 Free technical library
Free technical library
Chips for digital frequency synthesizers KF1015PLZA, KF1015PLZB. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Application of microcircuits
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
High-speed microcircuits KF1015PLZA and KF1015PLZB are designed to build modern digital frequency synthesizers with PLL for HF, VHF and decimeter wave bands. The devices are manufactured using CMOS technology with a polysilicon gate.
Microcircuits of the KF1015PLZ series are produced in a plastic 16-pin miniature package 4308.16-1 (Fig. 1). Weight of the device - no more than 0,3 g.

Ris.1
The microcircuit includes (see the block diagram in Fig. 2) a reference frequency generator, a reference frequency divider, an amplifier-shaper of input RF pulses, a binary frequency divider path with a programmable division ratio, consisting of a two-module preliminary frequency divider by 31 or 32, five-bit prescaler control counter, twelve senior digits of a programmable divider and a logic control unit, a frequency-phase detector and twenty-bit receiving and buffer registers.
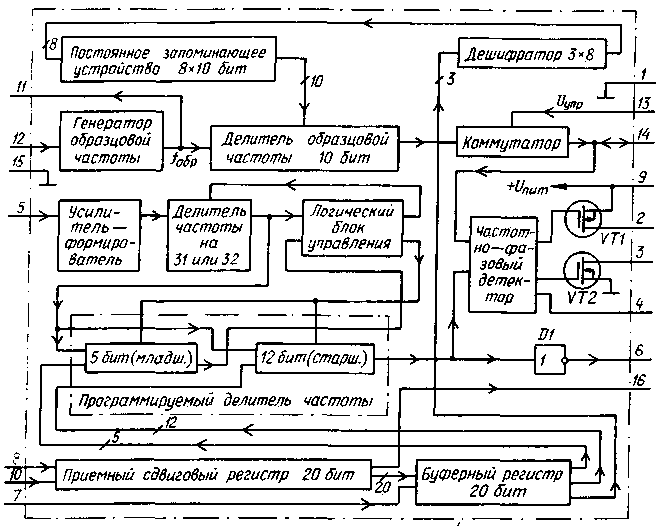
Fig.2 (click to enlarge)
The microcircuit included in a typical circuit with attached components is capable of operating in digital synthesizers with a PLL of the meter and decimeter ranges with reduced power consumption.
Pinout of the microcircuit: pin. 1 - common for the receiving and buffer registers, the path of the programmable frequency divider and the frequency-phase detector, negative power output; pin. 2 - charging output of the frequency-phase detector (drain of a field-effect transistor with a p-channel); pin. 3 - bit output of a frequency-phase detector (drain of a field-effect transistor with an n-channel); pin. 4 - control output of indication of phase synchronization in the PLL loop; pin. 5 - RF input of the amplifier-shaper of the path of the programmable divider; pin. 6 - programmable divider output; pin. 7 - input permission to rewrite information from the receiving register to the buffer (T); pin. 8 - input of clock pulses for recording information (C); pin. 9 - positive power output; pin. 10 - input recording information about the division coefficients (D); pin. 11 - output for connecting a quartz resonator; exemplary frequency generator output; pin. 12 - output for connecting a quartz resonator; signal input of an external reference frequency generator; pin. 13 - input signal to turn off the output of the divider of the reference frequency (at level 1); pin. 14 - output of the reference frequency divider (at level 0 on pin 13) or input of the frequency-phase detector (at level 1 on pin 13); pin. 15 - common for the generator and the reference frequency divider, negative power output; pin. 16 - control output of the receiving register.
Main characteristics at Tacr.av=25±10°C and supply voltage 5 V
Rated supply voltage, V ............... .4,5...5,5
Programmable Frequency Divider Path Divider Limits ......992-131071
Programmable Divider Step .................................................. 1
Dividing ratios of the reference frequency divider ..................100,200 400,512, 640,800, 1000,1024
Programmable divider input frequency interval, MHz, for KF1015PLZA ........ .50...1000 KF1015PLZB ..........20...800
Reference frequency divider input frequency interval, MHz ..............................1 ...50
Sensitivity of the shaping amplifier, Veff, (lower value - for frequency within 50...500 MHz) ..............0,2...0,9
Sensitivity at the input of the reference frequency generator (for an external quartz oscillator), mVeff. .................100...150
Maximum current consumption, mA, no more ............... 15
Output impedance of the outputs of the frequency-phase detector, Ohm, no more
Output impedance of the reference frequency divider, Ohm, not more than ..........200
Output impedance of the control output of indication of phase synchronization, Ohm, not more than .................................200
Output impedance of the exemplary frequency generator, Ohm, not more than .......... 200
The input current of the input for rewriting information from the receiving register to the buffer (pin 7), the input of clock pulses for writing information (pin 8), the input for recording information about the division ratio (pin 10) and the input of the signal to turn off the output of the reference frequency divider (pin. 13), µA, not more than ......................±1
The input current of the RF input of the amplifier-shaper (pin 5) and the input of the reference frequency generator (pin 12), µA, for a low level signal, not less ... -30 high level, not more than . .+30
Limit values
Limit values of supply voltage, V ........3...6
The highest electrostatic potential, V, not less than ............... 150
Ambient temperature operating range, °С ... .-60 ... +70
Limit values of ambient temperature, °С ................-70;+85
On fig. 3 shows one of the possible schemes for switching on the device. When choosing a quartz resonator for a reference frequency generator, it must be taken into account that the resonator must operate at a parallel resonance, the frequency of which is greater than the serial frequency. By connecting a coil with an inductance of 10 μH in series with the resonator, it is possible to approach the frequency of the series resonance, the value of which is usually marked with a quartz resonator.

Fig.3 (click to enlarge)
By adjusting the capacitor C1, stable generation is achieved, which can be seen by removing the signal from the pin. 11 microchips. In normal mode, this signal is a sinusoid with a double amplitude of 1 ... 1.2 V with a constant component of about half Upit.
If an external stable quartz oscillator is used as a reference, its output signal with a voltage of 100 ... 250 mV is fed to the pin. 12 through an isolation capacitor with a capacity of 1000 ... 10 pF.
A significant reduction in power consumption (when operating at a frequency of up to 600 MHz) can be achieved by lowering the supply voltage to 3,3 ... 4 V. In this case, the current consumption decreases to 4 ... .
Authors: V. Melnik, V. Nikitin, Moscow; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Application of microcircuits.
See other articles Section Application of microcircuits.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Wheat and peas will grow faster
15.01.2018
Researchers from the English Research Institute in Norwich, the universities of Queensland and Sydney have developed a technology for accelerated crossing of plants. Scientists and engineers have reduced the life span of one generation of plants, from seed to seed, to eight weeks. This breeding rate allows for up to six experimental crops per year; this is three times more than usual.
Why plant growth is important, explains study leader Brande Wulff: "A crowded planet needs large yields and disease and pest resistant crops. The faster we can test new varieties, the faster we can give farmers new, better crops." ".
Plants grown using the accelerated method look just as good as normal plants and produce as many seeds as those grown in the usual time frame. New varieties of agricultural plants bred using accelerated crossbreeding technology will be on the market in 10 years, Wolf said.
In greenhouses for accelerated crossing, light is 22 hours; additional lighting after sunset and even at noon is provided by economical LEDs. Room settings. such as humidity and temperature are monitored at all times by a system of sensors and regulators. To date, the authors of the study, published in Nature Plants, have managed to harvest six crops a year of the following crops: wheat, durum (durum "pasta" wheat), barley, beans and peas.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Life forms unknown to science live in the human intestine
▪ To remember, you need to retell
▪ Compact photorelays with increased insulation voltage 3,75 kV
▪ Xiaomi car running on HyperOS
▪ Short Throw Projector LG PH450UG-GL
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Electric meters. Article selection
▪ article by Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec. Famous aphorisms
▪ article Who Discovered Australia? Detailed answer
▪ article Operator for the dispatching service of elevators. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Installation of external electrical wiring. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Reversible broadband cascade. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: