Hidden wiring indicator on microcircuits. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Indicators, detectors, metal detectors
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
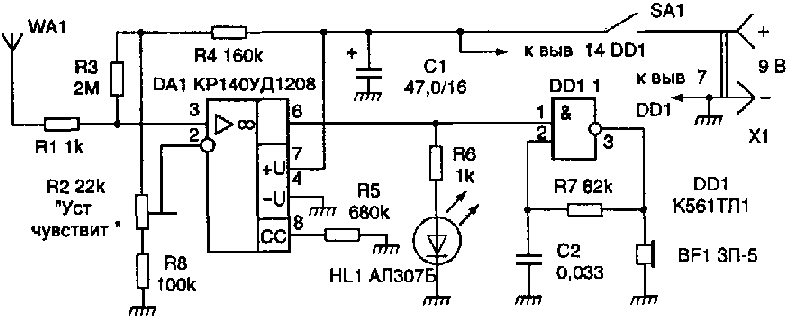
scheme concealed wiring indicator shown in fig. 1. It consists of two nodes - an AC voltage amplifier based on a micropower operational amplifier DA1, and an audio frequency oscillation generator assembled on an inverting Schmitt trigger DD1.1 of the K561TL1 microcircuit, a frequency setting circuit R7C2 and a piezoelectric BF1.
When the WA1 antenna is located close to the current-carrying wire of the mains, the EMF of the industrial frequency of 50 Hz is amplified by the DA1 microcircuit, as a result of which the HL1 LED lights up. The same output voltage of the operational amplifier, pulsating at a frequency of 50 Hz, starts the audio frequency generator.
The current consumed by the device's microcircuits when powered from a 9 V source does not exceed 2 mA, and when the HL1 LED is turned on - b ... 7 mA. The power source can be a battery 7 D-0,125, Corundum or similar foreign production.
Sometimes, especially when the desired electrical wiring is located high, it is difficult to observe the glow of the HL1 indicator and an audible alarm is quite enough. In this case, the LED can be turned off, which will increase the efficiency of the device. All fixed resistors - MLT-0,125, tuned resistor R2 - type SPZ-38B, capacitor C1 - K50-6. The WA1 antenna is a foil pad on a board about 55x12 mm in size.
(click to enlarge)
The circuit board is placed in a case made of dielectric material so that the antenna is in the head part and is as far away from the operator's hand as possible. On the front side of the case there is a power switch SA1, an LED HL1 and a sound emitter BF1. The initial sensitivity of the device is set by a tuning resistor R2. An unmistakably mounted device does not need to be adjusted.
Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Indicators, detectors, metal detectors.
See other articles Section Indicators, detectors, metal detectors.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Technology of three-dimensional imaging of cells and tissues under the skin
29.03.2016
Scientists from Stanford University have created a new technology for three-dimensional imaging of cells and tissues under the skin. The development could improve the diagnosis and treatment of some forms of cancer and blindness.
The technology was named MOZART (MOlecular imaging and characterization of tissue noninvasively At cellular ResoluTion). “We tried to look into the body of a living organism and see information at the level of one cell. Until now, there was no way to do this,” said Adam de la Zerda, one of the authors of the study. The technology will allow doctors to track how tumors invisible under the skin respond to treatment, as well as how individual cells are released from the tumor and move around the body.
The scientists used non-toxic gold nanorods that vibrate at lower frequencies or wavelengths of light, according to the Stanford University website. These vibrations scatter light in a special way that can be registered with a microscope. The technology can detect tumors in the skin, colon and esophagus, as well as abnormal blood vessels that appear in the early stages of macular degeneration, a major cause of blindness, the scientists said.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Wavecom includes Lua interpreter support
▪ Protection of robotic vehicle sensors from insects
▪ Hardware Optimization Reduces 5G Power Consumption
▪ Samsung is developing a 600-megapixel sensor
▪ AIWA TVX-F21D1 - CRT TV with built-in DVD player
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Protection of electrical equipment. Article selection
▪ article Methods of extraction and disinfection of water in conditions of autonomous existence. Basics of safe life
▪ article Why does the appearance of the starry sky change during the year? Detailed answer
▪ article Working on a film wrapping machine type DEM-L8-12, 4255-SA, etc. Typical labor protection instruction
▪ article Contactless proximity sensors. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Selection of wire diameter when it is necessary to replace one wire with two or three. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: