
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Small square antenna. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
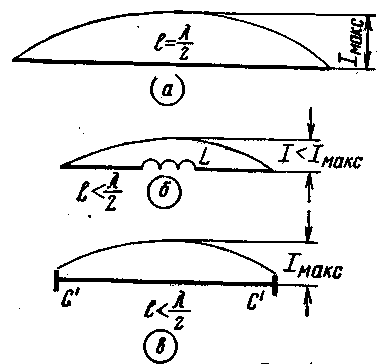
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / HF antennas Among the problems that short-wave radio amateurs have to face, the main one, perhaps, is the problem of manufacturing a sufficiently effective and at the same time not very complicated antenna in terms of design. There is no doubt that a rotating directional antenna can provide the best results. However, almost all antennas of the final type are quite bulky and structurally complex, which makes it difficult for many amateurs to use them. In the article published below, a method is proposed for significantly reducing the geometric dimensions while maintaining a sufficiently high efficiency of antennas, which will undoubtedly be of interest to shortwave workers. The author deliberately does not give a specific design of the antenna, since he hopes that a wide range of shortwavers will test the described method on antennas with different degrees of reduction, designed for different ranges, having different design. In recent years, many descriptions of various short-wave small-sized antennas have appeared on the pages of the amateur radio press, in which electrical extension to a resonant length is achieved using reactive elements (inductances, capacitances, line segments). By reducing the geometric dimensions, the installation of the antenna is facilitated and the design of the supporting devices is simplified. Some radio amateurs treat such antennas with a certain skepticism, explaining that any geometrically reduced antenna works worse than a full-sized one. One cannot but agree with this. Indeed, with any type of shortening of the vibrator, the area limited by the diagram of the distribution of the current flowing through it (hereinafter referred to as the "current area") and, consequently, the efficiency of the antenna decreases. However, the degree of reduction in efficiency depends not only on the degree of geometric reduction, but also on the method of electrical extension of the antenna. In addition, sometimes it turns out that a smaller antenna in real conditions works even better than a full-size one due to the redistribution of energy losses and radiation, for example, when a smaller antenna is installed at a much higher height above the surrounding area. Small antennas, obviously, can also attract the attention of radio amateurs who, for whatever reason, do not have the opportunity to install a full-sized antenna. Fig. 1a shows a full-size half-wave vibrator; 1c - vibrator, the electrical elongation of which is achieved due to the capacitive load at the ends. For each vibrator, the current distribution along it is shown. As can be seen from the figures, the maximum current area is observed for a full-size vibrator.
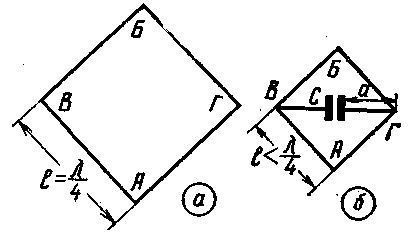
For the other two vibrators, we see that with a significant degree of electrical elongation, the current area tends to a rectangle with height Imax in the case of switching on the capacitance, and in the second case, to a triangle with height I Figure 2a shows a square vibrator with one of its corners facing down. With a symmetrical power supply to the antenna at point A or B, the voltage antinode will be at points C and D, and the current antinode at points A and B. The vibrator can be electrically extended, including the inductance in the wire break at point A or B, or the capacitance between points C and D. The latter method is also more advantageous in this case. As a result, we obtain a vibrator in the form shown in Fig. 2b with geometric dimensions smaller than that of the square in Fig. 2a, but with the same resonant frequency.
For the purpose of practical verification of the feasibility of electrical extension of a square antenna with the help of a capacitance, an experiment was carried out on a reduced model at a frequency of about 100 MHz. The square is made of wire with a diameter of 1,2 mm. The size of the side of the square is 76 cm. The results of the experiment are shown in Table 1. Table 1
As can be seen from the table, with an increase in the length of the wire a (Fig. 2, b), the resonant frequency of the square decreases, although the capacitance C is not yet connected. This is due to the fact that the horizontal wires themselves electrically lengthen the antenna due to the additional capacitance they form. When connecting capacitance C, equal to 20 pF, the resonant frequency of the vibrator was reduced by half compared to the original. Estimated efficiency values, depending on the ratio of the dimensions of a small-sized antenna to the dimensions of a conventional one, without taking into account losses in insulators, are shown in Table 2. Table 2
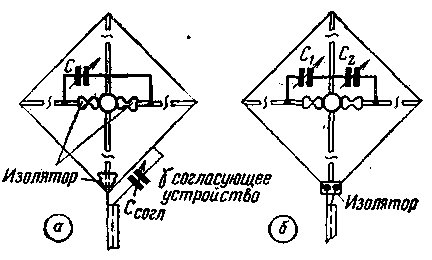
Electrically elongated vibrators are elements from which a multi-element antenna can be assembled. Below we consider the construction of a "double square" made of elements electrically elongated with the help of a capacitance. If the feed point of the antenna is chosen at vertex A, then in the case of electrical symmetry of the antenna, the voltage at point B will be 0. The voltage at point A will depend on the power supply circuit of the antenna. So. when using the g-matching scheme, which is widespread among radio amateurs, the voltage at point A will also be close to zero. Generally speaking, this allows the use of a metal pipe as a vertical rod that is not insulated from the vibrator wires. However, with a slight violation of symmetry, a current will appear in the vertical rod, which will disrupt the normal operation of the antenna. The role of the horizontal part of the vibrator can be performed by a supporting metal rod, but it must be broken in the middle and isolated from the vertical rod. A tuning capacitor of variable capacitance is connected to the same point on the horizontal rod. A sketch of such a design is shown in Fig. 3a.
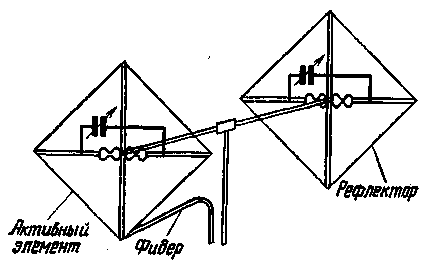
Figure 3b shows a design in which two capacitors (C1 and C2) are used. The frame is powered by a cable without a matching device. The rotors of the capacitors are at a small potential approaching zero when the antenna is symmetrical. By changing the ratio between the capacitances C1 and C2, it is possible to symmetricalize the antenna. If there is no such need, then a double block can be used as variable capacitors. The value of the capacitance of the capacitors depends on the range for which the antenna is designed and on the degree of its electrical extension. For all practical cases, a maximum capacitance value of 50 pF is quite sufficient. Particular attention should be paid to insulators, since they are included in the voltage antinodes and mainly determine the amount of high-frequency energy losses. Insulators made of low-loss materials (porcelain, polystyrene, fluoroplast, etc.) should be used. The passive element of the antenna is performed in a similar way. The spacing between vibrators remains the same as for full size antennas. A general view of a two-element antenna is shown in Fig.4.
Specific antenna dimensions for a particular amateur band are not given, as they depend on the desired degree of reduction in geometric dimensions and on the dimensions of the supporting structural details. A possible error when marking the length of the wire is easily compensated when tuning the antenna with capacitor C. Author: Inzh.S. Bunimovich (UB5UN); Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ A floating city will be built in the Pacific Ocean ▪ Transcend ESD380C High Speed Portable SSD ▪ Mercedes-Benz C-Class with autopilot
▪ site section Acoustic systems. Article selection ▪ article by Joseph Ernest Renan. Famous aphorisms ▪ article How to explain extrasensory perception? Detailed answer ▪ Article Building Maintenance Specialist. Standard instruction on labor protection ▪ article VGA tester. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: