
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Study time programmer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
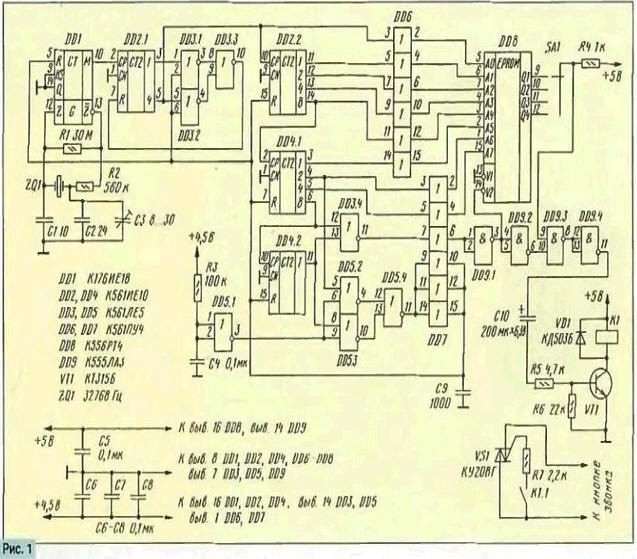
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches The device proposed by the author is designed to automatically make calls in schools and other educational institutions in accordance with the current class schedule. Unlike the electronic programmer of training time described at the time ("Radio", 1985, No. 11, p. 30,31, XNUMX), it eliminates the need for everyday switching on, allows a short-term power outage without disrupting operation, provides the ability to select any of four pre-compiled call programs. The device also differs in a simpler circuitry solution. Schematic diagram of the programmer is shown in fig. 1. It consists of a minute pulse generator (DD1). a divider that forms pulses from them with a period of 5 minutes (DD2.1, DD3.1-DD3.3). counting-logic block (DD2.2 and DD4-DD7). EPROM (DD8) and a bell enable unit (DD9. \ / T1, \ / S1). The programmer works like this. Pulses with a duration of 1 min from output 10 of the DD1 microcircuit are fed to the divider, and from it (pin 5 DD2.1) pulses with a period of 5 min (4 min duration of logical zero and 1 min - logical unit) enter the input of the counting logic block, the outputs of which (vyv. 2, 4, 6,10,12, 15 DD6 and 2. 4 DD7) are connected to the address inputs of the PROM DD8. Every 4 and 1 minutes for 10 hours and 40 minutes, the information at these inputs will alternately change from 0 to 255 in the binary number system. This time is quite enough to make calls during the two-shift work of the school. During the entire specified time, outputs 6 and 11 of the DD4 chip will have a logic zero level, which, after passing through the elements DD3.4, DD7 and DD9.1, will enter the sample input V2 of the PROM DD8. At the outputs of this microcircuit, in accordance with the written program, either logical zeros or logical ones appear. The call is activated when a logical unit is present at the outputs of DD8. It happens in the following way. Since at the outputs 6, 11 of the DD4 microcircuits there is, as mentioned above, a logic zero level, the same voltage will be at the inputs 4. 5 of the DD9.2 element of the DD9 microcircuit. This means that at the inputs 9. 10 element DD9.3 will be at this time the levels of a logical unit, at its output 8 - the level of logical zero, and at the output 11 of the element DD9.4 - the level of a logical unit. As a result, capacitor C10 will begin to charge and current will flow through the winding of relay K1. The relay will work and its contacts will close the circuit between the control electrode and the anode of the triac VS1. which will turn on the call. When a logical unit level appears at the output 6 or 11 of the DD4 chip, the same level is set at the input of the PROM \/2 sample and at the inputs 4, 5 of the DD9.2 element. This means that at the output 6 of this element and the output 11 of the element DD9.4 there will be a logic zero level. In this position, the capacitor C10 will not be charged, the current through the coil of the relay K1 will not flow and the bell will not ring. A day after turning on the programmer at outputs 4 and 11 of the DD4 chip. and consequently, a logical unit will appear at the output 11 of the DD5 chip and the counters will be reset to zero. As a result, the programmer will automatically resume its work. Setting the counters to zero at the moment the programmer is connected to the network is provided by element DD5.1 To increase the load capacity of CMOS microcircuits, their outputs are connected to the inputs of TTLS microcircuits through level converters. Schematic diagram of the power supply unit of the study time programmer is shown in fig. 2. Before turning on the machine, switch 8A1 (Fig. 1) to select the desired call program, and then at the time of the start of classes, for example, exactly at 8:30. sequentially turn on the switches ZA2 and ZA1 (Fig. 2). At this point, the bell will ring, announcing the start of classes. The machine is turned off for the weekend and during the summer holidays with the SA1 switch (Fig. 2).
Parts of the programmer are recommended to be mounted on a board made of foil fiberglass. It is desirable to pickle the power buses, and make the remaining connections with a thin stranded wire. Capacitors C5-C8 should be evenly distributed over the power rails of the microcircuits. During installation, fixed resistors MLT-0,125, the oxide capacitor of the programmer C10 - K50-16 were used. and the rest - KM. Quartz resonator ZQ1 - at a frequency of 32 Hz. The K176IE18 chip can be replaced with K176IE12, KR556RT4 - with KR556RT11. and K555LAZ - to a similar series K155, 531. Relay K1 - any with a response voltage of about 4 V and a response current of up to 30 mA. With a higher operating current, the KT315B transistor (see Fig. 1) must be replaced with a more powerful one, for example, KT603, KT608 with any letter index. It is also desirable that the relay contacts are designed for a voltage of 220 V. In the author's version of the programmer, the RES64A relay (passport 4.569.724) is used. The power supply transformer must have a power of at least 5 W and a voltage on the secondary winding of 7 ... 9 V. The transistor VT1 (Fig. 2) should be installed on the heat sink. Instead of KT815A, KT817, KT807 with any letter index are suitable. Capacitors C1-C2 - K50-6. As a 5A1 switch (see Fig. 1) and SA1 switches. SA2 (Fig. 2) you can use any available. It is only important that they are located in a convenient place. The device itself should be placed in a small case and hung on the wall next to the call button. Establishing the programmer consists in setting the required duration of the call by selecting the capacitor C10. In conclusion, let's dwell on programming the PROM KR556RT4. Schemes of devices for programming microcircuits have been repeatedly described (1-3). There is also a detailed description of the programming process. The desired address code in accordance with the schedule in which a logical 1 is written to the PROM can be found by the formula: A(n) =(T(n)-T(0))1/2.5, where A(n) - address code in decimal number system (n=1,2...); T(0) - start time of classes, min; Т(n) - bell activation time, min. Let's explain how to use this formula for a specific call schedule: 8 hours 30 minutes - 9 hours 15 minutes - 1st lesson, first shift; 9 h 15 min - 9 h 20 min - break: 9:20 - 10:05 - 2nd lesson, first shift, etc. 18:15 - 19:00 - 6th lesson, second shift. In this case
Therefore, in the PROM on the output, for example, Q1, it is necessary to write logical 1. when the code is set at the address inputs: 0000000. A00010010 - 0. A1 - 1. A2 - 0. A0 - 4). 1 (i.e., the address input of the AO must be logical 5. A0-6.A0-7, AZ-0.A00010100-0.A1-0.A2-1. A0 - 4), etc. Three others call schedules can be written to outputs Q1-Q5. Literature
Author: A.Krutovtsov, Atyrau, Kazakhstan
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ N-trig and NVIDIA to improve touch input in mobile devices ▪ Case for smartphone - car key
▪ section of the site for the Musician. Selection of articles ▪ article How does a chameleon change its colors? Detailed answer ▪ article Aerosleigh Triumph. Personal transport ▪ article Control of a motorist. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Transmitter for fox hunting. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: