
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING stable thermostat. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
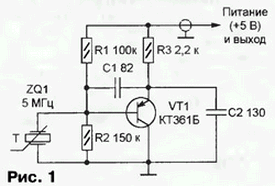
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers A wide variety of sensors are used in automatic temperature control devices: from the simplest mercury thermal contactors TK and TPK to specialized microcircuits. But if it is required to maintain a given temperature with high accuracy for time intervals ranging from days to tens of years, only devices based on temperature-sensitive quartz resonators with subsequent conversion of a temperature-dependent frequency into a control signal for heaters or coolers of a thermal chamber provide the necessary stability. A diagram of a quartz self-oscillating temperature-to-frequency converter (CAPTCH) is shown in fig. 1.
A serial thermosensitive cutoff quartz resonator PY at a frequency of 5 MHz with a linear temperature-frequency characteristic and a temperature coefficient of 185 Hz/°C is used [1]. It can be replaced by a temperature-sensitive resonator RK-112 manufactured by a plant in the city of Volzhsky, Volgograd region, containing a piezoelectric plate cut yхbI/10° 54'/9° 45'51''. The CAPTC is performed as an independent unit located inside the heat chamber, connected to the main unit of the thermostat by a coaxial cable. The power supply voltage is applied to the generator via a cable and a signal is obtained depending on the temperature of the quartz resonator ZQ1 of frequency f(T)=5000000+185T, where f is the frequency, Hz; T - temperature, °C. The main block of the thermostat is built according to the scheme shown in fig. 2.
Resistor R2 serves as a load for CAPTCH. Further, the signal of the temperature-dependent frequency through the amplifier-shaper on the transistor VT2 and the element DD1.3 is fed to the input C of the second trigger of the DD2 microcircuit. A similar input of its first trigger receives a reference frequency signal from an oscillator based on elements DD1.1, DD1.2 with a thermostable quartz resonator ZQ1 cut AT. Frequency-phase detector [2] consists of two triggers chip DD2, element DD1.4, resistors R9, R11, diodes VD2, VD3 and capacitor C5. Its output voltage is logic low if the temperature-dependent frequency is higher than the reference frequency, and high if it is lower. An intermediate voltage level is possible only if the frequencies are exactly equal, which does not happen in practice, since the oscillations of the generators are not synchronous. At a high level at the output of the frequency detector, transistors VT4 and VT5 open, applying voltage to the heater installed in the thermal chamber. At the same time, the HL1 LED lights up. Through an emitter follower on a transistor VT3, a temperature-dependent frequency signal can be fed to an electronic frequency meter. The zener diode VD1 with the transistor VT1 form a voltage regulator for the supply of microcircuits. When setting up the thermostat, first of all, resistor R3 is selected, achieving a symmetrical pulse shape at the output of element DD1.3. The capacitance of the capacitor C3 is selected so that at a given temperature the reference frequency is equal to the temperature-dependent frequency generated by the CAPTC. The heat stabilizer is operated at the stand for certification of medical electronic digital thermometers. The heat chamber of the stand has a volume of 60 cm3, its walls are made of foam plastic 30 mm thick. The heater consists of two MLT-2 56 Ohm resistors connected in parallel. 45 minutes after switching on, the temperature of 40 °C is set and maintained in the chamber. Tests have shown that the stabilization temperature drift does not exceed 0,005 °С per one degree change in the temperature of the exemplary resonator (ZQ1 in Fig. 2) and 0,02 °С per year. Thus, within five years, when the device is operated at room conditions, the error in maintaining the temperature in the chamber will not exceed 0,1 °C. Literature
Author: V.Solodovnik, M.Cheban
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ QR codes on Moscow street signs ▪ FUJITSU develops RFID chip with FRAM memory ▪ Night lighting from living plants ▪ Candies that restore tooth enamel
▪ site section Welding equipment. Article selection ▪ article Green grapes. Popular expression ▪ article How did Paris manage to kidnap Helen? Detailed answer ▪ Article Franchise Specialist. Job description ▪ article Mordant to imitate oak wood. Simple recipes and tips ▪ article Phase presence indicator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: