The lamp changes color. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Yellow, almost sunlight, floods the book lying under the table lamp. Easy and enjoyable to read; but an hour, an hour and a half passes, and you notice that this color scheme is starting to get boring. Correcting the situation is very simple: you turn the control knob, and the color of the lampshade gradually changes. You can choose any color from the solar spectrum - from red to dark blue, and you can change not only the color itself, but also its saturation.
This is how the light filter I developed for the lamp works. The principle of its operation is based on subtractive subtraction of colors, and its fundamental difference from many others is that I used liquid dyes of three colors - yellow, purple and blue.
The design of the filter is shown in Figure 1. The cylindrical body contains four colorless glasses, three of which can move along its axis. The glass is moved by cam rings. Thus, by rotating them, you can change the gap from zero to maximum between any two adjacent glasses.
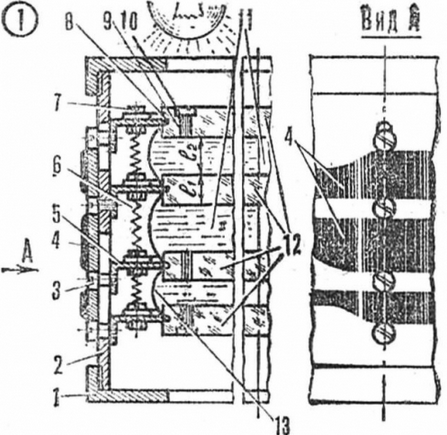
Rice. 1. Light filter device: 1 - cover, 2 - body, 3 - fixing screw, 4 - cam ring, 5 - bracket, 6 - spring, 7 - screw, 8 - sealing cord, 9, 10 - filling hole and plug screw , 11 - liquid dyes, 12 - glass, 13 - polyethylene cavity.
Liquid dyes of the required concentration fill the space between the glasses. By changing the gap, we thereby change the color saturation or, in other words, the density of the corresponding color. Well, since combinations of any two of the three main subtractive colors of different densities give all the colors of the spectrum, the total color is determined by the ratio of the thicknesses of the layers of liquid dye, and the color saturation is determined by the thickness of the layers.
As a dye, I used solutions of chromium (K2CrO4) - (yellow), potassium permanganate KMnO4 (magenta) and blue ink "Rainbow" for fountain pens. Their concentrations are chosen arbitrarily.
Glass, preferably organic, has a groove around the circumference, designed to secure polyethylene bellows with its help, compensating for the excess volume of liquid when the glasses come together. The fur itself is not difficult to make: the appropriate number of rings are cut out of polyethylene film, and their edges are welded by heating.
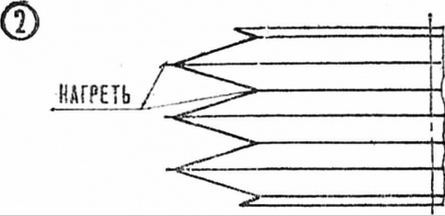
Rice. 2. Polyethylene fur device
That's all, actually. I deliberately did not touch upon the issues of installing such a light filter on a lamp - in each specific case the connection will be carried out in its own way.
Author: A.Pirogov
 See other articles Section Lighting.
See other articles Section Lighting.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
The threat of space debris to the Earth's magnetic field
01.05.2024
More and more often we hear about an increase in the amount of space debris surrounding our planet. However, it is not only active satellites and spacecraft that contribute to this problem, but also debris from old missions. The growing number of satellites launched by companies like SpaceX creates not only opportunities for the development of the Internet, but also serious threats to space security. Experts are now turning their attention to the potential implications for the Earth's magnetic field. Dr. Jonathan McDowell of the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics emphasizes that companies are rapidly deploying satellite constellations, and the number of satellites could grow to 100 in the next decade. The rapid development of these cosmic armadas of satellites can lead to contamination of the Earth's plasma environment with dangerous debris and a threat to the stability of the magnetosphere. Metal debris from used rockets can disrupt the ionosphere and magnetosphere. Both of these systems play a key role in protecting the atmosphere and maintaining ... >>
Solidification of bulk substances
30.04.2024
There are quite a few mysteries in the world of science, and one of them is the strange behavior of bulk materials. They may behave like a solid but suddenly turn into a flowing liquid. This phenomenon has attracted the attention of many researchers, and we may finally be getting closer to solving this mystery. Imagine sand in an hourglass. It usually flows freely, but in some cases its particles begin to get stuck, turning from a liquid to a solid. This transition has important implications for many areas, from drug production to construction. Researchers from the USA have attempted to describe this phenomenon and come closer to understanding it. In the study, the scientists conducted simulations in the laboratory using data from bags of polystyrene beads. They found that the vibrations within these sets had specific frequencies, meaning that only certain types of vibrations could travel through the material. Received ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Created a biodegradable transistor based on proteins
24.03.2012
A team of scientists using advanced methods from various fields of science created a transistor based on proteins present in the human body. According to the calculations of developers from Tel Aviv University, the new technology can become the basis for various flexible electronic nanodevices with the ability to biodegrade.
One of the problems with using silicon as a semiconductor is that the silicon transistor must be built from the top down. Manufacturers take a sheet of silicon and actually "cut" a microchip out of it. This method limits the possibilities of transistors, especially in terms of miniaturization and flexibility. Thus, silicon is rapidly becoming obsolete, and recycling of obsolete electronics is expensive and pollutes the environment.
Scientists used the latest advances in chemistry and biology to create the perfect transistor. They studied various combinations of blood, milk and mucus proteins in order to create self-organizing molecules that form semiconductor films at the nanoscale. In the case of blood proteins, for example, it was possible to obtain films with a thickness of about 4 nanometers, which is 4,5 times thinner than using modern silicon technologies. With the help of three different types of proteins, you can create a complete electronic circuit with unique capabilities. For example, a blood protein has the ability to absorb oxygen, which allows the production of semiconductors from certain chemicals.
In turn, milk proteins form fibers that form the structure of transistors, while mucosal proteins have the ability to hold red, green, and blue fluorescent dyes. Thus, the circuit can emit the white light required for advanced optics. In general, the natural features of each protein give researchers the opportunity to control the properties of an organic transistor: change conductivity, memory, fluorescence, etc.
Protein-based transistors could revolutionize electronics. They are ideal for small, flexible devices because, unlike silicon, they do not break. This will make it possible to launch a new generation of flexible screens, mobile phones, biosensors, microprocessors, and so on. At the same time, this electronics will be biodegradable and will not harm the environment.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ ASUS Zenfone Series Smartphones
▪ All ultrabooks with Windows 8 - touchpads
▪ Revealed the secrets of children's memory
▪ Wireless charging of an electric car - fast and safe
▪ Maple seeds will double the flight time of drones
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Spectacular tricks and their clues. Article selection
▪ tomograph article. History of invention and production
▪ article How much fusion energy can be obtained from a liter of ordinary water? Detailed answer
▪ Borago article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Designs based on a computer mouse. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Folding corner. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: