
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Temperature regulator. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power regulators, thermometers, heat stabilizers Interest in temperature controllers continues unabated. Unfortunately, the required element base is not always available, and the absence of one or more elements limits the possibility of repeating one or another design. I assembled my version of the temperature controller for the "balcony" vegetable store in 1988, and so far it has been working flawlessly. Simplicity, availability of the element base, a minimum of adjustments create the conditions for repeating the device even for novice radio amateurs. The regulator is built on the basis of a well-known phase power regulator based on a trinistor. Details of the features of such devices can be found in the article by Chernoy V. "Features of trinistor regulators" ("Radio", 1979, No. 4, p. 40).
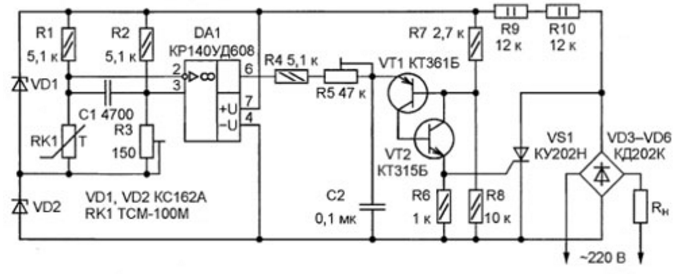
The scheme of the proposed device is shown in fig. 1. A temperature-sensitive bridge (thermistor RK1, resistors R1 - R3) and a comparator DA1 are added to the trinistor regulator taken as the basis. To stabilize the supply voltage and set the operating point of the comparator, two zener diodes (VD1, VD2) are installed. The voltage from the output of the comparator through resistors R4, R5 is supplied to the capacitor C2 and an analogue of a unijunction transistor, made on transistors VT1, VT2. The pulse generated by the analog from the emitter VT2 is fed to the control electrode of the trinistor VS1. A feature of this device is the absence of oxide capacitors, which significantly increases reliability. The supply of the ripple voltage control unit causes an additional delay in turning on the trinistor, which leads to a decrease in power at the load by up to 10%. Resistor R5 is the maximum power regulator at the RH load (if there is no need for power regulation, this resistor can be excluded). When using resistance thermometers TSP-1P, TSM-100M as a temperature-sensitive element RK100, the sensitivity of the regulator is not worse than 2 °C. It is possible to use thermistors not only with a positive temperature coefficient of resistance, but also with a negative one. To do this, it is enough to swap the conclusions 2 and 3 of the comparator DA1. Moreover, the use of thermistors of the ST1 series and the like will increase not only the speed of the controller due to smaller dimensions and, accordingly, the lower thermal inertia of the sensor, but also the accuracy of regulation due to a larger temperature coefficient. Establishing the regulator comes down to setting the desired temperature with a tuning resistor R3. When adjusting and operating the device, it is necessary to follow the rules of electrical safety, since all its elements are under the mains voltage of 220 V.
On fig. 2 shows one of the first author's versions of the temperature controller. As a heating element, a spiral of nichrome wire with a diameter of 0,3 mm and a resistance of about 500 Ohm, stretched on porcelain rollers, was used. The power of such a heater does not exceed 100 W, which is quite enough to maintain a temperature of +4 °C in a well-insulated storage facility with a volume of 250 liters. The use of tubular electric heaters (TEHs) simplifies the design, improves reliability and safety. However, it is rather difficult to select a heating element of small (100 ... 150 W) power, even connecting them in series.
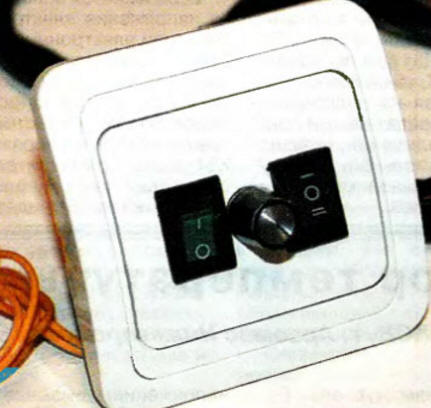
The described device can be adapted to automatically control the exhaust fan in the kitchen. A diagram of such a device is shown in fig. 3a. It reacts to the temperature difference between the upper and lower sensors when a powerful heat source, such as a gas stove, is turned on. Silicon diodes VD1, VD2 are used as sensors, which together with resistors R1, R3, R4 form a measuring bridge. The upper sensor (VD1) is installed next to the ventilation duct, and the lower one (VD2) - at a height of 0,6 ... 0,7 m from the floor. Almost any diode can be used, but it is advisable to choose a pair with close current-voltage characteristics. To connect the sensors to the device board, you must use a shielded wire, for example, KMM 2x0,12 or similar. Establishing the device comes down to setting the response threshold with a tuned resistor R3. The variable resistor R7 is a frequency controller next to the ventilation duct, and the lower one (VD2) is at a height of 0,6 ... 0,7 m from the floor. Almost any diode can be used, but it is advisable to choose a pair with close current-voltage characteristics. To connect the sensors to the device board, you must use a shielded wire, for example, KMM 2x0,12 or similar. Establishing the device comes down to setting the response threshold with a tuned resistor R3. Variable resistor R7 - frequency controller fan rotation. The device has been operated since 2005 with a duct fan "VENTS 150K" with a power of 24 W. On fig. 3b shows a fragment of the device circuit using a single-junction transistor of the KT117 series. The placement of its parts in the case of a dual network switch is shown in fig. 4, and the appearance - in Fig. 5 (in the center - the control knob for the variable resistor R7).
The design and dimensions of the board, printed or surface mounting for the proposed devices are not fundamental and are determined by the available parts. Capacitors C1, C2 in all versions of the device are ceramic, but it is better to use film capacitors, for example, the K73 series, as they are more stable. Possible replacement of OU KR140UD608 - KR140UD708 or another with similar characteristics. Transistors - any series of KT315, KT361 or KT3102, KT3107.
Trinistor KU202N and diodes KD103A are interchangeable with similar ones in terms of permissible current and voltage. Ballast resistors R9, R10 (see Fig. 1) and R11, R12 (see Fig. 3) can be replaced by one or more resistors, it is only important that their resulting resistance is 24 kOhm, and the dissipation power is at least 4 W . To reduce the heating of the elements in the fan control device (see Fig. 3), the resistance of the ballast resistors (R11, R12) can be increased to 18 kOhm. Author: I. Serebryannikov
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Artificial analogue of the sucker of a fish-stick ▪ Controlling technology with the power of thought ▪ MSP430FR5969 - high-performance microcontroller with FRAM memory
▪ section of the site Factory technology at home. Article selection ▪ article Ionizing radiation and ensuring radiation safety. Basics of safe life ▪ How England developed in the late 1950s. and the 1960s? Detailed answer ▪ article by Skorzoner. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Discoloration of resins. Simple recipes and tips
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: