Emotion meter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Electronics in medicine
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Professions, pilot, cosmonaut, tester of flight space technology. require absolute health and exceptional emotional stability from a person. To determine the degree of emotional stability of each person, you can use a device called emotsiometron. A similar device was developed and manufactured in the Club of Young Technicians of the Novosibirsk Akademgorodok.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE
It is known that the resistance of certain parts of the human body depends on the activity of the sweat glands. It is controlled by the nervous system. Any emotional arousal or neuropsychic stress causes the sweat glands to work more intensively, which ultimately leads to a decrease in the resistance of the human skin.
Our device registers changes in skin resistance. Special electrodes are used for contact with the human body. They are strengthened on those areas of the skin that contain the maximum amount of sweat glands. For example, the hand is convenient: one electrode is applied to the palm, the other to its back (Fig. 1).
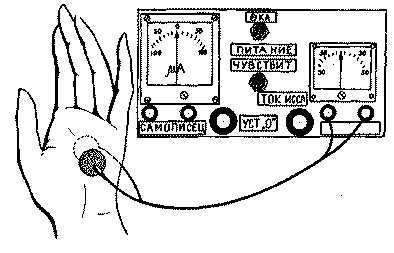
Rice. 1. This is how the degree of emotionality of a person is measured
INSTRUMENT DIAGRAM
By means of connecting wires, the electrodes are connected to the terminals CL1, CL2 of the device (Fig. 2). Potentiometer R1 sets the current in the external circuit (through the human hand). The current value in the range of 20-50 μA is controlled by the IP1 pointer device. Registration of current changes associated with emotional arousal is carried out by an IP2 microammeter connected in a bridge circuit. Having fixed the electrodes on the hand, using a variable resistor R5, the IP2 arrow is set to 0.
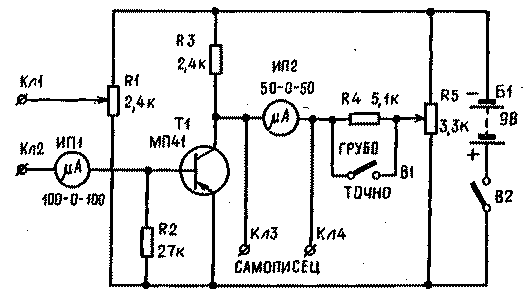
Ris.2
Switch B1 select the sensitivity of the device. When B1 is closed, resistor R4 is short-circuited and the sensitivity of the device is at its highest. In the open position of the switch, it decreases by 5 times.
A recorder is connected to the terminals KLZ, KL4, which records the time of a person's reaction to a stimulus: light, sound, etc.
DETAILS AND CONSTRUCTION
The device uses microammeters: IP1-M494 for 100 μA, IP2-M592 for 50 μA with zero in the middle of the scale or any other with a full deflection current of the needle of 100 μA. Transistor T1 MP39-MP42. It is desirable that the collector reverse current does not exceed 5 μA.
The circuit is powered by two 3336L batteries connected in series. Structurally, the device is made in a metal case measuring 80X120X250 mm.
Electrodes with a diameter of 10-20 mm, a thickness of 2-5 mm are made of zinc, silver or silver-plated foil and amalgamated: covered with a paste of kaolin mixed with a saturated solution of zinc sulfate. Kaolin can be purchased at a pharmacy, and zinc sulfate is in every school chemistry room. The electrodes are then wrapped in clean gauze soaked in what is known as saline. It is not difficult to make it: a tablespoon of ordinary edible salt is stirred in a glass of water. Both electrodes are tied to the arm with a bandage. Now you can start experimenting.
CARRYING OUT THE EXPERIMENT
The subject is in a darkened room in a comfortable lying or sitting position. One or two seconds after the appearance of the stimulus, the arrow of the device moves by a certain amount, registering the reaction of the subject to sound, light, or touch to the body. If a person has good emotional stability, the arrow deviations will be insignificant.
Author: A. Terskikh, Novosibirsk; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Electronics in medicine.
See other articles Section Electronics in medicine.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Seebeck magnetic effect
25.10.2013
A group of researchers from Switzerland and the United States for the first time experimentally confirmed the existence of the so-called magnetic Seebeck effect.
The usual Seebeck effect, also known as the thermoelectric effect, is the appearance of an electric field in a set of dissimilar conductors, the contacts of which are heated to different temperatures. This is due to the fact that the kinetic energy of electrons in hot regions is on average higher than in cold regions. The phenomenon was discovered by the German physicist Thomas Johann Seebeck in 1821.
As part of the new work, scientists heated yttrium iron garnet, a chemical compound of iron oxide with yttrium oxide. The mobility of electrons in this connection is not enough for the occurrence of an electric current. In this case, however, the "heat current" affects the spins of the electrons. As a consequence, they dynamically change, which, in turn, leads to the appearance of a magnetic field.
The Seebeck magnetic effect itself was predicted by the physicist Sylvain Brechet, head of the scientific team that made the discovery, just two years before the discovery itself. The prediction was based on the thermodynamic formalism once developed by the famous Swiss physicist Ernst Stückelberg.
According to scientists, the new effect can be used in spintronics - electronics, in which spins are used instead of electric charges to work. In recent years, active research has been carried out in this area - for example, some experts suggest using graphene in spintronics.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ hangover cure gadget
▪ Ecological synthesis of urea
▪ Photosynthesis battery
▪ The moon is rusting
▪ Sharks navigate by the Earth's magnetic field
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Your stories. Article selection
▪ The left hand doesn't know what the right hand is doing. Popular expression
▪ article What phrase of Frederick the Great helped chess players get tax breaks? Detailed answer
▪ article Serpentine. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Measuring technique. Directory
▪ article Cap, under which everything disappears. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: