
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Acoustic dimmer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
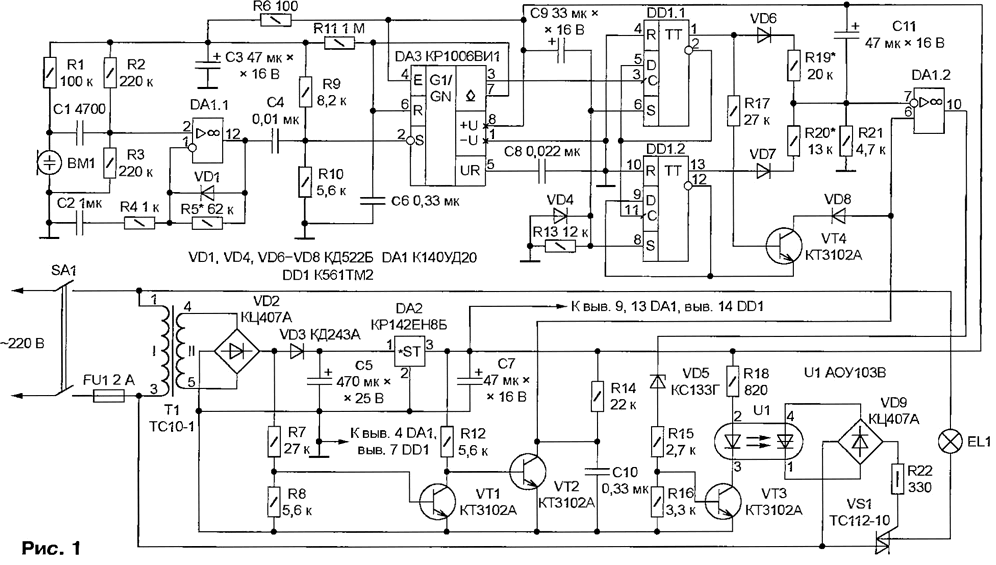
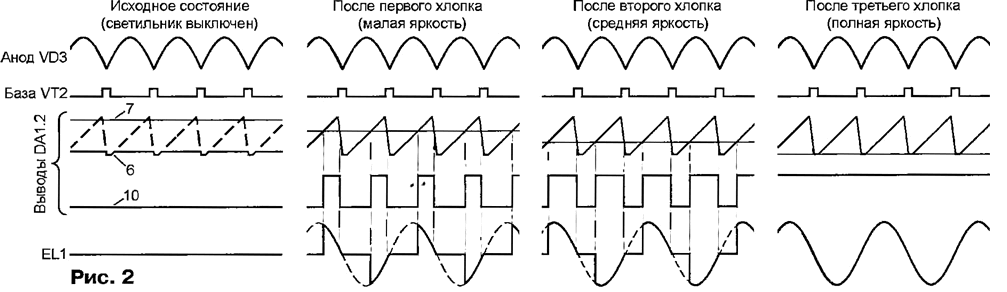
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Lighting The proposed regulator allows you to remotely, simply by clapping your hands, turn on and off a floor lamp or other lamp with incandescent lamps and select one of three levels of its brightness. The change in brightness, including when turned on, occurs smoothly, which significantly extends the life of the lamps. Clapping hands was chosen as a control signal for the reason that, in terms of acoustic characteristics, it differs markedly from speech or music. Of course, it is impossible to exclude the regulator from being triggered by other sharp sounds (pyrotechnic explosions, car horns or exhausts), so you should not use this device outside a well soundproofed room. The power consumed by the dimmer does not exceed 4 VA and depends mainly on the no-load current of the primary winding of the power transformer. This is several times less than what a music center with a built-in clock or a TV consumes in standby mode. The controller circuit is shown in fig. 1. The signal received by the BM1 microphone is fed to the amplifier - op-amp DA1.1. The voltage divider R2R3 sets the operating point of the op-amp. Through the resistor R1, the electret microphone is supplied with a supply voltage. Capacitor C1 is separating. The gain of the negative half-waves of the signal is one more than the ratio of the resistance values of the resistors R5 to R4. Positive "cuts off" the diode VD1. With sufficient amplitude (more than 0,9 V), the signal from the output of the amplifier triggers the DA3 single vibrator, generating a rectangular pulse with a duration of approximately 0,4 s, depending on the time constant of the R11C6 circuit. Until the pulse has ended, no noise effects on the BM1 microphone have any effect, which prevents unpredictable changes in the state of the regulator. Resistors R9 and R10 not only set the initial voltage at pin 2 of the single vibrator DA3, but together with capacitor C4 form a filter. It passes only high-frequency components, which are rich in the clapping spectrum, and suppresses low-frequency components inherent in other signals and interference. Two trigger microcircuit DD1 form a counter that counts the number of claps (pulses single vibrator DA3). Resistors R19-R21 and diodes VD6, VD7 - ADC, the output voltage of which (the inverting input of the op-amp DA1.2) depends on the state of the triggers, i.e., on the number of claps. Capacitor C11 provides a relatively slow transition from one voltage level to another. When the power is turned on, a positive pulse generated by the R13C9VD4 circuit sets the counter to its initial state with a high logic level at pins 1 and 13. The voltage at the inverting input of the DA1.2 op-amp is maximum, since the resistors R19 and R20 are connected essentially in parallel through open diodes VD6 and VD7. In the same state, the VT4 transistor is open, since its emitter has a low logic level from the inverse output of the DD1.2 trigger (pin 12), and current flows through the resistor R17 in the base circuit. The purpose of this transistor will be discussed below. After the first clap, both triggers will change their state and the voltage at the inverting input of the op-amp DA1.2 will become zero, since the diodes VD6 and VD7 will be closed. The second clap will set a high level at the output of the DD1.1 trigger, leaving the state of the DD1.2 trigger unchanged. Now the diode VD6 is open, VD7 is closed, and the output voltage of the ADC forms a resistive divider R19R21. The third clap will change the state of both triggers. Diode VD6 will be closed, and VD7 will be open. The output voltage will set the divider R20R21. And finally, the fourth clap will return the device to its original state. Further clapping will cause the same cycle to repeat. Timing diagrams of signals at the characteristic points of the dimmer are shown in fig. 2 An unsmoothed pulsating voltage is applied to the base of the transistor VT1 from the anode of the diode VD3 (the output of the rectifier on the diode bridge VD2). At the end of each half-cycle and at the beginning of the next, this transistor is closed for some time, and VT2 is open and discharges the capacitor C10. After closing the transistor VT2, the capacitor is charged through the resistor R14 and the voltage at the non-inverting input (pin 6) of the op-amp DA1.2 grows almost linearly. Op-amp DA1.2 (serving in this case as a comparator) generates at the output (pin 10) a sequence of positive pulses, the duration of which is greater, the lower the voltage at the inverting input (pin 7) of the op-amp. If it is zero, the output of the op-amp is a positive constant voltage, and if it exceeds the amplitude of the sawtooth at pin 6, the output voltage of the op-amp is close to zero, but not equal to it due to the characteristics of the op-amp device, so that at a low voltage level at the output of the op-amp DA1.2 transistor VT3 was securely closed, a zener diode VD5 is provided, which "cuts off" excess voltage. With a certain combination of resistor values R19-R21, the voltage at the inverting input of the op-amp DA1.2 in the initial state of the regulator may turn out to be less than the "saw" amplitude, as a result, the EL1 lamp will not turn off completely. To exclude such a situation, a transistor VT4 is provided, which was discussed above. When it is open, the sawtooth voltage is limited to a very low level. Diode VD8 eliminates the influence of the transistor VT4 on the operation of the generator, when the pin 13 of the trigger DD1.2 is set to a high logic level. The emitting diode of the optocoupler U3 is included in the collector circuit of the transistor VT1. If the transistor is open, the photodistor of the optocoupler is also open, which closes the control circuit of the triac VS9 through the diode bridge VD22 and resistor R1. Depending on the proportion of the duration of each half-cycle, during which the triac is open, the effective value of the voltage supplied to the EL1 lamp and the brightness of its glow change. Since the triac opens in both positive and negative half-cycles, the flickering of the lamp is imperceptible even at low brightness. Setting up a dimmer starts with setting the required acoustic sensitivity. Please note that with an increase in the value of the resistor R5, not only the sensitivity increases, but also the likelihood of false positives from extraneous sounds. The levels of intermediate brightness levels can be changed at your discretion by selecting the values of the resistors R19 and R20. An increase in the capacitance of the capacitor C11 leads to a slower increase or decrease in brightness after the next pop. The printed circuit board of the dimmer and the location of the elements on it are shown in fig. 3. Capacitors C6 and C10 must be film series K73-9 or K73-17. Ceramic capacitors (K10-17 or imported) are undesirable here because of the large TKE. However, they can be used as C1, C2, C4 and C8. Oxide capacitors - any suitable in size and operating voltage. The power of resistors R18 and R22 should not be less than that indicated in the diagram.
The KS133G zener diode can be replaced with another one (for example, imported) with the same or slightly lower voltage and possibly a lower minimum stabilization current. As a VD3 diode, any rectifier with a permissible forward current of at least 0,3 A is suitable, instead of the rest - diodes of the KD510, KD521, KD522 series. Transistors VT1-VT4 - any p-pn structures with a permissible collector current of at least 100 mA and a coefficient h21E of more than 50. The K140UD20 microcircuit can be replaced with KR140UD20A, K561TM2 - with K1561TM2, and instead of the integrated stabilizer KR142EN8B, use KR1157EN12 (with any letter index), KR1170EN12 or imported with a stabilization voltage of 12 V and a permissible load current of at least 50 mA. The BM1 electret microphone can be replaced by an electrodynamic one, in which case the resistor R1 should not be installed. Triac TS112-10 can be replaced with KU208V or KU208G. With a total lamp power of more than 100 W, the triac must be installed on a heat sink. Fusible insert FU1 is selected with a trip current that is 1,5 ... 2 times the rated current of the lamp. Transformer T1 - any one that provides voltage on the secondary winding of 12 ... 16 V at a current of at least 50 mA. If possible, preference should be given to a transformer with a minimum value of the no-load current of the primary winding. The described acoustic dimmer is easy to turn into a sensor. It is enough to replace the BM1 microphone and the resistor R1 with a metal plate connected to the left (according to the diagram) terminal of the capacitor C1. The regulator will operate when the plate is touched by hand. Author: S. Belyaev, Tambov
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Found a way to influence the development of microbes ▪ Birth control pills affect fear ▪ Silence in the operating room ▪ Earth's magnetic field has a clear cycle
▪ section of the website Basics of First Medical Aid (BFA). Selection of articles ▪ article Carrying sheet materials. Tips for the home master ▪ article How does a Rentokil mousetrap work without any bait? Detailed answer ▪ Ajgon article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Microwave ovens (MW). Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: