The phototransistor is a smoke detector. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Indicators, detectors, metal detectors
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
In a fire-fighting device, the principle of operation of which is shown in Fig. 1, a field effect phototransistor having a high sensitivity to changes in illumination is used. The luminous flux from the lighting lamp L1 passes parallel to the window of the phototransistor, and in the absence of smoke, no current flows through the phototransistor.
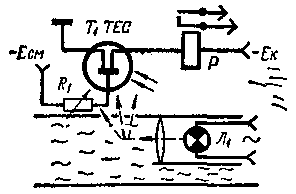
Fig. 1
The appearance of even faint smoke causes light to scatter, some of which enters the phototransistor window. The collector current increases under the influence of the luminous flux, the executive relay R is activated, which turns on the power supply circuit of the device that gives the alarm signal with its contacts.
For similar purposes, an ordinary phototransistor can be used, which is an integral part of a trigger assembled according to the circuit in Fig. 2.
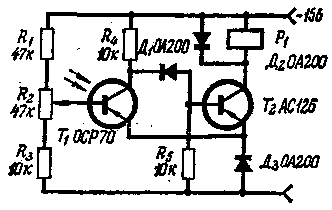
Fig. 2
Light control in this device is as follows. In the standby state, transistor T1 is lit, current flows through it, no current flows through transistor T2 and the relay winding P1. Dimming the light output reduces the current through the phototransistor. Transistor Tg goes into saturation mode, its collector current triggers the relay and closes the contacts in the power supply circuit of the signaling device.
Literature
- "Toufe I Electronigue", 1969, No. 332
Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Indicators, detectors, metal detectors.
See other articles Section Indicators, detectors, metal detectors.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Atomic television
30.08.2022
NIST scientists demonstrate the use of Rydberg-state rubidium atoms as receivers that can receive live video and even play video games. A stable radio signal is applied to a glass container filled with atoms in the Rydberg state. The modulated output is then fed to a TV, where an analog-to-digital converter converts the signal into a video graphics array format for display. This work is part of the NIST on a Chip program.
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) have adapted their atomic radio to detect and display color television and video games.
Atom-based communication systems are of practical interest because they can be physically smaller and more tolerant of noisy environments than conventional electronics. The addition of video can improve radio systems, for example in remote locations or in emergencies.
The NIST receiver uses atoms prepared in high-energy Rydberg states, which are extremely sensitive to electromagnetic fields, including radio signals. These sensors also measure the signal strength associated with the International System of Units (SI).
Scientists use two different color lasers to produce gaseous rubidium atoms in Rydberg states in a glass container. The team had previously used a cesium atom setup to demonstrate a basic radio and a headphone device to increase sensitivity by a factor of XNUMX.
To prepare for video reception, a stable radio signal is applied to a glass container filled with atoms. The team can detect energy shifts in the Rydberg atoms modulating this reference signal. The modulated output is then fed to the TV. An analog-to-digital converter converts the signal to a video graphics array format for display.
For live video display or video game display, this input signal is sent from the camcorder to modulate the original reference signal, then applied to a horn antenna, directing the transmission to the atoms. The researchers use the original reference signal as a reference and compare it to the final video output detected through the atoms to evaluate the system.
The scientists studied the size of the laser beam, the power and the detection methods required by the atoms to produce standard definition video. The beam size affects the average residence time of atoms in the laser interaction zone. This time is inversely proportional to the receiver bandwidth; that is, less time and a smaller beam give more data. This is because the atoms move in and out of the interaction zone, so smaller areas result in a higher "update" signal and better resolution.
The researchers found that the small beam diameter (less than 100 micrometers) for both lasers resulted in much faster response and color perception. The system achieved data transfer speeds in the order of 100 megabits per second, which is considered excellent for video games and home Internet. Research is ongoing to increase system capacity and data rates.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Invisible QR codes
▪ A new way to cool air
▪ Ancient penguin feathers
▪ Cleansing the blood instead of a heart transplant
▪ The largest asteroid
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Winged words, phraseological units. Selection of articles
▪ article Organizing an emergency bivouac. Basics of safe life
▪ article What is the solar corona? Detailed answer
▪ article Engineer of pumping units. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article On the use of harmonic resonators in MK devices. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Sixteen words. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
Comments on the article:
Boris
Helpful! Happy to refresh my memory.
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: