
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Microwave motion sensor for burglar alarm. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
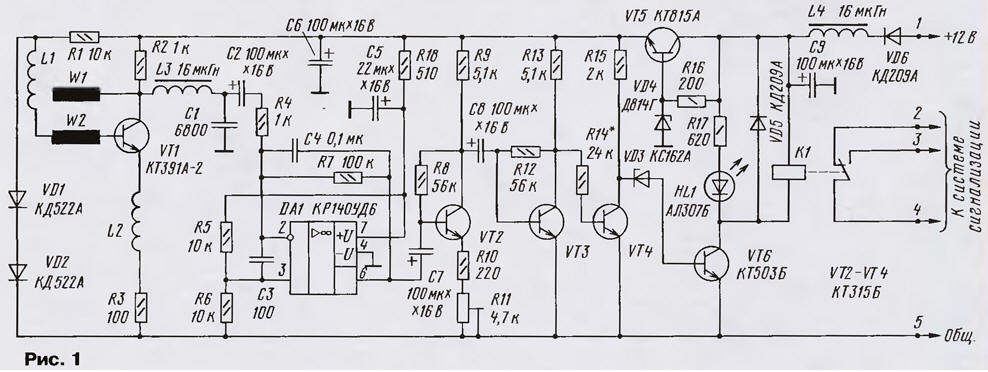
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Safety and security Based on the design proposed by A. Khabarov (see the article "Motion Sensor" in "Radio", 2001, No. 10), I decided to make a microwave motion sensor for my security alarm. Since the sensor was powered from the power supply of the alarm system with a 12-volt acid battery in the buffer, I excluded the mains rectifier, replaced the DA1 stabilizer with a parametric one on one transistor and a zener diode, and replaced the VT2, U1, DA3 stages with a three-stage transistor switch with an electromagnetic relay at the exit. An analysis of information previously downloaded from the Internet on foreign security microwave motion sensors revealed the following features of the circuitry of these sensors, namely: 1. The input amplifier is always separated from the microwave autodyne by an isolation capacitor, and in some devices, along with an isolation capacitor, an L-shaped RF suppression filter is also included. 2. The input operational amplifier (op amp) is always inverting. 3. Between the input amplifier and the comparator there is always one, and more often two gain stages, separated from the input amplifier by an isolation capacitor. Based on the foregoing, I took A. Khabarov's microwave autodyne as a basis, and completely redid the entire low-frequency part. The result of the development is a device, the scheme of which is shown in Fig. 1. The microwave autodyne on the transistor VT1 and the topology of its printed circuit board are left unchanged. The input filter amplifier on the op-amp DA1 is an inverting one. The RF trap filter L3C1 prevents the microwave signal from reaching the input of the op-amp DA1. By power, the input amplifier is decoupled from the rest of the device by the R18C5 filter. Cascades on transistors VT2 and VT3 - two stages of bass gain. This is followed by a two-stage UPT on transistors VT4 and VT6. The role of the comparator is performed by the zener diode VD3 and relay K1. Comparation occurs at thresholds comparable to the supply voltage, and all stages are DC-coupled by isolation capacitors, which ensures high thermal stability. Structurally, the sensor is assembled on a double-sided printed circuit board (Fig. 2). Since the board does not have plated holes, the mounting of parts should be done carefully so as not to block access to the solder points with parts that can be soldered later.
The sensor housing is a soap dish with dimensions of the cavity of the inner part 95x55x19 mm and external dimensions of the outer part 100x61 x20mm. The sensor housing is mounted on a textolite or aluminum base with dimensions of 180x70 mm on stands 10 mm long, through which M3 countersunk screws pass. Board racks inside the soap dish are M3 nuts with textolite washers superimposed on them. The board itself is also fastened with M3 nuts. Through the holes in the corners of the board, the screws for fastening the soap dish and the board pass. Through the hole in the center of the board from the side of the parts, a rack with an M3 through thread is attached. A hole with a diameter of 3 mm is drilled along the axis of this rack in the lid of the soap dish. Through this hole, the cover of the soap dish is fixed with an M3 screw screwed into this rack. The stand can be made from any material. The board's conductors can be tinned, with the exception of the resonator and slot antenna, which should be polished to a mirror finish. This can be done with GOI paste diluted in engine oil. After assembling the board, the resonator and slot antenna should be covered with a thin layer of rosin diluted in acetone or alcohol to prevent their oxidation over time. On the base, in addition to the body with the sensor, a standard junction box UK is installed for connecting the sensor to the security system. The sensor board is connected to the contacts of the UK box with a ribbon cable through a slot in the body of the soap box. If the sensor is supposed to be used with a circular pattern, then it is made on a non-metallic base and mounted on a non-metallic surface of the protected object. In this case, the sensitivity of the sensor must be set taking into account the movement of people in neighboring unguarded premises and outside the building. With a pie chart, the base mounts can be less than 10 mm, up to and including mounting the case directly to the base. The sensor is fixed to the wall or other structure of the object with screws through holes with a diameter of 4 mm, which are drilled at the corners of the base. Coils L1 and L2 contain 10 turns of 0,25 diameter wire wound on a 0,8 mm mandrel. Micropower op amps, for example, KR1UD140, should not be used as DA12, since they have a high output impedance and do not provide the required current load capacity. Resistor R14 is selected when adjusting the sensor, depending on its purpose and conditions of use. The lower the resistance of this resistor, the lower the sensitivity. R14 is soldered to wire posts driven into holes in the PCB. Relay K1 should be selected so that it operates stably at a voltage of 10 V. You can use a RES55A relay for 12 V. Do not use high-current non-reed relays RES10, RES15, etc., as they can give a large "drawdown" of the supply voltage due to the voltage drop on the loop and the protective resistor in the power circuit installed in the control panel of the security system. A large "drawdown" of the supply voltage when the relay K1 is triggered can cause a self-oscillating process in the sensor. During testing of the sensor, it turned out that you can easily set the sensitivity to 3 m in the absence of false positives and a circular radiation pattern. Sensitivity is regulated by resistor R11 in the range of 0,5 ... 5 m. With a sensitivity of more than 4 m and a circular diagram, the sensor starts to operate from its own noise. The pulses generated by the sensor are compatible with control panels designed for use in the signaling loop of pulsed magnetic-contact and shock-contact sensors. When the sensor board or its plastic case is installed on a metal panel 1,5 times larger than the sensor board with a gap of 10 mm, the radiation pattern becomes a sector of 120 °, and the sensitivity increases by 2 times. During long-term tests of such a sensor with a sensitivity of 5 m, no false alarms were found. The thermal stability of the sensor was tested by heating it to +70°C and cooling it down to -20°C. In this case, only a change in sensitivity of about 20% was recorded. The disadvantage of the sensor is its high criticality to lowering the supply voltage. It should not fall below 11 V, but the voltage increase is limited only by the thermal regime of the VT5, VD4 stabilizer. If there are no powerful sirens in the system, the L4 choke can be replaced with a jumper. I want to draw the attention of those who will develop their own board for the sensor: the microwave autodyne must be separated from the installation side by a closed circuit of the common wire circuit, otherwise the sensor responses may be accompanied by a “ringing” at the pulse fronts with a frequency of hundreds of hertz. Author: A.Isaev, Zheleznogorsk-Ilimsky, Irkutsk region.
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ 75,6 TB of data on a piece of quartz ▪ Creation of electrically conductive nanostructures using water and air
▪ section of the site Power supply. Article selection ▪ article Drink the cup to the bottom. Drink the cup to the bottom. Popular expression ▪ article How is lace woven? Detailed answer ▪ Claytonia pierced leaf article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Probe without battery. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: