A simple logic probe. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Measuring technology
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Using a probe, the circuit of which is shown in the figure, you can determine the voltage level at the output of logic elements, control the passage of pulses and detect an open in the electrical circuit. When a logic 1 is applied to the input of the probe, transistor V1 enters saturation mode, and transistor V2 closes; As a result, LED H1 lights up with a red glow. If a logical 0 is applied to the input of the probe, then the transistor V1 will be closed, and V2 will be open. At the same time, LED H2 lights up with a green glow.
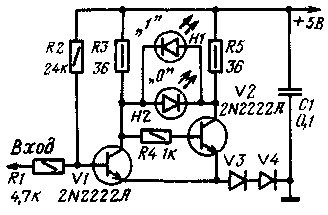
Resistor R3 is chosen so that if there is a high resistance at the input of the probe (an open in the circuit of the checked logic element), both LEDs do not light up.
The passage of a pulsed signal of a rectangular shape of positive polarity should cause the glow of one LED, and the negative - the other.
In a logic probe, you can use, for example. transistors of the KT342 series. Diodes V3, V4 - any low-power silicon, LEDs - AL102B (H1) and AL102V (H2).
Literature
- "Wireless World" (England). 1976 September
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Measuring technology.
See other articles Section Measuring technology.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Coolest star emitting radio waves found
25.07.2023
Astronomers from the University of Sydney have made an exciting discovery by detecting radio emission from an ultracold brown dwarf. This dwarf is a ball of gas that "boils" at a temperature of about 425 ° C without nuclear reactions. Usually such stars do not emit radio waves, so the reason for this phenomenon remains a mystery.
The star T8 Dwarf WISE J062309.94-045624.6 lies about 37 light-years from Earth. Its radius is from 0,65 to 0,95 of the radius of Jupiter, and the mass is 4-44 times the mass of the largest planet in the solar system (the exact value of the mass has not yet been determined). Even though this brown dwarf is not the coldest, astronomers have only observed radio emission from hotter stars so far.
Size comparison of various objects: Sun, low-mass star, brown dwarf, Jupiter, Earth. Brown dwarfs occupy an intermediate position between the smallest stars, where nuclear reactions of hydrogen take place, and large gas giants. Image: NASA/JPL
The emission of radio waves from stars is associated with the presence of strong magnetic fields. It is hypothesized that ultracold brown dwarfs do not have a fast enough rotational dynamic to generate strong magnetic fields that would be visible from Earth. However, about 10% of them still emit radio waves. Astrophysicists cannot yet explain the reason for this phenomenon.
One of the key hypotheses is that the fast rotation of ultracold brown dwarfs plays an important role in the formation of strong magnetic fields. When the magnetic field of such a star is intertwined with an atmosphere moving at a speed different from the ionized atmosphere, it can generate electrical currents. The emergence of electrons in the region of the star's magnetic pole, combined with its rotation, causes periodic flashes.
"Finding a brown dwarf that emits radio waves at such a low temperature is an important discovery," the authors of the study note. They believe that further observation of the properties of this star will help confirm the hypothesis or collect new data that explain the generation of a strong magnetic field in these cool stars.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Huawei is already working on 6G connectivity
▪ Hyrope smart jump rope
▪ Mercedes electric cars with wireless charging
▪ Robot policeman
▪ Safe magnetic socket
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Radioelectronics and electrical engineering. Article selection
▪ article Science can do a lot of geeks. Popular expression
▪ article Why do opossums carry offspring? Detailed answer
▪ article Vein loop. Travel Tips
▪ article LED strip in a table lamp. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Transceiver YES-97 (GPA and PIP). Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: