
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Network power supply for CB radio. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
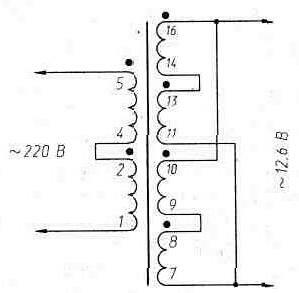
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Civil radio communications CB radio stations that have appeared on our market are designed, as a rule, to be powered by 10 ... 12-volt batteries. The current consumed by such a station in the receive mode is 0,02 ... 0,3 A *, and in the transmit mode (at Pout \u4d 1 W) - 1,5 ... 20 A. On fig. XNUMX shows a schematic diagram of a stabilized rectifier that allows you to power such a radio station from an alternating current network. The heat sink of the VT1 transistor is made in the form of a 63x23x5 mm duralumin plate placed "on edge". For better thermal contact, it is recommended to introduce heat-conducting paste under the transistor, for example, KPT-8. The remaining elements of the rectifier are mounted on a printed circuit board measuring 67x40 mm. Diodes VD1-VD4 are also placed "on edge". The mounted board is installed vertically and so that the heat sink of the transistor VT1 and the diodes VD1 ... VD4 are well blown by the upward air flow. An alternating voltage source of 12,6 V (this value, we note, is from a number of nominal ones) can be a transformer with a power of at least 30 W, for example, TN36, TN46, etc. TN-type transformers have two, three or four 6,3-volt windings, allowing both serial and parallel connection. Possible switching of a four-winding transformer of this type, designed for power supply from a 127/220 V network, is shown in fig. 21.
The main parameters of the network block: Output voltage Un...................................................... ....................... 8...14 V; Maximum load current In max .............................................. ......... 1,5 A; Ripple voltage DUn................................................. ................ <10 mV; Output impedance Rout.................................................... ............... 0,04...0,07 Ohm. The supply of a stabilized rectifier of this configuration from a 12,6 V AC source makes it possible to do without any protection of the radio station in the power circuits. Even with a breakdown of the pass transistor VT1, the voltage at the radio station will not rise above 15 ... 16 V (in transmission, it will not even exit the operating mode, only an alternating current background will appear in the signal). And in the event of a short circuit in the load circuit, the current given off by the stabilizer will independently decrease to almost zero, since the transistor VT1 will be closed in this mode. The unit can be used to power a radio station that consumes much more current in transmit mode. But it is better in this case to use the KT1D transistor as VT825 (Ik max \u20d 21 A, h750e \u18000d 1 ... XNUMX). With an increase in In, it will be necessary to increase the capacitance of the capacitor CXNUMX accordingly. Otherwise, the ripple voltage on it is DUcorr@6*10^3 In / C1 (DUvypr - in volts, In - in amperes, C1 - in microfarads) will be excessive, periodically removing the transistor VT1 from the stabilization mode. In the one shown in Fig. 22 stress diagram Uke@1,5 V is the minimum collector-emitter voltage of the transistor VT1, at which it still retains its functions.
With a significant increase in load current, it will be necessary to increase the heat sink area under the transistor VT1 accordingly and, of course, use a more powerful step-down transformer, for example, TH10 (load current up to 6 A), TH11 (7,8 A or 8,7 A, depending on the type of core ), a number of others. It may be necessary to replace the silicon diodes VD1-VD4 with their rather large forward voltage drop Upr \u1d 1,2 ... 303 V with germanium D3 (current up to 304 A), D5 (305 A) or D10 (0,25 A), in which Upr \u0,3d 2 ... 2998 V, or on silicon with a Schottky barrier 2D219B (V), XNUMXDXNUMXG, etc., having Upr@0,4 V.
*) 0,02...0,07 A - in portable radio stations, 0,2...0,3 A - in car radios. Publication: cxem.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ NXP Unveils Ultra-Compact, High-Precision MEMS Frequency Synthesizer ▪ Cell division recreated outside the cell ▪ material absorbing carbon dioxide ▪ Sleepy cows give sleeping milk ▪ Cooler Master G Power Supplies 500, 600 and 700 W
▪ site section Lightning protection. Article selection ▪ article Through thorns to the stars. Popular expression ▪ article Why can't animals talk? Detailed answer ▪ article Sausage cheese smoker. Job description ▪ article Resettable fuse Phoenix. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: