Circuits for HF antennas. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / HF antennas
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Among Soviet and foreign shortwaves, the W3DZZ dipole antenna is quite widespread, which works well for reception and transmission, is quite simple to manufacture and is in good agreement with the widespread 75-ohm cables RK-1 and RK-3.
On the bands (14,21 and 28 MHz), the antenna has a complex radiation pattern, which allows you to work with almost equal success in any direction.
A diagram of such an antenna with an indication of the dimensions is shown in fig. one.
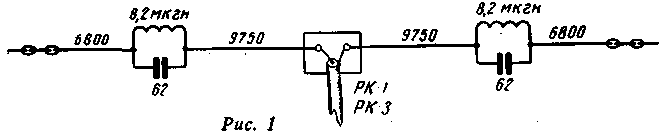
Rice. 1 (click to enlarge)
Many shortwavers are frightened off by the apparent complexity of manufacturing circuits built into the antenna sheet, which are subject to rather high requirements for moisture resistance, mechanical and electrical strength.
The present article is devoted to the production of such contours. Capacitors of 62 pF and inductances of 8,2 μH are attached to the lids of two identical plastic boxes (you can use sandwich boxes). Under the capacitors, an additional sheet of mica is placed.
The outputs from the circuits are carried out through ceramic bushings (the authors used bushings from the antenna shield of the RSB radio station), and in the circuits, permanent air capacitors from the same station were used, assembled on a ceramic base with a plate area of 50X30 mm. Capacitors of another type can also be used, but their capacitance should be 62 pF, and the breakdown strength should be at least 2,5-3 sq.
The coils are wound with PEL 2,0 wire and mounted on getinax plates for greater rigidity. Each coil contains 27 turns, winding diameter - 30 mm, winding length - 75 mm.
More precisely, the inductance and capacitance of the circuit can be adjusted using an LC bridge, but good results are obtained without such fine tuning; it is enough to tune each circuit with the help of a GIR to a frequency of 7,05 MHz, changing the length of the coil winding within a small range.
To increase the mechanical tensile strength of the box, a textolite plate 1,5-2 mm thick is superimposed on its upper plane. Tubular bolts of ceramic bushings pass through it and the box cover.
Brass plates are laid under the heads of the through-bolts, to which, after preliminary twisting, sections of the antenna cord of the required length are soldered. Under the nuts of these bolts, double petals are laid, to which the contour details are soldered.
To protect the ceramics of the bushings from contamination and precipitation, they (each separately) are covered with textolite circles with a diameter of 90 mm.
In the bottom cover, to prevent the accumulation of condensed moisture, six holes with a diameter of 2-3 mm are drilled along its edges.
The halves of the box are fastened with a strapping of insulating tape or nylon cord. All parts of the bolts and soldering that go out are painted over with nitro enamel or BF-2 glue.
An antenna with a feeder made of cable RK-1 and RK-3 has been successfully used by the authors for a long time. With poor transmission, a large number of communications were made both by telegraph and by telephone with all continents using transmitters of no more than 100 watts,
SWR measurements showed that on the 7, 14, 21 and 28 MHz bands it does not exceed two, and on the 3,5 MHz band - no more than three.
The disadvantage of the antenna is its large length (about 34 m), which, with a significant weight of the feeder cable, forces it to be placed on three supports.
Authors: A. Ilyin (UB5PB), N. Soprun (UB5YE), Cherkasy; Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section HF antennas.
See other articles Section HF antennas.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Clouds are falling on Titan
03.04.2012
Clouds are falling on Titan because it's springtime on that moon of Saturn. As Robert West of the Jet Propulsion Laboratory told the 42nd Moon and Planetary Science Conference in California, the latest data from the Cassini probe shows a sharp drop in the methane haze enveloping Titan. Earlier Cassini images of Titan captured this cloud cover about 500 km above the surface of this Saturnian moon. According to images taken in late February, they are now at an altitude of 360 km, about the same as that recorded by Voyager in 1981.
Titan also has seasons, but its year is about thirty times longer than Earth's. When Cassini arrived there in 2004, it was winter on Titan, and methane vortices were blowing clouds up. These clouds covered the entire moon, except for its north pole, where the most powerful vortex raged, generally blowing the clouds to the sides. Now the picture is reversed - the methane haze shrinks sharply around Titan, and the main vortex begins to emerge at its south pole.
“It all looks very impressive,” says another of the Cassini project participants, John Spencer from the Southwestern Research Institute. “You see how this world is changing right before your eyes, and dramatically and completely unexpectedly. You just have to look and wait what happens next.
Scientists, not without reason, suggest that the observed fall of clouds is one of the features of the seasonal cycle of Titan, but they cannot yet explain the mechanism of this fall.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Laser flash is not a hindrance to the sensor
▪ Routers Tenda W308R, W309R, W322U
▪ Snapdragon 8 Gen 2 processor
▪ Texas Instruments reveals details of its 45nm process technology
▪ Hedgehog robots for exploration of satellites and asteroids
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Field strength detectors. Article selection
▪ article Water membrane. Tips for the home master
▪ article How did ancient astronomers imagine the universe? Detailed answer
▪ article Financial consultant. Job description
▪ article Car amplifier on a TDA1557Q chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Merging paper. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: