadmium cell has a fairly high internal resistance, which is inversely proportional to the amount of charge accumulated in the cell: the lower the charge, the higher the resistance.
Due to the presence of internal resistance, part of the energy of the charging current is converted into heat. Therefore, it is necessary to start the charge with a small current, otherwise the energy dissipated in the internal resistance in the form of heat will lead to the failure of the element.
As the charge increases, the internal resistance of the cell decreases. The lower the resistance, the less heat is dissipated and the more efficiently the charge of the cell flows. In addition, more charging current can now be passed through the cell, which will further speed up the charging process. In practice, it is possible to complete the charge cycle at a current significantly higher than the initial current.
However, it is very difficult to regulate and maintain such a charge mode. For simplicity, manufacturers recommend the maximum safe current regardless of battery condition.
For disk nickel-cadmium cells, this current does not exceed 330 mA. Even a completely discharged cell with a high internal resistance can be charged with such a current without fear. However, the answer to the question has not yet been received: what amount of charge will not harm the element?
The charging current mentioned above can only be maintained until the battery is fully charged. This usually takes 4 hours. If you continue recharging, there is a danger of overcharging the cell, which can lead to a decrease in battery life or, worse, destruction of the cell. Thus, if the battery is only half discharged, it can be easily recharged without even knowing it.
This is why the manufacturer recommends slow recharging. For a disk element, the charging current should not exceed 100 mA. With slow charging, you can charge the cell without fear of overcharging for the recommended 14 hours required to charge a fully discharged cell. In fact, it is possible to constantly lightly charge the element without fear of its destruction: the charge rate is quite low and excess energy is easily dissipated by the element.
Author: Alexander Torres; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
See other articles Section Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Sex problems on Mars
03.06.2018
The idea of colonizing Mars is not just science fiction; NASA and space agencies around the world are working hard to determine what it will take for humanity to take root on the Red Planet. Humankind faces various problems, such as growing food sources or an unfavorable habitat. But the biggest problem for colonization, scientists see - sex.
In a new research paper, an international team of scientists is studying the problems of humans being born on the surface of Mars.
The first and most obvious obstacle is the low gravity environment, which can pose a serious threat to the processes of conception and pregnancy, which seem so simple on Earth. Scientists are aware of the problems of astronauts who have spent months and in some cases years in space. Lower gravity causes muscles to deteriorate rapidly and can even weaken bone structure. In addition, astronauts sometimes experience vision problems and even changes in the shape of their brains.
The study explores the inherent challenges of sustaining a small colony of settlers on the planet. The concept of "love" should not stand in the way of survival. In addition, some people will never be allowed to have children due to undesirable traits that pose a danger to the colony as a whole.
But the most frightening thing is that in the course of colonization, a new kind of person may appear that can thrive on Mars, but cannot live on Earth.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Photonic chip converting waves with high efficiency
▪ Sensor for biometric breath authentication
▪ Smartphone use improves memory
▪ Phobos will be destroyed by Mars
▪ MCP1810 - Lowest Iq LDO in the industry
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Tips for radio amateurs. Selection of articles
▪ article by Lucius Cornelius Sulla. Famous aphorisms
▪ article Why do some people have curly hair? Detailed answer
▪ article Agave furcroid. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ Multicombi article. A series of combined multivibrators. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Overhead power lines with voltage above 1 kV. Rapprochement of overhead lines with airfields and heliports. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: