Refinement of the dynamic head 25GDN-1-4. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Speakers
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Widespread low-frequency dynamic heads 25GDN-1-4 (old name 10GD-34, modern analogue 25ZT-1-4), fig. 1, were installed in two-way acoustic systems 6AC-2, 6AC-9, 10AC-9, 6MAS-4, in all modifications of S-30 and others as LF - MF links. The head 6GDV-1-16 (3GD-2) often served as a high-frequency link [1]. In some editions of the 35AC-1 three-way speaker systems, it was used as a midrange link. However, the sound quality of these systems in the mid-frequency range leaves much to be desired. Radio amateurs have repeatedly raised the issue of improving the sound quality of loudspeakers based on this head.

a)

b)
Rice. Fig. 1. Low-frequency head dynamic 25GDN-1-4 (10GD-34): a - general view; b) - dimensions and installation dimensions.
The frequency response of the 25GDN-1-4 head has significant irregularities in the midrange. Starting from 1 kHz, a smooth rise in sound pressure, and above 4,5 kHz, a sharp decline (Fig. 2). The S-30 series speaker filter has a crossover frequency of 5 kHz, while the 6AC-2 has a crossover frequency of 10 kHz. As a result, we have a significant dip in this frequency range, which, in turn, significantly degrades the sound quality of the emitter. In addition, the dust cap does not have the necessary rigidity, especially the polymer metallized one. At large amplitudes of vibrations of the moving system, clicks and bounces are audible. The 6GDV-1-16 head has a fundamental resonance frequency of 4,5 kHz and cannot operate at this frequency and near it without distortion, as a drawback, the presence of some hiss should be noted.

Rice. 2. Frequency response of sound pressure head dynamic 25GDN-1-4 (10GD-34)
To increase the upper limit of the frequency range of the speaker to 10-12 kHz, you can, for example, use an additional cone that is inserted inside the diffuser (Fig. 3). In this case, at high frequencies, the main cone ceases to work due to its relatively flexible connection with the voice coil, and a small diffuser, rather rigid and light, is put into operation [2].

Rice. 3. Loudspeaker with an additional diffuser.
Speaker systems of the S-90 family have typical disadvantages. The article "Modernization of AC 35AC-012 (S-90)" [3] describes a method for eliminating them for the head 15GD-11A (20GDS-1-8) structurally very similar to 25GDN-1-4, which can be successfully applied to the latter - replace the native dust cap with a cap from the head 10GDSh-1-4 (10GD-36K), which has the shape of a cone - a horn (Fig. 4). The diameters of their voice coils are very close - 25,7 mm for 10GDSh-1-4, and 25,4 mm for 25GDN-1-4.

Rice. 4. High-frequency passive horns (cones) 10GDSh-1-4.
Work is carried out in the following order. First, the dust cap is soaked with solvent 646 or 647. It is carefully removed with a scalpel (Fig. 5, a). It is advisable to use a non-magnetizable tool. Careless movement of a steel object can damage the speaker elements! Wipe with a cotton swab dipped in the same solvent, the glue diffuser. Lubricate the lower part of the horn and the upper part of the voice coil with Moment glue. Dry for 10-15 minutes. Again, both parts are smeared and immediately connected, pressing with a certain force (Fig. 5, b).

a)

b)
Fig5. Low-frequency dynamic head 25GDN-1-4: a - removing the dust cap; b - gluing the horn.
The design of the horn was developed for the dynamic head 10GDSh-1. For 25GDN-1-4 it should be adjusted. The adjustment consists in gradually cutting off its edge, measuring, after each cut, the frequency response of the speaker. The operation is repeated until the most even frequency response curve is obtained in the middle frequencies. By cutting off approximately 10 mm of the edge of the horn, measurements are taken. The second and subsequent cuttings should be carried out very carefully, cutting off no more than 3 - 1 mm (in descending order). As a result, the side surface of the horn inside was about 7 mm (from the dustproof element of the cap to the trim edge) - fig. 6, a. Trimming is performed with nail scissors, since they turned out to be the most acceptable tool for this type of work, they have miniature rounded cutting surfaces. The cut edge, to stiffen, is impregnated with BF-2 glue, slightly diluted with ethyl alcohol.

a)
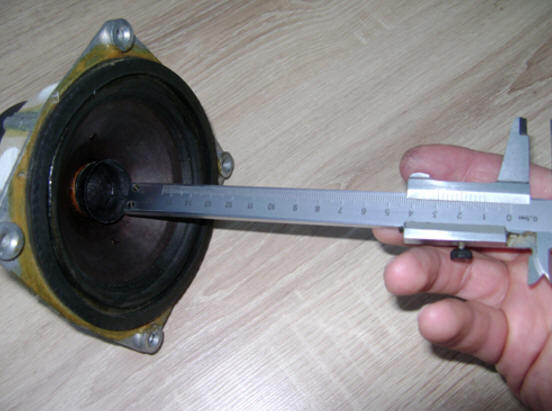

b)

at)
Rice. Fig. 6. Formation of the horn of the dynamic head 25GDN-1-4: a - cutting process; b - measurement of the height of the wall; c - view at the stage of completion.
Frequency response measurements are made using a condenser microphone (preferably measuring), placed on the same axis as the head *, within 30 - 40 cm, a computer and the RightMark 6.2.3 program. The microphone is connected to the line input of the computer's sound card, and the speaker is connected to the amplifier of the computer speakers. Run the program RightMark 6.2.3 and measure the frequency response of sound pressure [4,5].
Such refinement made it possible to expand the frequency band reproduced by the 25GDN-1-4 head to 10 kHz (!), and get rid of the structural overtones of the dust cap. When listening and comparing the modified heads with the original one, a noticeable expansion of the high-frequency reproduction band was found, which is observed on the frequency response graph of the sound pressure - fig. 7. Despite the measurement errors, signal distortions introduced by the amplifier, microphone, environment, we can conclude that the desired result has been achieved.
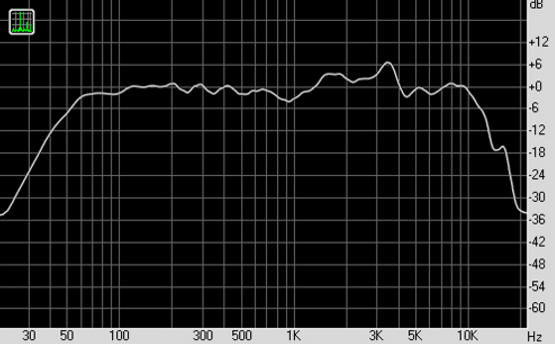
Rice. 7. Frequency response of the sound pressure head of the dynamic head 25GDN-1-4 equipped with an additional emitter.
The dynamic head 25GDN-1-4 after such refinement can be used as a low-frequency, mid-frequency and broadband, both in computer speakers and in automobiles (it is easily mounted in regular places under the acoustics of the front doors of most car models), small-sized subwoofers, etc.
Note. In order to eliminate the negative effect of an acoustic short circuit on the measurement results, the 25GDN-1-4 head is placed in a box with an open back wall, covered with sound-absorbing material from the outside and from the inside. The speaker is mounted on the front panel from the outside. Otherwise, the air resonating in the head hole will introduce distortion. On the frequency response graph, this manifests itself in the form of peaks and dips.
Literature
- Burko V., Lyamin P. Household acoustic systems: operation and repair. Reference manual. Minsk, "Belarus", 1996, p. 224.
- Sapozhkov M. Acoustics. Textbook for high schools. M., "Communication", 1978, p. 138.
- Marchenko V. Modernization of AC 35AC-012 (S-90). radioradar.net/radiofan/audio_equipment/35ac_012.html
- Marchenko V. Measuring microphone. radioradar.net/radiofan/measuring_technics/measuring_microphone.html
- Afonin S. Creation of acoustic systems at home. M., "Eksimo", 2008, p. 90-96.
Author: Vladimir Marchenko
 See other articles Section Speakers.
See other articles Section Speakers.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024
In a modern technology world where distance is becoming increasingly commonplace, maintaining connection and a sense of closeness is important. Recent developments in artificial skin by German scientists from Saarland University represent a new era in virtual interactions. German researchers from Saarland University have developed ultra-thin films that can transmit the sensation of touch over a distance. This cutting-edge technology provides new opportunities for virtual communication, especially for those who find themselves far from their loved ones. The ultra-thin films developed by the researchers, just 50 micrometers thick, can be integrated into textiles and worn like a second skin. These films act as sensors that recognize tactile signals from mom or dad, and as actuators that transmit these movements to the baby. Parents' touch to the fabric activates sensors that react to pressure and deform the ultra-thin film. This ... >>
Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024
Taking care of pets can often be a challenge, especially when it comes to keeping your home clean. A new interesting solution from the Petgugu Global startup has been presented, which will make life easier for cat owners and help them keep their home perfectly clean and tidy. Startup Petgugu Global has unveiled a unique cat toilet that can automatically flush feces, keeping your home clean and fresh. This innovative device is equipped with various smart sensors that monitor your pet's toilet activity and activate to automatically clean after use. The device connects to the sewer system and ensures efficient waste removal without the need for intervention from the owner. Additionally, the toilet has a large flushable storage capacity, making it ideal for multi-cat households. The Petgugu cat litter bowl is designed for use with water-soluble litters and offers a range of additional ... >>
The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
The stereotype that women prefer "bad boys" has long been widespread. However, recent research conducted by British scientists from Monash University offers a new perspective on this issue. They looked at how women responded to men's emotional responsibility and willingness to help others. The study's findings could change our understanding of what makes men attractive to women. A study conducted by scientists from Monash University leads to new findings about men's attractiveness to women. In the experiment, women were shown photographs of men with brief stories about their behavior in various situations, including their reaction to an encounter with a homeless person. Some of the men ignored the homeless man, while others helped him, such as buying him food. A study found that men who showed empathy and kindness were more attractive to women compared to men who showed empathy and kindness. ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Martian soil - radiation protection
22.10.2012
European Space Agency specialists, together with scientists working at the GSI accelerator in Germany, will test the potential suitability of lunar and Martian soil as a radiation shield.
During this two-year ESA project, it is planned to test whether the lunar and Martian soil can protect astronauts from cosmic radiation. This is of great importance for the future exploration of the Moon and Mars, as it affects the design of the first lunar and Martian settlements, the choice of equipment and the cost of expeditions.
ESA specialists had to use in their project the only accelerator in Europe capable of accelerating heavy atomic nuclei to ultra-high speeds - it is with such particles that astronauts will have to meet outside the Earth. The accelerator is located at the Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research (GSI).
GSI simulates high-energy galactic radiation, which has already tested the protective properties of such common materials as aluminum, water, polyethylene, and a number of composites. Now, based on data on the conditions on the Moon and Mars, they will create a model of the soils of these celestial bodies and test their ability to delay cosmic radiation.
At first glance, the problem of protecting people from cosmic radiation is simple: you need to make the protection thicker - that's all. However, even if we write off the high cost of putting heavy protection into orbit, this problem is more complicated than it seems. For example, a thick metal shield, which is bombarded by heavy high-energy particles, itself begins to produce secondary radiation - sometimes even more harmful than the primary one.
Currently, scientists know that water and polyethylene are better at protecting against cosmic radiation than, for example, aluminum. The best result is shown by a new hydrogen-saturated material developed by scientists from the British company Cella Energy. Interestingly, this material was originally created to store hydrogen fuel. However, for the construction of permanent lunar and Martian bases, the best option would be to use local materials. Therefore, the ESA focused on the alien soil.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Flipped 3D printer
▪ Rearview Mirror with Android
▪ Video club for Japanese pensioners
▪ Virtual reality for pain relief
▪ Dry ice vs fog
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Home workshop. Article selection
▪ article Tender and amazing. Popular expression
▪ article What determined the ability of grasshopper hamsters to hunt poisonous scorpions? Detailed answer
▪ article Deputy Head of the Customer Service Department. Job description
▪ article 144 MHz Antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Charger for electric shaver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese











 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: