
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING UMZCH with a power of 320 watts on the STK4231 chip. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Transistor power amplifiers In recent years, radio amateurs are increasingly using power amplifiers on microcircuits. For many applications, it becomes impractical to assemble an amplifier on separate elements; in most cases, such amplifiers require the establishment of a protection device, setting the quiescent current of the output stage, etc. Integrated amplifiers are actually made according to the "soldered and ready" principle. Various versions of such amplifiers have already been repeatedly recommended on the pages of the magazine, however, the maximum (i.e., with nonlinear distortion of 10%) output power of amplifiers on a single chip is usually limited to 100 ... 120 W, at least when using chips from an affordable price category . Even when using two TDA7294 chips in bridging, the power in the load does not exceed 200 watts. But what if you need to assemble a more powerful amplifier, for example, for a disco? This describes a power amplifier on an integrated circuit that allows you to get output power up to 300 watts per channel. The amplifier uses a hybrid chip STK4231-II manufactured by SANYO. This microcircuit is dual-channel, so only one microcircuit is required for the bridged switching option. When assembling an amplifier on such a microcircuit, a little more parts are required than for an amplifier on the TDA7294, however, it has a number of advantages and, most importantly, allows you to get a much more powerful amplifier. The microcircuit is much easier to mount on the heat sink, since its substrate is not connected to the heat-conducting surface of the case and it can be directly connected to the heat sink or amplifier case (for the TDA7294 microcircuit, the minus of the power source is connected to the substrate). This can often be critical, as isolating the heatsink from the chassis can sometimes be tricky. Schematic diagram of the power amplifier on STK4231-II is shown in fig. 1. Main technical parameters of the amplifier
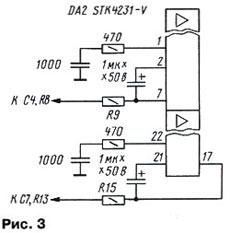
The amplifier is powered by an unstabilized source of bipolar voltage 2x (45 ... 55) V. The input signal to one of the amplifiers of the DA2 chip goes directly to pin 3, and to the second (pin 20) - through an inverting buffer amplifier on the op-amp DA1. The op amp is powered by voltage stabilizers +15 and -15 V, made on DA3, DA4 microcircuits. From the same stabilizers, if necessary, you can also power a preamplifier with tone controls or crossover filters. The gain of the power amplifier can be changed by selecting the feedback resistors R6 and R11. Their resistance in both arms of the amplifier should be the same. On transistors VT1 - VT4, a current protection unit is made that prevents the microcircuit from failing in the event of an overload. With an increase in current through one of the resistors R18, R28, the voltage drop across it increases, which leads to the opening of the transistor VT2 or VT1, respectively. This, in turn, leads to the operation of a thyristor analog on transistors VT3, VT4, and the microcircuit is blocked. To disable the blocking, turn off and turn on the amplifier again. If there is no need for a protection device, then you can not solder transistors VT1 - VT4 and related elements to the board - this will not affect the operation of the amplifier. Other variants of the protection device can be used with the amplifier, taking into account the property that when connected to the common wire of resistors R25, R31, the amplifier is blocked. The microcircuit has a node that prevents clicks in the speakers when the power is turned on and off. To do this, pin 8 of the DA2 microcircuit receives a constant voltage supplied through the VD2 diode and the corrective circuits from the winding of the power transformer. The amplifier has been tested in operation with a real load with a resistance of 5,3 ohms; the output power is somewhat less with a load resistance of 8 ohms. A single-sided printed circuit board has been developed for the amplifier, the drawing of which is shown in Fig. 2. In the design, you can use resistors C5-16 with a power of 5 W (R16-R18, R28-R30), MLT-1 (R22, R31, R38, R39), the rest - MLT-0,25 or MLT-0,5. Oxide capacitors - K50-35 or imported for a voltage of 63 V. The rest of the capacitors are film (K73 groups) or ceramic (except for the TKE H50 and H90 groups). Op-amp DA1 can be replaced with K140UD7, KR140UD17, TL071, etc. KT502E transistors can be replaced with 2SA1207, KT814G, VT3 - with 2SC2911, KT815G, VT4 - with 2SA1209, KT814G. Inductors L1, L2 are wound with a wire with a diameter of 1 mm on resistors R17, R29 turn to turn in one layer along the length of the resistor. The STK4231 microcircuit has two versions - with indexes II and V. The switching circuit for STK4231-V differs slightly from that recommended for the STK4231-II microcircuit, in which pins 1, 2, 21 and 22 are not used. For STK4231-V, additional elements are connected to them, as shown in fig. 3; all other conclusions are connected in the same way. The amplifier with STK4231-V has a lower harmonic coefficient - 0,08%.
Such an UMZCH can be powered both from a transformer mains power supply, and from a more modern pulsed one. The power of the power supply should be chosen 30...40% more than the maximum power of the amplifier itself. An amendment to this article should also be taken into account: output 12 DD3.2 (see the diagram in Fig. 2 in the article) must be connected to output 3 DD3.1, and not as shown in the diagram. In addition, to limit the first inrush current when the UPS is turned on, it is useful to introduce a thermistor into the primary rectification circuit. When using a switching power supply in the amplifier circuit, instead of the KD226A (VD2) diode, use KD212, and reduce the capacitance of the capacitor C14 to 1000 pF. When assembling the described amplifier, special attention must be paid to fastening the microcircuits to the heat sink. The introduction of mica gaskets for insulation at such an amplifier power is unacceptable. Microcircuits allow heating up to 70 ° C during normal operation, but it is advisable not to exceed this temperature. It is advisable to use forced cooling by a fan. The heat sink can be installed pin (needle), in extreme cases, ribbed, acting as the rear or side walls of the amplifier case. It is possible to fasten the microcircuit with screws using heat-conducting paste to a copper plate 3 ... 5 mm thick, and then a plate with the same paste to a dissipating heat sink. The dimensions of the plate should be 2...4 times larger than the dimensions of the microcircuit used. In this case, the efficiency of heat transfer will be maximum. With proper assembly and the use of known-good parts, the described amplifier does not require adjustment. When powering the pre-amplifier from stabilizers DA3, DA4 (see Fig. 1), it is only necessary to select resistors R38, R39 so that the voltage at the input of stabilizers DA3, DA4 is within 20 ... 30 V. Author: I. Korotkov; Publication: cxem.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Women's brains age more slowly ▪ Fake news spreads online faster than the truth
▪ section of the site Electrician's Handbook. Article selection ▪ article Like Christ in the bosom. Popular expression ▪ article What is bobsleigh? Detailed answer ▪ article The functional composition of Fergusson TVs. Directory
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: