Electronics against mosquitoes. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Home, household, hobby
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Summer comes, and with it mosquitoes and all sorts of other midges appear. Everyone knows how annoying mosquitoes are, especially at night.
The proposed device allows you to protect yourself from all insects, and if you increase the frequency of the generator to ultrasound, then from dog barking. The device diagram is shown in Fig. 1, and the printed circuit board is shown in Fig. 2.
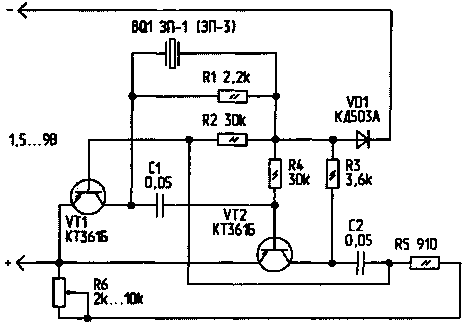
Ris.1
The sound-reproducing element of the device is a piezo emitter ZP-1 (ZP-3, ZP-22) or any other, for example, from a wrist watch.
Consider the operation of the device. Diode VD1 is necessary to protect against incorrect power connection to the circuit. The device is powered by +1,5 V galvanic cells (the supply voltage can be increased up to +9 V). As the voltage increases, the radiation power of the device increases.
Resistors R2...R4 and R5, R6 set the operating point of the transistor VT1 and VT2. When voltage is applied to VT1, C1 is charged, a pulse from C1 briefly opens VT2, VT2 charges C2, which briefly opens VT1, and the cycle of operation is repeated again.
The oscillator frequency depends on the capacitances C1 and C2 and the resistance R6.
You can turn on several more emitters in series with BQ1, then the output power will increase.

Ris.2
In the device, except for KT361B, any similar transistors can be used. It is desirable to use ceramic capacitors.
The device almost does not need adjustment. You just need to select the elements (R2, R4, C1, C2) that set the frequency of the generator. Next, a frequency meter is connected in parallel to R1 and the generation frequency is measured. It should be around 20 kHz. If the frequency is less, it is set by adjusting R6.
The device consumes very low current (about 1,5 mA), so one battery is enough for several months of operation.
It is desirable that during operation the device be located as close as possible to the ceiling, because. mosquitoes prefer higher places for day and night "parking".
Author: K. Kurashko, Brest; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
 See other articles Section Home, household, hobby.
See other articles Section Home, household, hobby.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Installation for removing carbon dioxide from the ocean
06.03.2024
UCLA, working with Singapore's national water agency, has agreed to build the world's largest ocean plant to remove carbon dioxide from water. The facility is expected to be able to extract 3650 metric tons of greenhouse gases from the ocean annually and produce 105 metric tons of carbon-negative hydrogen.
Average global carbon dioxide emissions in 2020 were 4,3 metric tons per capita, according to the World Bank. Based on this data, scientists from the University of California decided to focus on capturing CO2 from the oceans to reduce the amount of greenhouse gas entering the atmosphere.
The Equatic project, launched in Los Angeles and Singapore, has produced successful results. Equatic is moving on to the next phase of the project - construction of the full-scale Equatic-1 plant at a cost of $20 million. The support of the authorities of Singapore and the University of California ensures the successful completion of the project.
The Equatic plant uses electrolysis by passing a current through seawater to split water into hydrogen and oxygen and convert dissolved CO2 into a solid material based on calcium and magnesium. This process increases the ocean's ability to sequester carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases.
Construction of the Equatic-1 facility is scheduled to begin within the next 18 months. The capacity to remove one metric ton of CO2 per day will initially be established, with plans to increase this to 2024 tons of CO10 per day by the end of 2 using 10 modules. After this, 2025 more modules will be installed in 9 to complete the second phase of construction.
The project idea was proven successful after a pilot plant in Singapore successfully removed 0,1 metric tonne of CO2 per day. A full-scale Equatic-1 plant will be capable of processing 100 times that amount, as well as producing approximately 300 kg of carbon-negative hydrogen per day.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Tablets are better for vision than books
▪ gold mining bacteria
▪ artificial shrimp
▪ Seagate BarraCuda 510 M.2 SSDs
▪ Only half of US residents use landlines
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Spy stuff. Article selection
▪ article What is a director's script. video art
▪ article What is a comet? Detailed answer
▪ article Second discovery of cavitation. Children's Science Lab
▪ article Chips K155IE6 and K155IE7. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Digital volume control. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
Comments on the article:
Nicholas
It's necessary to manage so to powder the brains of even an experienced electronics engineer !!! Why was it necessary to turn the circuit of a conventional symmetrical multivibrator inside out? In addition, the circuit assembled according to the given ratings gives out frequencies from 600 to 900 hertz - so this "publication" is complete FUFLO !!! Electrical engineer for computer repair...
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: