
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Acoustic design of multiband loudspeakers. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Speakers The most widespread among foreign radio amateurs are two- and three-way acoustic systems. Often, to further improve the return at low frequencies, the loudspeaker case is equipped with a phase inverter. I use other techniques to improve the performance of loudspeakers with two and three signal frequency separation bands. Two-way loudspeaker with slot inverter. Typically, the inverter hole is rectangular in shape and is located slightly below the hole of the low-frequency driver. Since the phase inverter improves the sound only at low frequencies, where there is practically no radiation directivity, the location of the hole, as well as its shape, is not important for the normal operation of the phase inverter. The main thing is that its area should be equal to about half the area of the diffuser. In view of the foregoing, an original design of a two-way loudspeaker with a phase inverter slot located on the rear wall was proposed. The design of this loudspeaker can be understood from the sketch shown in Fig. 1.
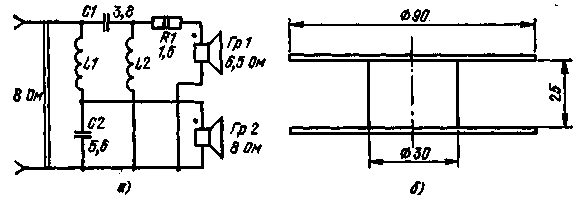
The first design feature of the loudspeaker is a slotted hole 26 mm wide and 860 mm long, i.e., the entire length of the rear wall. The second feature is the prismatic shape of the case: the width of the front panel is 610mm, the back panel is 190mm. The lower and upper walls are rectangular in size 285x650 mm with two truncated corners. This is done for the convenience of placing the speaker on the floor, in the corner of the room. This accomplishes two goals at once. First, the loudspeaker is placed in a place in the room where it does not interfere. Secondly, an additional boost of low frequencies by several decibels is created due to the reflection of the signal from the two side walls and the floor of the room. The loudspeaker enclosure is made of plywood or chipboard with a thickness of about 20 mm. Laths for side braces with decorative fabric with a cross section of 90x50 mm - made of pine. The junctions of the side walls with the upper and lower walls are reinforced with rectangular plates with a cross section of 40x40 mm, also made of soon. To eliminate the effect of signal reflection at medium and higher frequencies, a quilted layer of natural or mineral wool with a thickness of at least 50 mm is placed inside the case. Such a coating must be made over the entire inner surface of the housing. When repeating the design, you can use a low-frequency head of type 6GD-12 and a high-frequency head of type 3GD-31, adjusting the dimensions of the holes on the front panel taking into account the dimensions of the diffusers of domestic heads. With this combination of drivers, the loudspeaker is able to effectively reproduce signals in the frequency range from 40 Hz to 16 kHz. The input power of the broadband signal can reach 6-8 W. The crossover filter should have a crossover frequency of about 3 kHz. On fig. 2a shows a schematic diagram of a crossover filter for joint operation with a low-frequency head with a resistance of 8 ohms and a high-frequency head with a resistance of 6,5 ohms. In this case, the resistor R1 is necessary to equalize the load resistance of the high- and low-frequency filter outputs. If you use a domestic 8 ohm high-frequency head, the resistor R1 must be excluded.
In the manufacture of coils, cardboard frames can be used with the dimensions indicated in Fig. 41,6. In this case, the L1 coil should contain 100 turns, L2 - 120 turns of PEV-3 wire with a diameter of 0,9-1,1 mm. The required capacitances of capacitors C1 and C2 can be obtained by connecting in parallel several capacitors of the 160 V MBM type with capacities of 1,0, 0,5 and 0,1 μF. Loudspeaker with reverse exponential horn Currently, among amateurs and professionals, the so-called small-sized speaker systems, abbreviated as MAC, are very popular. Small in size, easy to use, with a wide bandwidth of reproducible frequencies, they are becoming more and more widespread. True, they have a number of shortcomings. The most significant is the relatively low return in the entire frequency band. For normal operation of such loudspeakers, an input power of about 10 W or more is required, while for conventional types of loudspeakers it is 2-3 times less. This drawback is compensated to some extent by the increased power of modern low-frequency amplifiers. MAC loudspeakers have another drawback due to the specific non-linear distortion created by the cone. The fact is that such loudspeakers use special low-frequency heads with a very light diffuser suspension. Due to this, the natural resonant frequency of the heads is very low and reaches 10-16 Hz. When the head is installed in a housing with good sealing, its resonant frequency increases by 2-3 times, reaching the value required for high-quality sound reproduction, equal to 20-45 Hz. The damping of the diffusers of such heads occurs due to the elasticity of the air contained in the internal volume of the loudspeaker housing. In this case, the diffuser works like a compressor piston, alternately compressing and expanding the air inside the housing. For this reason, lightly suspended woofers are called compression or air-suspended cone drivers. The reason for the additional non-linear distortion created by low-frequency MAC drivers is that the front and rear surfaces of the cone of these heads have different acoustic impedances. The front surface is in contact with open space, and the rear surface is in contact with air enclosed in a sealed loudspeaker housing. Obviously, in order to eliminate additional specific non-linear distortions of low-frequency heads, it is necessary to equalize or at least bring together the acoustic impedances of both surfaces of the diffuser. In one of the magazines, a brief description of a two-way small-sized loudspeaker was published, in which the harmonic distortion of this type was significantly attenuated. With external dimensions of 196x236x300 mm and weight of 4,9 kg, the loudspeaker provides effective sound reproduction in the frequency band from 60 Hz to 16 kHz at a nominal input power of 10 W. The essence of the improvement is the use of a reverse exponential horn as an additional acoustic load for the low-frequency driver. The horn is made in the body of the front panel of the loudspeaker with a thickness of 20 mm, as shown in Fig. 3, a. The view of the front panel from the front side is shown in Fig. 3b. The inner surface of the loudspeaker case is lined with a layer of wool about 50 mm thick, and the magnetic system of the head is additionally pressed by a wooden support inserted between the back wall and the magnetic system. The loudspeaker case is sealed with nitro-glue, which is used to coat all joints and connections from the inside. The front panel on the front side is covered with a thin radio fabric, the body itself is pasted over with an imitation film or veneered with precious woods.
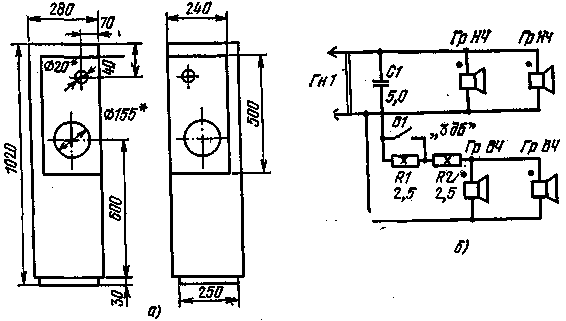
When repeating the design, you can use a compression low-frequency head of the 6GD-5 type and a high-frequency head ZGD-31. In this design, it is recommended to use a crossover filter with a crossover frequency of about 3 kHz. True, the head of the 3GD-31 type is somewhat larger than the high-frequency head used by the author of the design. This will require some reworking of the front panel. But you can do without alterations if you use a high-frequency head of the 2GD-36 type. The use of a head of the 2GD-36 type makes it possible to expand the band of effectively reproducible frequencies up to 18-20 kHz. True, there is one peculiarity here. Some samples of heads of this type have a relatively high frequency reproduction of low frequencies - about 6-3 kHz. Therefore, it may be necessary to change the crossover frequency from 6 to 1 kHz. To do this, it is enough to reduce the number of turns of the coils L2 and L2 of the filter according to the scheme of Fig. 70 to 90 and 1, respectively, while reducing the capacitances of capacitors C2 and CXNUMX by half Loudspeaker with extended polar pattern Observations have shown that broadband and multiband loudspeakers, in which the diffuser openings are located in one, usually frontal plane, have one drawback due to the narrowness of the radiation pattern. The orientation in the horizontal plane is especially noticeable. Because of this, the zone of manifestation of the stereo effect narrows, the reproduction of the higher frequencies of the signal is weakened. To combat this drawback, various means are used, including the inclusion of additional loudspeakers placed in a certain way relative to the main loudspeakers, the separation of mid- and high-frequency heads separately, the reduction of low-frequency signals of a stereo system into one mono signal, etc. Amateur radio practice shows that that an increase in the number of loudspeakers clutters up the living space, leads to an increase in the number of connecting conductors. Therefore, it is more expedient to create such loudspeakers that would have a wide radiation pattern in the horizontal plane and would not take up much space. On fig. 4,a shows sketches of the loudspeaker case, and in fig. 4b is a schematic diagram of its separation filter. As can be seen from the figure, the loudspeaker has a pair of low and high frequency heads connected in parallel. High-frequency heads are connected through the simplest crossover filter, consisting of a capacitor C1 and resistors R1 and R2.
According to the design description, low-frequency heads are rated for 15 W, high-frequency ones - for 10 W each. Thus, the loudspeaker can be used to work with ULF up to 30 watts. High-frequency heads have practically no effect on power due to the relatively high crossover frequency of about 6 kHz. The main advantage of the loudspeaker is a wide horizontal radiation pattern of 270° at frequencies up to 12 kHz. This is achieved, as shown in Fig. 4, a, by placing pairs of high and low frequency heads in mutually perpendicular planes, and such an arrangement of four heads does not increase the cross section of the loudspeaker housing. A feature of the filter (Fig. 4, b) is the presence of an additional resistor R1, closed by contacts B1. With open contacts, the amplitude-frequency characteristic of the loudspeaker is uniform throughout the entire reproducible frequency band (from 60 Hz to 18 kHz). When the contacts are closed, there is an additional increase in output at higher frequencies (from 7 to 18 kHz) by about 3 dB. Such a correction may be required when there are many soft objects in the room: curtains, curtains and other materials that strongly absorb the energy of high-frequency sound vibrations. The peculiar placement of the heads in the loudspeaker opens up new possibilities for coordinating the placement and mutual position of the loudspeakers in a stereo installation, taking into account the acoustics of the room. Figure 5 shows how this can be achieved by turning the loudspeakers horizontally. So, if the room is medium in size, and the walls are not draped, then we can recommend placing the loudspeakers as shown in Fig. 5, a. In this case, the loudspeaker enclosures can be pushed close to the side walls. In the same room with soft (draped) walls, it is recommended to place loudspeakers no closer than 0,7 m from the side walls (Fig. 5, b).
If the room is narrow, then you can direct the main radiation of the loudspeakers towards the side walls. Due to re-reflection and re-emission from the walls, it is possible to obtain the effect of an extended stereo base (Fig. 5, c, d). In a large room, when the loudspeakers are spaced relatively far from each other, it is possible to create the effect of their convergence, for which it is necessary to direct the main radiation of the loudspeakers towards each other (Fig. 5, e, f). When repeating the design, it is recommended to use for each instance of the loudspeaker two heads of the 4GD-4 or 4GD-35 type for the low-frequency path and two heads for the high-frequency path. In this case, the nominal signal power supplied to the loudspeaker can reach 8 watts. When using heads of the 4GD-36 type, the nameplate power of which is 8 W, short-term overloads up to 16 W are allowed. Of course, the diameter of the cutouts in the panels must be coordinated with the dimensions of the diffuser holders of domestic heads. It should be noted that in recent years a large number of amateur and professional loudspeakers, broadband and multiband, have appeared in which a greater or lesser part of the radiation is directed towards the walls of the room. In the loudspeaker in question, on average, about half of the input power is allocated to side radiation. The designs of radio amateurs are known, where out of nine broadband heads of the same type, only ... one radiates to the front. The remaining eight have the main radiation directed to the rear, towards the wall of the room, i.e., only 10% of the power supplied to the loudspeaker is spent on radiation towards the listener. True, the remaining 90% of the radiated power does not disappear without a trace. Radiation to the side and back, reflected from the walls and floor, partially reaches the listener in the form of a scattered reflected signal, the perception of which creates the illusion of being in a spacious concert hall. By changing the position of such loudspeakers relative to the walls and floor, turning them in some way in a horizontal plane relative to the listener, it is possible to achieve the best sounding of electroacoustic equipment for a given room. Three way loudspeaker A lot has been said about three-way loudspeakers before. Figure 6 shows a sketch of the design of a three-way loudspeaker. The loudspeaker housing is made of chipboard with a thickness of about 20 mm. The bottom of the hull is missing. A gap about 25 mm high and 200 mm long was left between the floor and the side walls. Its purpose is to create additional in-phase radiation at the lower frequencies of the reproduced signal.
Unusual is the very placement of the heads. So, the mid-frequency head is installed on the top wall. Low- and high-frequency heads are placed on an inclined panel. Both panels, top and sloping, are draped with fabric along the contour indicated in Fig. 6 by a dashed line, creating the illusion of a classic rectangular shape of the loudspeaker cabinet. This arrangement of the heads allows the use of good reflective and scattering properties of the relatively low ceilings of a modern home in order to obtain a spatial rather than a point source of sound. When repeating the design, one low-frequency head of the 4GD-43 type, a mid-frequency head of the 4GD-8E type and a high-frequency head of the ZGD-31 type can be used. In this case, the top and sloping panels of the drawer should be changed accordingly. To correct the resistance of the high-frequency head, a constant resistor of 10-12 ohms can be connected in parallel with its outputs. In view of the above, the nominal power supplied to the loudspeaker can be 5 watts. Literature:
Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ KNX Twisted Pair Transceiver STMicroelectronics STKNX ▪ Light leads to the quantum world and the acceleration of supercurrents
▪ site section Computer devices. Article selection ▪ article How many people, so many opinions. Popular expression ▪ article Why does a whale have a fountain? Detailed answer ▪ article The functional composition of Daewoo TVs. Directory
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: