
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING How CDs sound (speculation and reality). Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
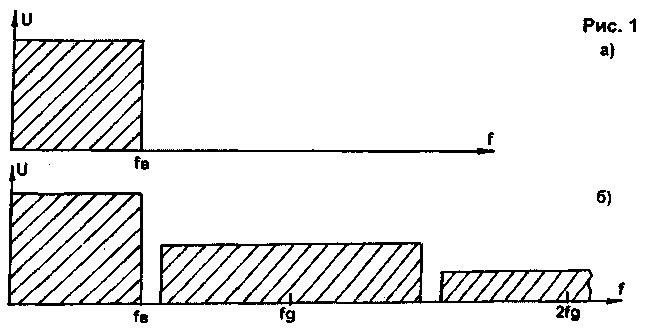
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment The digital format for recording audio CDs (CDs) Audio CD has firmly established itself in the consumer audio equipment market. In popular amateur and professional literature, various authors have repeatedly spoken out about the advantages and disadvantages of this format. In this article, based on my experience, I will try to dispel some misconceptions. In [1], the author points out the inexpediency of copying compact cassettes from CDs, referring to the fact that the sound quality of a CD, in his opinion, can be equated to the sound quality of analog sound reproducing equipment of the 3rd class. In this article (which is very interesting), the author questioned Shannon's theorem (or, as it is called in Russian literature, Kotelnikov's theorem). Let us assume that the input of the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) receives a signal with a uniformly distributed spectrum in the frequency band from 0 to 20 kHz (Fig. 1a). If an analog-to-digital conversion is carried out with a sampling frequency fg = 44,1 kHz (slightly higher than according to Shannon's theorem), and then an inverse digital-to-analog conversion is performed at the same fg, then spurious bands with central frequencies that are multiples of fg (Fig. 1b). Simplistically, this phenomenon can be called the transformation of elementary sinusoidal signals into signals of complex shape (for example, the case described in [1] of converting a single sinusoidal signal of 20 kHz into a meander with the same frequency).
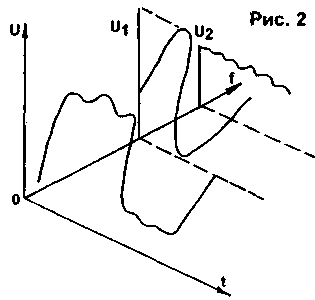
To further understand the essence of what is happening, let's turn to the conversion of harmonic periodic signals from the time domain to the frequency domain. Figure 2 graphically displays this process. In the time plane UOt, a graph of a periodic signal is plotted. If we decompose a graphed function using the Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT), Fast Hartley Transform (FHT), or Modern Discrete Cosine Transform (DCT) into harmonics and plot their amplitude with a shift along the Of frequency axis, we can see that the original signal in its spectrum contains two harmonics with amplitudes U1 and U2. In practice, the time dependence of the amplitude is observed using oscilloscopes, and the frequency dependence is observed using spectrum analyzers.
If we carry out the DCT of sinusoidal and rectangular signals with a frequency of 20 kHz at fg = 40 kHz, we get the result shown in Fig. 3 a and b, respectively. As you can see, in the spectrum of a rectangular signal, in addition to the fundamental frequency, there are many harmonics with frequencies that are multiples of the fundamental and amplitudes that decrease with increasing harmonic number. Using a low-pass filter (i.e., cutting out all the "extra" harmonics), you can get a sinusoidal signal from a rectangular one. This process can be provided by both analog and digital methods.
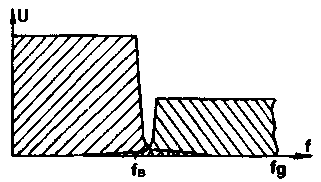
If now, knowing that at the output of the DAC, the signal from the sinusoidal becomes rectangular, i.e. spurious bands appear in the spectrum (Fig. 16), use a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency fcp = 20 kHz, all spurious bands that are multiples of fg can be removed from the resulting signal. Active low-pass filters of the nth order are usually found in all CD players, if not directly in the circuit, then as part of integrated DACs. Parasitic harmonics in the signal appear due to the imperfection of the frequency response of the low-pass filter included at the input and output of the ADC and DAC (Fig. 4). As a result, superposition of the spectra of the signals generated by the DAC occurs, and the level of parasitic components is the lower, the "steeper" the frequency response of the low-pass filter and the greater the attenuation in its stopband.
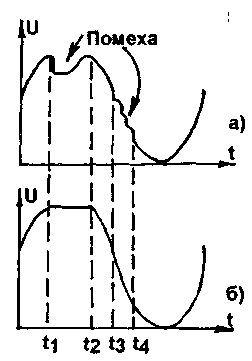
Increasing fg by a factor of 4 or 8 relative to the Nyquist frequency (the upper frequency of the signal) allows you to slightly push the components of the signal spectrum at the DAC output, however, this unreasonably increases the digital data stream, which cannot be reduced using the AudioCD standard. Only by improving the characteristics of the low-pass filter before the ADC and after the DAC, it is possible to deal with the increase in interference created by side parasitic bands. Modern PCDs with a low-pass filter of at least 6 orders relatively successfully cope with the task of filtering the signal after the DAC, providing attenuation of spurious noise of at least 90 dB. The bandwidth of the sound channels in this case is 20 ... 21600 Hz with an unevenness of 5 * 10-3 db. These parameters are noticeably superior to similar parameters of analog sound reproducing equipment of all classes. From the above, we can conclude that when sampling a signal with fg = 2fB, it is necessary to tighten the requirements for the low-pass filter at the output of the DAC PKD. In [1], the author also reports on signal compression before recording on CD, as well as on the formation of a frequency cut in the recordings made from these CDs in the region of 20...200 Hz. More precisely, the blockage reaches a frequency of 1 kHz, which is considered a reference for audio frequency technology. As follows from the theory of noise immunity, when transmitting signals (including audio), signals with a large dynamic range and frequency band, it is advisable to compress before transmission, which was successfully introduced into practice by the American researcher Dolby. The expansion of the signal is carried out in the VPC at the request of the user. It is worth noting that in most CD-ROM drives that play CDs, the expander is actually absent. Its function is replaced by a low-pass filter, which is available in the vast majority of sound cards and in active speakers ("Bass" button), which raises the bass level, but cannot be a complete analogue of an expander. The digital part of the PCD has the ability to both correct and mask errors, and both errors due to the poor quality of the recording on the CD itself and defects in its surface can be corrected. However, this function of the PKD cannot be overestimated, since the codes used in it for verification correct a finite number of errors, and their number during the operation of the PKD (mechanical damage), unfortunately, grows. Thus, when playing low-quality CDs, especially those that have undergone intensive use, the sound quality of CDs is sharply reduced. Let me give you this fact as an example. A three-bit correction code of a four-bit word (with Hamming correction) corrects no more than 1 error. Therefore, it is necessary to have such a record that the error occurs no more than 1 time per 7 bits of information. Of course, more powerful correction codes are used in the VPC, but there is still some limit to the number of errors. An important role is also played by the quality of the equipment on which the CD is recorded; the quality of the matrix from which CDs are replicated during their mass production; as well as the operating conditions of the CD. There is an opinion that the same piece of music, recorded on a CD on different equipment, sounds differently. This is true because the VCD tries to correct (disguise) errors that occur when playing back CDs recorded using poor quality equipment. Schematically, the process of occurrence and masking of errors is shown in Fig.5. Let at the moments t1-t2 and t3-t4 the signal is affected by impulse noise (Fig. 5a). The corrective device tracks it and replaces it with adjacent "unaffected" readings (Fig. 56), i.e. interpolates the signal. However, if you apply DCT to the received signal and analyze its spectrum, you can see spurious bands in it. If the low-frequency filter at the DAC output successfully “fights” with the high-frequency components, then lower-frequency interference is superimposed on the resulting signal, creating specific distortions, especially noticeable during long-term interference.
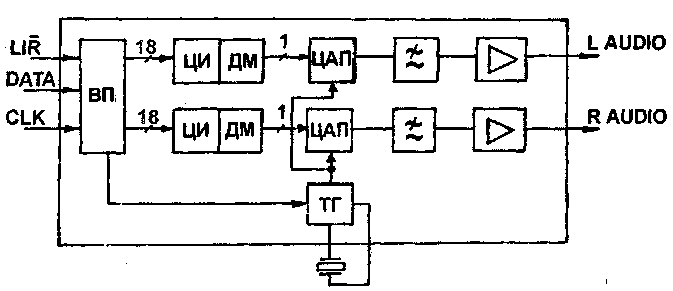
There is an indication in the literature that the so-called "single-bit DACs" have worse parameters than multi-bit ones. In particular, a greater value of phase jitter ("jitter") is observed in single-bit DACs. Figure 6 shows a functional diagram of a single-bit DAC CS4328 from Crystal Sem. Serial data (can be presented in 4 formats) is fed into the input converter (IP), which converts them into 18-bit parallel streams of two channels. Signals through digital interpolators (DI) are fed to digital delta modulators (DM), which form one-bit data streams with 64-fold "oversampling". Further, the signals are fed to single-bit DACs, a sixth-order low-pass filter, and through buffer amplifiers are fed to the output of the circuit.
Since the microcircuit uses simpler and cheaper single-bit DACs, the cost of the device decreases with a slight deterioration in its parameters. The clock generator (TG) driving the DAC is locked by the PLL to the incoming CLK clock, which reduces jitter. The switched capacitor filter allows the circuit to be used at any clock frequency (i.e., there is no need to reconfigure the low-pass filter). The dynamic range of the chip reaches 93 dB. Undoubtedly, at the time of the release of the first VRMs, devices of this class had characteristics comparable to or exceeding those of high-end analog sound reproducing equipment. The circuit solutions of various manufacturers differed in variety, which caused the promotion of models of both high and low quality to the market. Coming to replace the CD multi-profile DVD-ROM (audio version) allows you to solve the problem of filtering parasitic harmonics in the spectrum of the output signal by digital methods, as well as by increasing the sampling frequency. Because DVD technology uses MPEG-2 Audio compression, i. frequency-amplitude representation of the signal by DCT with subsequent reduction of redundancy, it becomes possible to effectively digital filter using digital signal processors. The capacity of a single layer DVD is 4,7 GB versus 680 MB CD, which allows large amounts of data to be written to DVD. However, since the same electronic devices (ADC, DAC, etc.) will be used in circuit solutions, problems with jitter reduction, etc. will also be acute. Firms producing electronic components will solve them by designing more modern and high-quality devices. At the same time, the PKD is the most complete replacement for obsolete analog sound reproduction equipment. Literature 1. Skulkin I. On the quality of sound on compact discs. - Radio amateur, 1998, N1.C.19 Author: V. Fedorov, Lipetsk; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Optimal combination of crops and solar panels ▪ Man and chimpanzee: the differences are not so great ▪ Musical camouflage for fireflies ▪ Pasteurization of beer with electricity
▪ section of the site Instructions for use. Article selection ▪ article by Herbert Marcuse. Famous aphorisms ▪ article Organization of the work of authorized (trusted) persons for labor protection ▪ article Distant relatives of cinema. physical experiment
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
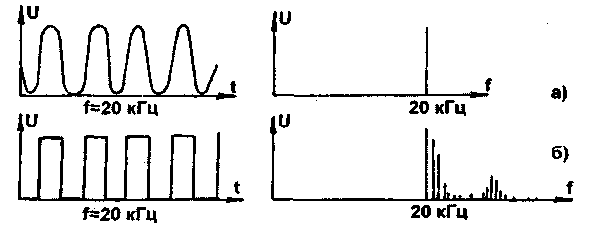
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: