
|
|
Lecture notes, cheat sheets
Insurance business. Cheat sheet: briefly, the most important
Directory / Lecture notes, cheat sheets Table of contents
1. ESSENCE OF INSURANCE Insurance is a special type of economic relations designed to provide insurance protection for people and their activities from various kinds of dangers. Insurance protection can be defined as the conscious need of individuals and legal entities to create special insurance funds to restore property, health, ability to work and personal income of both the participants in the creation of these funds and third parties. The insurance fund is an economic necessity and is an obligatory component of social reproduction in any economy. The fund can be formed at the expense of material, in-kind, monetary resources, while the latter form of the fund is the most universal. The economic essence of insurance consists in the creation of monetary funds at the expense of contributions from parties interested in insurance and intended to compensate for the damage of persons participating in the formation of these funds. Since the insurance risk is probabilistic in nature, the insurance fund is redistributed both in space and in time. Thus, compensation for damage to affected persons occurs at the expense of the contributions of all those who participated in the formation of insurance funds. Insurance is a relationship to protect the property interests of individuals and legal entities, the Russian Federation, constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities in the event of certain insured events at the expense of monetary funds formed by insurers from the insurance premiums (insurance premiums) paid by them, as well as at the expense of other funds of insurers . Insurance activity (insurance business) - the field of activity of insurers for insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance, as well as the field of activity of insurance brokers, insurance actuaries for the provision of services related to insurance, with reinsurance. The purpose of organizing the insurance business in the Russian Federation is to ensure the protection of the property interests of individuals and legal entities, the Russian Federation, the constituent entities of the Russian Federation and municipalities in the event of insured events. The objectives of the organization of the insurance business are 1) the implementation of a unified state policy in the field of insurance; 2) the establishment of insurance principles and the formation of insurance mechanisms that ensure the economic security of citizens and business entities on the territory of the Russian Federation. Insurance is a special type of economic activity associated with the redistribution of the risk of damage to property interests among participants in insurance (insured) and carried out by specialized organizations (insurers) that ensure the accumulation of insurance premiums, the formation of insurance reserves and the implementation of insurance payments in case of damage to insured property interests. 2. FUNCTIONS OF INSURANCE Insurance in a market economy performs certain functions, expressing the public purpose of this category. risk function connected with the fact that the presence of risk allows insurance to exist and develop. The insured risk is understood as dangers and accidents, due to the possible occurrence of which the insurer undertakes to pay the amount of insurance compensation to the injured party. Accidents and dangers should be precisely possible, and not inevitable. Circumstances that may cause losses must also not be the result of intentional or gross actions on the part of the insured. It is within the framework of the risk function that the monetary form of value is redistributed among insurance participants in connection with the consequences of random insurance events. The variety of forms and types of risks leads to the emergence of various industries and sub-sectors of insurance. Warning function is implemented by financing at the expense of a part of the insurance fund of preventive measures to eliminate or reduce the degree of insured risk, and, consequently, the damage from this risk. For example, part of the funds collected from fire insurance finances fire prevention measures, as well as measures aimed at reducing the possible damage from a fire. Social function associated with the provision of material assistance to insured persons in the event of a health disorder, disability as a result of illness or accidents. Compulsory or voluntary health insurance finances medical expenses for the treatment and rehabilitation of the health of insured persons. Insurance can also provide compensation for lost income due to illness, disability of the insured. In personal insurance, it is additionally allocated savings function insurance, which is associated with the accumulation of certain amounts of money under personal insurance contracts. Investment function is that at the expense of temporarily free funds of insurance funds, the economy is financed. Insurance companies accumulate large amounts of money that are intended to compensate for damage, but until the insured event occurs, they can be temporarily invested in various securities, real estate, etc. Control function insurance is to ensure that the formed insurance reserves correspond to the actual obligations of the insurance company, as well as control over the placement and use of insurance reserves. In accordance with the control function, on the basis of legislative and instructive documents, financial insurance control over the correct conduct of insurance operations is carried out. In addition, the control function is implemented in establishing the fact of an insured event and related risky circumstances and is ensured by the terms of the concluded insurance contract with the involvement of experts and competent authorities in matters of insurance expertise. 3. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE INSURED RISK insurance risk is a hazard or accident against which insurance is provided. Insured risk is realized in an insured event through damage. All risks arising in the economic activities of enterprises and organizations or in the daily life of the population are divided into two groups: risks that can be insured and non-insurable risks. An insured risk is a risk that is characterized by the probability and randomness of the occurrence of an event, and which can also be assessed in terms of the likelihood of an insured event and the quantitative amount of damage. Depending on the source of danger allocate: - insurance risks associated with the manifestation of natural forces - floods, earthquakes and other natural phenomena that cause damage to the insured object. In addition, insurance risks of a man-made nature are distinguished - explosions, fires, droughts, etc. - insurance risks associated with purposeful illegal actions of a person in the process of appropriation of material goods, - theft, robbery, vandalism, etc.; - insurance risks of long-term life insurance and pension insurance are separated into a separate group, which is associated with fundamentally different approaches to calculating insurance rates in these types of insurance. Depending on the amount of liability of the insurer risks are divided into two groups: - universal - risks included in the standard scope of the insurer's liability, for example, risks when insuring property against fire; - individual - characteristic of unique objects of insurance (for example, works of art, antiques). When insuring such objects, an individual insurance contract is prepared, which describes the risks that may arise during the operation or transportation of these objects. A special group is made up of specific insurance risks, which include catastrophic and abnormal risks. The group of catastrophic insurance risks is characterized by potentially significant damage on an especially large scale, the group of anomalous risks includes risks that affect such insurance objects that cannot be attributed to certain groups of the insurance population. 4. PARTICIPANTS OF INSURANCE RELATIONSHIPS Policyholder - a legal or capable natural person who has concluded an insurance contract with the insurer or who is such by virtue of law, who is obliged to pay the insurance premium to the insurer, and in the event of an insured event has the right to demand an insurance payment from the insurer. The insured person is a person in whose life an insured event must occur, directly related to the person or circumstances of his life (personal insurance) or affecting the safety of his property rights and property (property insurance). With regard to personal insurance contracts, it is established that the insured person or his heirs are beneficiaries, unless otherwise provided in the contract. Beneficiary - an individual or legal entity appointed by the policyholder as the recipient of insurance payments under the insurance contract. In the event that the beneficiary is not indicated in personal insurance, it is natural persons - the heirs of the insured. Unlike the policyholder, the beneficiary can be not only a fully capable person, but also a minor, as well as a minor citizen (for example, minor heirs of a deceased insured in personal insurance). An insurer is a legal entity of any organizational and legal form, created for the purpose of carrying out insurance activities (according to the legislation of the Russian Federation - an insurance organization or a mutual insurance company) and having a license to carry out insurance activities in the territory of the Russian Federation. The subject of direct activity of insurers cannot be industrial trade and intermediary and banking activities. Insurance agent - a legal or capable natural person acting on behalf of the insurer and on his behalf in accordance with the powers granted. The insurance agent acts as an attorney of the insurance company and performs the actions entrusted to him on behalf and at the expense of the insurer. Insurance broker - an independent legal or natural person licensed to conduct insurance intermediary operations. An insurance broker acts on behalf of and on behalf of the insured or in reinsurance - on behalf of and on behalf of the insurer for direct insurance. Brokerage in insurance, reinsurance or co-insurance is an intermediary activity for the purchase or sale of insurance services, which implies the promotion of an agreement between the parties interested in insurance, which involves negotiating insurance according to the will of the insured, the ultimate goal of which is to determine the conditions and forms of insurance mutually acceptable to sides. insurance actuaries - subjects of the insurance business: citizens of the Russian Federation who have a qualification certificate and carry out, on the basis of an employment contract or a civil law contract with an insurer, the activity of calculating insurance tariffs, insurance reserves of the insurer, evaluating its investment projects using actuarial calculations. 5. CONCEPTS THAT CHARACTERIZE THE GENERAL CONDITIONS OF INSURANCE ACTIVITY Insurance contract - an agreement between the insured and the insurer, by virtue of which the insurer undertakes, in the event of an insured event, to make an insurance payment to the insured or a third party. in favor of which the insurance contract is concluded, and the policyholder undertakes to pay insurance premiums within the established time limits. insurance certificate (insurance certificate, insurance policy) - a document certifying the conclusion of an insurance contract and transferred by the insurer to the policyholder with the insurance rules attached. Insurance object - property interests that do not contradict the legislation of the Russian Federation: 1) related to the life, health, ability to work of citizens - in personal insurance; 2) related to the possession, use, disposal of property - in property insurance; 3) associated with compensation by the insured for the harm caused by him to the person or property of an individual or legal entity - liability insurance. Sum insured - the amount of money determined by the insurance contract or established by law, on the basis of which the amounts of the insurance premium and insurance payment are determined. When insuring property, the sum insured cannot exceed its actual value at the time of conclusion of the insurance contract. The parties that have entered into the contract cannot dispute the insured value of the property specified in the insurance contract, unless the insurer proves that he was deliberately misled by the insured. Insurable interest - this is a measure of material interest in insurance, an element that predetermines the possibility of the existence of an insurance institution. The insurable interest is of a property nature and includes property that is the object of insurance, the right to it or an obligation in relation to it, i.e. everything that may become the subject of causing material damage to the policyholder or in connection with which the policyholder's liability to third parties may arise. persons. The property nature of the insurable interest makes it possible to objectively determine its value, that is, to subject it to a monetary value. Insurance liability - a set of rights and obligations of the insurer for the protection and protection of property or other interests of the insured, provided for by the insurance contract. It arises from the moment the insurance contract comes into force and extends to the entire period of its validity. The insurance liability system determines the ratio of the sum insured of the insured property and the actual loss. Insurance case - this is an event that has taken place, provided for by the insurance contract or the law, upon the occurrence of which the insurer's obligation arises to make an insurance payment to the insured, the insured person, the beneficiary or other third parties. Mutual Insurance Society - a non-profit organization that is created to insure the property interests of its member-participants. The mutual insurance company operates on the basis of the charter. The participants of the company bear joint and several obligations for the results of the company's activities. At the expense of their contributions, they form an insurance fund. 6. INDUSTRIAL AND NON-INDUSTRY INSURANCE CLASSIFICATIONS Identification of industries and sub-sectors can be attributed to the first level of classification. The insurance industry is understood as a separate sphere of insurance of property interests related to the consequences of insured events for homogeneous or related insurance objects of legal entities, individuals, which has special principles and methods of insurance protection for these insurance objects, the formation and use of insurance funds. In addition to insurance industries, there are also sub-sectors of insurance, as well as types of insurance. Insurance sub-sector - a set of types of insurance of close or related in content and origin of property interests from their characteristic insurance risks according to their characteristic conditions, types of their insurance protection and the formation of insurance reserves. The type of insurance is understood as insurance of homogeneous insurance objects of the same origin and property interests related to them from one or a combination of insurance risks according to the conditions established for all or individual objects, methods of their insurance protection, formation and use of insurance funds. All links of the classification in the allocation of industries, sub-sectors and types of insurance are arranged so that each subsequent link is part of the previous one; the highest link is the insurance industry, the middle - the insurance sub-branch, the lowest - the type of insurance. Separate types of insurance are carried out in two forms - mandatory and voluntary, and this applies to all branches of insurance. Insurance objects are the property interests of the insured associated with his material, intangible values, i.e. with the objects of insurance. Insurance items - these are certain material values, including the natural habitat, and the results of their productive use, as well as intangible benefits (values) of legal entities, individuals, their communities, providing them with the achieved or expected level of economic, financial, other well-being and therefore protected from adverse, destructive events and their negative consequences. Insurance items may be: 1) buildings, structures, power machines and equipment, vehicles, animals, plantings, property rights, bank loans, other types of property; 2) natural environment, natural resources; 3) life, health, working capacity of individuals, their income; 4) damage subject to compensation in accordance with civil liability by the guilty person, caused by him to life, health and property of other persons, as well as to the natural environment. The non-sectoral classification of insurance is secondary and includes several classification features: 1) form of insurance; 2) type of insurance indemnity; 3) the type of hazards to be insured; 4) target nature of the insurer's activities; 5) the number of insured persons, etc. 7. CLASSIFICATION BY OBJECTS OF INSURANCE (INDUSTRIAL) The objects of personal insurance may be property interests related to: 1) the survival of citizens to a certain age or period, death, the occurrence of other events in the life of citizens (life insurance); 2) with causing harm to the life, health of citizens, the provision of medical services to them (insurance against accidents and diseases, medical insurance). The objects of property insurance may be property interests related to: 1) possession, use and disposal of property (property insurance); 2) with the obligation to compensate for the damage caused to other persons (civil liability insurance); 3) with the implementation of entrepreneurial activities (insurance of entrepreneurial risks). In accordance with the listed objects in the Russian Federation, two branches of insurance are distinguished - personal and property. However, it should be noted that liability insurance stands out as a separate industry, since it has quite a lot of characteristic features that distinguish it from property insurance and business risk insurance: firstly, in contrast to property insurance, in which the sum insured is determined by the actual value of the property or its in part, when insuring liability, the amount of the sum insured is determined by the parties to the insurance contract at their discretion; secondly, when concluding a property insurance contract, a specific recipient of insurance compensation is determined, which is indicated in the insurance contract, and when insuring liability, the contract is concluded in favor of third parties, since it is not known in advance who exactly may be harmed by the insured. In this way, it is advisable to single out not two, but three branches of insurance, personal, property and liability insurance. Personal insurance unites a large number of types, the objects of which are property interests related to the life, health and working capacity of the insured. The peculiarity of personal insurance is that it combines risk and social functions. Property insurance acts as a branch of insurance in which the object of insurance is property in various forms. The economic purpose of property insurance is compensation for damage caused by an insured event. The insured may insure property that is in his possession, use, disposal, respectively, not only its owner, but also a person temporarily owning, disposing or using this property, interested in its safety, can be the insurer of property. Liability Insurance - the branch of insurance in which the object of insurance is property interests related to compensation by the insured for the harm caused by him to the person or property of an individual, or the property of a legal entity. The Federal Law "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation" identifies 23 licensed types of insurance activities within the insurance industries, including reinsurance. 8. VOLUNTARY INSURANCE Voluntary insurance is carried out by virtue of law and on a voluntary basis, that is, it is carried out on the basis of an agreement between the insured and the insurer. The rules of voluntary insurance that determine the general conditions and procedure for its implementation are established by the insurer independently in accordance with the legislation governing insurance activities. At the same time, the law determines the general conditions of insurance, and the specific conditions for its implementation are determined by the contract concluded between the insured and the insurer. The voluntary form of insurance is not compulsory and provides policyholders with the opportunity to choose services in the insurance market. However, voluntary insurance is selective, since not all potential insurers are willing or able to participate in it, and for certain categories of persons, restrictions are established by law. Voluntary insurance is based on a number of principles. The first principle is the principle of voluntary participation in insurance, but this principle fully applies only to the insured, since the insurer does not have the right to refuse the insured if his will does not contradict the conditions of insurance. This principle guarantees the conclusion of an insurance contract at the first request of the insured. The second principle is the principle of selective coverage by voluntary insurance of individuals and legal entities, since not all insurers are willing to participate in it. In addition, under the terms of insurance, there may be restrictions on the conclusion of contracts (the age of the insured, his state of health). The next principle is the principle of limiting the period of voluntary insurance, which is determined by the fact that the beginning and end of the insurance period are separately stipulated in the insurance contract, since insurance compensation is payable only if the insured event occurred during the insurance period. The principle of paying one-time or periodic insurance premiums establishes that in case of voluntary insurance, the entry into force of the insurance contract is conditioned by the payment of the insurance premium. As a rule, non-payment of the next premium for long-term voluntary insurance leads to termination of the contract. 9. COMPULSORY INSURANCE Compulsory insurance - this is insurance carried out by virtue of law, from the standpoint of social expediency. This form of insurance differs from the voluntary one in that the potential insured has a statutory obligation to insure. When carrying out compulsory insurance, insurance liability is not limited in time for the objects of insurance established by law and the circle of insurers, it occurs automatically when an insured event occurs. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes the following cases of introduction of compulsory insurance: - if such insurance is associated with the risk of civil liability of a citizen or organization, which may arise as a result of causing harm to life, health or property of other persons or violation of contracts with other persons; - if such insurance involves the obligation to conclude an agreement in favor of a third party on insurance of his life, health or property in case of harm to the specified property interests; - if such insurance is imposed on the obligation of legal entities that have property under economic management and operational management that is state or municipal property. In cases where the insured is the state represented by its bodies or state unitary enterprises and the payment of insurance premiums is carried out at the expense of funds provided from the relevant budget, such compulsory insurance is called state compulsory insurance. Article 935 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation determines that in cases where the insurance obligation does not follow from the law, but is based on an agreement, including the obligation to insure property - on an agreement with the owner of the property or on the constituent documents of a legal entity that is the owner of the property, such insurance is not compulsory. In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, a person in whose favor, according to the law, compulsory insurance must be carried out, has the right, if he knows that insurance has not been carried out, to demand in court that it be carried out by the person who is entrusted with the obligation of such insurance. Compulsory insurance is based on the principles: - the principle of obligation: - the principle of continuous coverage by compulsory insurance; - the principle of automatic distribution of compulsory insurance to the objects specified in the law; - the principle of operation of compulsory insurance, regardless of the payment of insurance premiums by the insured; - the principle of perpetuity of compulsory insurance. - the principle of rationing insurance coverage. 10. CLASSIFICATIONS OF INSURANCE: BY TYPE OF INSURANCE COMPENSATION, BALANCE Classification of insurance by types of insurance compensation is based on the ratio of the sum insured and the insurance indemnity for damage suffered by the policyholder as a result of an insured event. The obligations of the insurance company towards the policyholder under the insurance contract may consist in compensating the policyholder for damage or in paying the agreed amount. Accordingly, damage insurance and sum insurance are distinguished. In cases damage insurance the insurance company on the basis of the insurance contract is obliged to compensate the insured for the actual amount of damage to the extent that it is covered by the sum insured. In this case, the sum insured must not exceed the actual value of the insured property. When insuring damage, only proven amounts of damage are subject to compensation, i.e., specific coverage of losses as a result of an insured event is carried out. Amount insurance occurs in life insurance, accident and illness insurance, and sometimes health insurance. With these types of insurance, in the event of an insured event, the insured pays the insured or the insured person a predetermined amount (insurance premium). Thus, when insuring the amount, we are talking about an abstract coverage of the needs of the insured, since the sum insured agreed upon in the contract is determined not by the value of material assets, but by the desire and ability of the insured. Balance classification of types of insurance is of interest primarily to policyholders in the face of business organizations, as it allows the head of the company to establish whether all business positions that are subject to insurance are indeed insured. Basis asset insurance constitutes the property interest of the insured, it is insurance of material assets. This type of insurance includes all major branches of insurance: 1) insurance of fixed assets; 2) production stocks; 3) work in progress; 4) finished products and goods; 5) possible losses on debt obligations. RџSЂRё liability insurance not property interest is insured, but the damage that arises from the passive obligations of an entrepreneurial organization without repayment. Liability insurance includes: 1) credit insurance; 2) legally defined obligations of an entrepreneurial organization; 3) damage occurring in case of rejection of claims. A combination of insurance of assets and liabilities is possible, for example, in the case of fire insurance of an industrial building. The sum insured for building fire insurance is determined based on the residual value of the building; it is a form of asset insurance. In the event of an insured risk in case of complete destruction of the building, the insurance indemnity will not be sufficient to restore it. К income insurance includes insurance of lost income as a result of the temporary cessation of the work of an entrepreneurial firm. 11. ESSENCE OF REINSURANCE Reinsurance - this is a system of economic relations, in accordance with which the insurer, accepting risks for insurance, transfers part of the responsibility for them on agreed terms to other insurers in order to create a balanced insurance portfolio and ensure the financial stability of insurance operations. Reinsurance is the transfer by the insurer (reinsurer) on the conditions specified in the contract of the liability assumed under the insurance contract to another insurer (reinsurer) in excess of the allowable amount of own retention. The transferable risk is called reinsurance risk, and the process involved in its transmission is called risk ceding, or reinsurance assignment. The reinsurer, i.e., the insurer that transfers the risk, is called assignor the reinsurer, that is, the insurer who accepts the risk, is called assignee. An insurer that has entered into a reinsurance contract with a reinsurer remains liable to the policyholder in full in accordance with the insurance contract. Upon the occurrence of an insured event, the reinsurer shall be liable in the amount of reinsurance obligations assumed. The relations of insurers on reinsurance of risks are regulated by contracts between them. The risk accepted by the reinsurer from the cedant may be subsequently fully or partially transferred to another reinsurer. This type of insurance is called retrocession and the transferred reinsurance risk is called retroceded risk. PuBy retrocession, part of the risks can be transferred to the original insurer. To avoid this, it is possible to make a clause in the reinsurance contract prohibiting the further transfer of risk. There are facultative and contractual methods of reinsurance. Optional method of reinsurance is that the reinsurer (assignor) and the reinsurer (assignee) are given the opportunity to assess risks that can be transferred to reinsurance in full or in part. A facultative reinsurance contract is an individual transaction relating mainly to one risk. It provides complete freedom to the parties to the contract: the reinsurer has the right to offer one type of liability, and the reinsurer - to accept or reject the reinsurer's proposal and put forward a counter-condition of the contract. The main disadvantage of facultative reinsurance is that by the time the insured event occurs, the risk may turn out to be either uninsured or partially reinsured, since the reinsurer has complete freedom to decide whether to accept the proposed risk for reinsurance or reject it. This will not allow the reinsurer to fully compensate for losses in excess of its potential financial capabilities. Contractual method of reinsurance (obligatory reinsurance) - a compulsory form of reinsurance in which all insurers operating in a given country are required by law to transfer in a prescribed proportion to a certain reinsurer (usually state) all the risks accepted for insurance. 12. PROPORTIONATE REINSURANCE Proportional reinsurance lies in the fact that the insurer and the reinsurer distribute among themselves the insurance liability, the insurance premium and the insurance compensation in a certain proportion, that is, with the shares accepted by them on their responsibility. The terms of the contract of proportional reinsurance provide that the reinsurer leaves on his responsibility (own deduction) a certain part of the sum insured and transfers the rest to reinsurance. Varieties of proportional reinsurance - quota reinsurance and reinsurance of excess amounts. Quota reinsurance - the simplest and easiest form of reinsurance to maintain. The insurance company-reinsurer, under the terms of the contract, undertakes to transfer to reinsurance the agreed part (share or quota) of the sum insured under all contracts concluded by it for certain types of insurance, and the reinsurer - to reinsure this part. Upon the occurrence of an insured event, the reinsurer is obliged to reimburse the insurance payment to the direct insurer in the established proportion. In addition, the terms of the quota reinsurance agreement may limit the maximum insurance amount accepted by the reinsurer for its responsibility. According to the established share, insurance premiums are transferred to the reinsurer, and in this share the reinsurer pays for the losses incurred upon the occurrence of an insured event. Usually the share of participation in reinsurance is expressed as a percentage of the sum insured. Reinsurance based on excess of amounts devoid of the disadvantages of quota reinsurance. The excess is the part of the sum insured that exceeds the level of the insurer's own retention, expressed in absolute figures, and which is the object of reinsurance. Accordingly, the excess of amounts agreement provides that the assignor transfers, and the reinsurer accepts for reinsurance, only those insurance contracts for which the sum insured exceeds the agreed amount (the amount of own deduction). In addition, in contracts transferred to reinsurance, the reinsurer leaves the same agreed amount of his own retention on his responsibility, and the reinsurer assumes obligations for the remaining part of the sum insured (excess). The maximum value of the sum insured transferred to reinsurance is set at a multiple of the assignor's priority, which is called a share or a line. If under the insurance contracts concluded by the insurer, the sums insured exceed the reinsurer's liability limit, then he may conclude similar reinsurance contracts with other reinsurers (contracts of the second excess, third excess, etc.). For the insurer, the main advantage of the excess of amounts agreement is the ability to independently set the amount of its own deduction in the amount corresponding to its financial capabilities, while leaving all insurance contracts on its responsibility, the sums insured for which do not exceed the amount of such deduction. In addition, this method allows the insurer to form an optimally balanced insurance portfolio in terms of sums insured. 13. NON-PROPORTIONATE REINSURANCE RџSЂRё disproportionate reinsurance the sum insured, insurance premiums and insurance indemnities are distributed between the insurer and the reinsurer not in the same proportion. The direct insurer pays all losses up to the amount agreed in the contract - the priority of the insurer. All losses exceeding the priority are subject to payment by the reinsurers, but also within the amount established by the contract. This amount is called the reinsurance coverage limit. The amount of the reinsurance premium is set in these reinsurance contracts as a percentage of the annual insurance premium received by the reinsurer for the portfolio of contracts transferred to reinsurance. The amount of this percentage is determined on the basis of an analysis of data from previous years. allowing to determine the expected volume of the reinsurer. Due to the fact that at the beginning of the validity period of the reinsurance contract, the amount of the insurance premium received by the insurer is unknown, as a rule, it pays the reinsurance premium in advance, and the final settlement is made at the end of the validity of the reinsurance contract. In some cases, the parties may establish a fixed amount of the reinsurance premium. There are two main types of non-proportional reinsurance - excess of loss and excess of unprofitability. Reinsurance of excess of loss serves to protect the insurance portfolios of insurers for certain types or insurance contracts from the largest and unforeseen losses. In accordance with the excess of loss contract, the reinsurer is obliged to make an insurance payment in the event that the amount of insurance compensation payable by the insurer exceeds the limit specified in the reinsurance contract (assignor priority). Thus, the reinsurer sets the priority in absolute amount and pays all losses that do not exceed the priority. Reinsurance of excess of unprofitability also provides protection for the entire insurance portfolio and not for specific risks. The reinsurer undertakes the obligation to make a payment in favor of the reinsurer in the event that the loss ratio for a particular type of insurance exceeds the value (priority) specified in the reinsurance contract. The direct insurer determines the percentage of loss that remains on its own deduction (priority), and the excess is given to reinsurance. The loss ratio specified in the contract, for example, 80%, means that the loss ratio up to 80% will be covered by the insurer from its own sources, and if in a given calendar year the loss ratio exceeds the specified percentage, then the excess in the amount of the established limit of 85% will be covered by the reinsurer. Another version of the excess of loss agreement may provide for the obligation of the reinsurer to make payments if the total amount of insurance payments of the reinsurer for a certain type of insurance for a specified period of time exceeds a certain absolute value. 14. ESSENCE AND FUNCTIONS OF THE INSURANCE MARKET Insurance market - an integral part of the financial market of the country, where the subject of sale and purchase are insurance products. Consumer properties of these products are very specific and different from other financial market products. The universality of insurance determines the direct connection of the insurance market with the finances of enterprises, the finances of the population, the banking system, the state budget and other financial institutions within which insurance relations are implemented. In such relations, the relevant financial institutions act as insurers and consumers of insurance products. Specific relations are formed between the insurance market and the state budget, as well as state off-budget funds, which is associated with the organization of compulsory insurance. The insurance market has stable financial relations with the securities market, the banking system, the foreign exchange market, where insurance organizations place insurance reserves and other investment resources. К general market The functions of the insurance market include the following: 1) commercial - insurance is an entrepreneurial activity aimed at making a profit; 2) price - implemented in the process of pricing for services provided by insurance companies in the insurance market. The price of an insurance service, being a market category, is formed under the influence of supply and demand; 3) informational - informing consumers of services about existing and newly emerging insurance services; 4) regulating - is carried out by creating rules for trade in insurance services in the insurance market, as well as by exercising control over the implementation of these rules. К specific include the following functions of the insurance market: 1) risk coverage - in the process of insurance, the negative consequences of risks are assumed by insurance companies; 2) facilitating access to additional sources of financing - for example, to a bank loan, since one of the obligatory conditions for obtaining the latter is insurance of the property of the borrowing enterprise; life and real estate insurance is a necessary condition for obtaining a mortgage loan by individuals for the construction or purchase of housing, and car insurance is a necessary condition for buying it on credit; 3) preventive - development and implementation of a set of measures to prevent and control the level of risk in the most important areas of economic and private life; 4) the formation of a specialized insurance fund - is implemented through a system of reserve and reserve funds that ensure the stability of insurance, a guarantee of payments. The insurance market is an economic space in which policyholders operate that form the demand for insurance services, insurance companies that satisfy this demand, insurance intermediaries that promote insurance services from insurer to insured. 15. THE MARKET OF INSURED AS AN ELEMENT OF THE INSURANCE MARKET The market of policyholders as an element of the insurance market is represented by several participants: 1) policyholders; 2) insured persons; 3) beneficiaries. Both individuals and legal entities can act as insurers. Under certain circumstances, beneficiaries and insured persons become direct participants in insurance legal relations. At the same time, a characteristic feature of the legal status of third parties - beneficiaries is that they enter into insurance legal relations not independently, but by appointing them as policyholders or insured persons in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. The possibility of participation of third parties in the insurance contract as independent entities is provided for in a certain way in relation to the following types of insurance: 1. Property insurance. The participation of an uninsured beneficiary is not allowed, as he has no interest in preserving the property. The participation of the insured beneficiary is allowed, since the property can be insured in favor of a person who has an interest in preserving the property. The participation of the insured non-beneficiary is not allowed, as it has no interest in preserving the property. 2. Liability insurance for causing harm. The participation of the uninsured beneficiary is determined by law; the contract is concluded in favor of persons who may be harmed. The participation of the insured beneficiary is not allowed, since the beneficiary is always a different person than the insured person or the policyholder. Such a person must be directly named in the contract, otherwise the risk of liability of the insured himself is considered insured 3. Liability insurance under the contract. The participation of an uninsured beneficiary is allowed in cases provided for by law. The participation of the insured beneficiary and the participation of the insured non-beneficiary is not allowed under pain of declaring the contract null and void. 4. Business risk insurance. The participation of an uninsured beneficiary is impossible (the contract is considered concluded in favor of the insured). The participation of the insured beneficiary and the participation of the insured non-beneficiary is impossible (the contract is void). 5. Contract of personal insurance. The participation of an uninsured beneficiary is possible with the written consent of the insured person. Participation of the insured beneficiary - the contract is considered concluded in favor of the insured person, if another person is not named as the beneficiary in the contract. Participation of the insured non-beneficiary is possible with the written consent of the insured person. 16. THE MARKET OF INSURERS AS AN ELEMENT OF THE INSURANCE MARKET Insurers are legal entities established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation for insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance and licensed. Insurers assess insurance risk, receive insurance premiums (contributions), form insurance reserves, invest assets, determine the amount of loss or damage, make insurance payments, and perform other actions related to the fulfillment of obligations under an insurance contract. Depending on the type of insurance services provided, there are insurance companies: 1) specialized, which provide services for only one specific type of insurance (for example, compulsory medical insurance services); 2) universal, which provide insurance services for various types and sectors of insurance (for example, insurance companies that provide personal and property insurance). The promotion of insurance services from the insurer to the insurers is carried out by insurance intermediaries Insurance agents and brokers act as intermediaries in the insurance market. The main legal feature of these intermediaries is that. that they are not direct, but indirect participants in insurance legal relations, act on the side of the insured or insurer as their representatives or intermediaries, receiving appropriate remuneration for this. Another important participant in the insurance market are mutual insurance companies. These are non-profit organizations that are created to insure the property interests of its member-participants and bear joint and several obligations for the results of insurance and the activities of the company. In accordance with the Federal Law "On the Organization of the Insurance Business in the Russian Federation" and the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, in order to coordinate their activities, represent and protect the common interests of their members, insurance entities may form unions, associations and other associations of insurers They are created in the form of non-profit organizations that are not entitled to conclude insurance contracts with policyholders, that is, directly engage in insurance activities, since they do not have the necessary state license. Participants in the insurance market include insurance actuaries - individuals permanently residing in the territory of the Russian Federation, having a qualification certificate and carrying out, on the basis of an employment contract or a civil law contract with an insurer, the activity of calculating insurance tariffs, insurance reserves of the insurer, evaluating its investment projects using actuarial calculations. An important component of the insurance business (and the market of insurers in particular) is the work professional assessors of insurance risks (accident commissioners). Accident commissioners (surveyors) carry out their professional activities either in the form of departments based on insurance companies, or in the form of separate independent survey companies. 17. MARKET OF INSURANCE PRODUCTS. CLASSIFICATION OF THE INSURANCE MARKET Market of insurance products as an important component of the insurance market, it is represented by a specific product offered on the insurance market - an insurance service. An insurance service can be provided on the basis of a contract (in voluntary insurance) or on the basis of a law (in compulsory insurance). Like any other commodity, an insurance service has a use value. The cost is the price of the insurance service, which is expressed in the insurance tariff, and then in the insurance premium, and the use value of the insurance service is the provision of insurance protection (insurance coverage). The purchase and sale of an insurance service is formalized by an insurance contract, in confirmation of which the policyholder is issued an insurance certificate (policy). The list of types of insurance that the insured can use is an assortment of the insurance market. In some cases, in addition to the types of insurance offered for wide use, individual insurance conditions can be developed for a specific object or insured. On industry feature allocate: 1) the personal insurance market; 2) property insurance market; 3) liability insurance market; 4) financial risk insurance market. In turn, each of the listed markets consists of separate segments. A market segment is a certain group of consumers of insurance services that has common characteristics and parameters of insurance. For example, the personal insurance market includes the life insurance market; health insurance market; pension insurance market, etc.; The property insurance market includes property insurance for individuals and property insurance for legal entities. On territorial basis allocate: 1) the national insurance market; 2) regional insurance market; 3) international insurance market. National (country) insurance market is a market where demand and supply for insurance services are formed within the country. Institutionally, the national insurance market consists of insurance companies, specialized reinsurance companies, insurance brokers, mutual insurance companies. Insurance activity in the national market is carried out within the framework of national insurance legislation, the control over the implementation of which is entrusted to the state body of insurance supervision. Regional insurance market - this is a market supply and demand in which are formed within a particular region (district, city). The regional market unites insurance organizations of individual regions of the country, interconnected by certain integration links. International insurance market- it is a combination of national and regional markets. This concept refers to international insurance organizations whose scope of activity extends to foreign countries and is characterized by the presence of a network of controlled branches and subsidiaries in other countries, the use of technological cooperation and specialization of controlled firms, control and coordination of the activities of branches and subsidiaries from one center. 18. EXTERNAL INSURANCE BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT External insurance environment is a set of external factors and conditions that directly or indirectly affect the results of an insurance company. Environmental factors insurance organization. Economic conditions in the country and region of activity of the insurer, characterized by the formation of conditions for the formation of a competitive insurance market. The stability or instability of the economic situation has a direct impact on the performance of the insurance company. political conditions, practically unaffected at the level of an insurance organization and representing a significant source of risks in the activities of any insurance company operating in Russia. For the business activity of all business organizations, including insurers, such factors as the stability of political power at the federal and regional levels and the possibility of a radical revision of existing property relations are currently significant. State regulation and support of entrepreneurship, affecting the business of insurers. The strengthening of the regulatory role of the state in insurance activities is reflected in the direct participation of the state in its formation, in legislative support and in the implementation of state supervision of insurance activities, in the protection of fair competition in the insurance market. Socio-cultural factors, providing for the need for insurance organizations to study the structure of the population, its religious preferences, cultural traditions, national characteristics, the development of a market mentality, social status, etc. When promoting certain types of insurance, one should take into account the ethnic characteristics of a particular society, for example, in Muslim culture accident insurance. demographic factors, which include the standard of living of the population, the purchasing power of potential insurers, the demographic processes taking place in society. These factors must first of all be taken into account when developing new insurance products, as well as when developing existing types of personal insurance. Results of scientific and technological progress in the basic sectors of the economy, the degree of development of new technologies and the level of their development. world market conditions, influencing the development of the insurance market in the Russian Federation as a whole. In the context of competition with foreign insurance companies, national insurers are forced to monitor the main trends in the global insurance market and take them into account in their activities. The direct influence of the external environment on the activities of the insurance company is carried out through subjects of the external insurance environment - state bodies exercising control over insurance activities (FSIS, the Central Bank of the Russian Federation), as well as through individuals and legal entities. acting as consumers of insurance services and having a direct impact on the performance of insurance companies. 19. INTERNAL INSURANCE BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT Internal insurance business environment is a set of internal conditions for the functioning of insurance business organizations. insurance company management - one of the important internal factors affecting the performance of the company. For the insurer, it is important to properly and optimally effectively organize systems and processes within the framework of individual insurance management functions. It is necessary to achieve effective functioning of the insurer's management apparatus. Insurance company staff - the main component of its activity. The individual characteristics of the insurance company's personnel, their qualifications and motivation are precisely the factors that determine the behavior of employees in the organization, and consequently, the results of the company's activities. One of the main factors of the internal environment controlled by the insurer is insurance product and related conditions of specific types of insurance, the level of quality of insurance services, the degree of their diversification, etc. In modern conditions, complex insurance products come to the fore, offering the most complete services of non-standard insurance coverage. An important component of the internal environment of an insurance company is pricing (tariff system) for insurance products. Decisions concerning tariffs for insurance services include determining their general level, range of fluctuations, the relationship between price and quality of services, the degree of importance of the price factor for the insurer, the reaction to the tariff policy of competitors, etc. Marketing is includes a system for organizing sales of an insurance product (insurance policies), generating demand for insurance services and developing measures aimed at promoting insurance services. When organizing a sales system for insurance services, the insurance company decides how to sell services - with the help of intermediaries - insurance brokers (or insurance agents) or sell directly to consumers, making the most of their own infrastructure in the form of agencies, branches, representative offices. Financial stability and solvency largely determines the position of the insurance company in the market and the degree of confidence in her consumers, financial institutions. The financial stability of an insurance company is understood as a constant balancing or excess of income over expenses for the insurance fund. Philosophy and internal culture of the insurance company, i.e., the ideological basis of its functioning, includes the system of values and priorities that guide the personnel of the insurance company when making decisions in the course of their activities, the psychological climate in the company, as well as the model of organizational behavior both within the insurance company (personnel policy), and and outside it (attitude towards policyholders, partners in insurance activities). It is this factor of the internal environment that forms the image of the insurance company and directly affects its competitiveness in the insurance market. 20. INSURANCE RULES The basic organizational and legal document of an insurance company are insurance rules, which usually reflect the following main provisions: 1) types of insurance contracts concluded in accordance with these insurance rules and in a certain territory; 2) items and objects of insurance; at the same time, it is stipulated which material, intangible values of legal entities and individuals and for what characteristics (parameters, properties) are not accepted for insurance by this insurance company; 3) subjects of insurance (insured person, insured person, beneficiary); 4) a list of insurance risks against which insurance is provided; 5) sum insured; 6) term of insurance; 7) insurance premium and insurance rate; 8) the procedure for concluding and operating an insurance contract; 9) the relationship of the parties in the event of an insured event. The rights and obligations of the insured and the insurer in the event of an insured event are established. The list of documents that must be presented by the insured, the insured or the beneficiary in order to receive insurance compensation or insurance coverage is determined. The terms for drawing up an insurance act, the terms and amounts of insurance payments are established, taking into account the deductible and the level of insurance coverage. Cases are determined in which the insurance company has the right to refuse to pay insurance compensation, insurance coverage 10) the procedure for considering disputes. First of all, the procedure for pre-trial settlement of disputes is stipulated, in case of impossibility of such settlement of the dispute, its resolution by the court is envisaged. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation establishes that the conditions contained in the insurance rules and not included in the insurance contract (insurance policy) are binding on the insured (beneficiary) if the contract (insurance policy) directly indicates the application of such rules and the rules themselves are set out in one document with the contract (insurance policy) or on its reverse side, or attached to it. In the latter case, the delivery of the insurance rules to the policyholder must be certified by a record in the insurance contract (policy). If the insurance rules are not set out in the insurance contract (on the back of the policy), and there is no record in the contract (policy) about the delivery of the rules to the policyholder, then in accordance with Art. 943 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, this can be regarded as the optional fulfillment by the insured (beneficiary) of the obligations established by the rules. The insurance company must keep a control copy of all insurance rules with a mark of the Federal Insurance Supervision Service, indicating the issued license-permission for the right to work precisely on the terms of these insurance rules. A special permit is also issued by the Federal Insurance Supervision Service for changes in the insurance rules relating to the essential conditions of insurance, in particular, the objects of insurance and the scope of the insurer's obligations. 21. INSURANCE CONTRACT AND THE PROCEDURE FOR ITS CONCLUSION Insurance contract - this is an agreement between the insured and the insurer that the insurer undertakes, in the event of an insured event, to make an insurance payment to the insured or another person in whose favor the contract is concluded, and the insured undertakes to pay insurance premiums (insurance premium) within the established time limits. Russian legislation sets special requirements to the form of the insurance contract: 1) it must be concluded in writing. Failure to comply with the written form entails the invalidity of the insurance contract (with the exception of compulsory state insurance contracts); 2) it can be concluded by drawing up an appropriate document signed by the parties, or by handing over to the insured an insurance policy or an insurance certificate (certificate) signed by the insurer; 3) it can be concluded by exchanging documents by postal, telegraph, teletype, telephone, electronic or other communication, which makes it possible to reliably establish that the document comes from the party under the insurance contract. significant those terms of the contract that are recognized as such in the relevant legislative and regulatory acts are considered. When concluding a property insurance contract, an agreement must be reached between the insured and the insurer: 1) on certain property or other property interest that is the object of insurance; 2) on the nature of the event, in case of the occurrence of which insurance is provided (insured event); 3) on the amount of the sum insured; 4) on the term of the contract. When concluding a personal insurance contract, an agreement must be reached between the insured and the insurer: 1) on the insured person: 2) on the nature of the event, in the event of the occurrence of which in the life of the insured person insurance is carried out (insured event); 3) on the amount of the sum insured; 4) on the term of the contract. If an agreement is not reached between the insurer and the policyholder on at least one of the listed conditions, the contract is considered not concluded. The text of the insurance contract also includes a list of so-called exceptions, i.e. grounds for exempting the insurer from paying insurance compensation (exclusions from the scope of insurance liability). The Civil Code of the Russian Federation defines the following exceptions: - exposure to a nuclear explosion, radiation or radioactive contamination; - military operations, as well as maneuvers or other military measures; - civil war, popular unrest of any kind or strikes. In addition (unless otherwise provided by the insurance contract), the insurer is exempt from paying insurance compensation for losses incurred as a result of seizure, confiscation, seizure or destruction of property by order of state bodies. The insurance contract comes into force from the moment the insured pays the first installment (unless otherwise provided by the contract or law). 22. RIGHTS AND OBLIGATIONS OF THE PARTIES UNDER THE INSURANCE CONTRACT In case of conclusion of an insurance contract the insurer is obliged. 1) familiarize the insured with the rules of insurance; 2) in the event that the policyholder takes measures that reduce the risk of an insured event and the amount of possible damage to the insured property, or in the event of an increase in its actual value, renegotiate (at the request of the policyholder) the contract taking into account these circumstances; 3) upon the occurrence of an insured event, ensure that the object of insurance is examined by an expert, draw up an act on the insured event with the participation of the insured and calculate the damage; 4) upon the occurrence of an insured event, make an insurance payment within the period established by the insurance contract or law, etc. As part of the agreement the insurer has the right: 1) participate in the rescue and preservation of the insured object; 2) check the condition of the insured object, as well as the conformity of the information provided by the insured about the object of insurance with the actual obligations, regardless of whether the conditions of insurance have changed or not; 3) refuse to fulfill contractual obligations or change the conditions in terms of compensation for damage or payment of the sum insured in cases where the policyholder: a) provided incorrect, i.e. knowingly false or incomplete information about the circumstances that are essential for assessing the degree of risk; b) failed to notify the insurer of significant changes in the insured risk, etc. In accordance with the current legislation in case of conclusion of an insurance contract the insured is obliged. 1) pay insurance premiums on time; 2) when concluding an insurance contract, inform the insurer of the circumstances known to the policyholder that are essential for determining the likelihood of an insured event and the amount of possible losses from its occurrence (insurance risk), if these circumstances are not known and should not be known to the insurer; 3) during the validity period of the insurance contract, comply with the obligations specifically agreed upon or contained in the insurance rules, aimed at reducing the risk or preventing danger; 4) notify the insurer or his representative about the occurrence of an insured event, as soon as the insured becomes aware of its occurrence, if the contract provides for a period and (or) method of notification, it must be done within the agreed time and in the manner specified in the contract, etc. The insured has the right: 1) conclude contracts with insurers on insurance of third parties in favor of the latter (insured persons); 2) when concluding insurance contracts, appoint individuals or legal entities (beneficiaries) to receive insurance payments under insurance contracts, and also replace them at their own discretion, before the occurrence of an insured event; 3) receive the sum insured under a life insurance contract, or for compensation for damage in property insurance, or for compensation for damage caused to third parties under civil liability insurance, within the sum insured and taking into account specific conditions under the contract, etc. 23. TERM OF INSURANCE CONTRACT. VOIDING According to the general rule the insurance contract is terminated expiration of the period for which it was concluded. However, the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility of early termination of the contract: in accordance with Art. 958, an insurance contract "is terminated before the date for which it was concluded, if after its entry into force the possibility of an insured event has disappeared and the existence of an insured risk has ceased due to circumstances other than an insured event. Such circumstances, in particular, include: 1) loss of the insured property for reasons other than the occurrence of an insured event; 2) termination of entrepreneurial activity in accordance with the established procedure by a person who has insured the entrepreneurial risk or the risk of civil liability associated with this activity. In case of early termination of the insurance contract due to the specified circumstances, the insurer is entitled to a part of the insurance premium in proportion to the time during which the insurance was valid. He must return the rest of the premium to the insured. insurance contract may be invalidated if, according to the current legislation, there are grounds to recognize it as such: 1) the insurance contract does not comply with the law or other legal acts; 2) the contract has been concluded for a purpose that is obviously contrary to the foundations of law and order and morality; 3) the contract is concluded by an incapacitated (or partially capable) citizen or under the influence of delusion, deceit, violence, threats, etc. The insurance legislation establishes the following special grounds for invalidation of the insurance contract: 1) if, after the conclusion of the insurance contract, it is established that, when concluding the contract, the insured informed the insurer of knowingly false information about the circumstances that are essential for determining the likelihood of an insured event and the amount of possible losses from its occurrence (insurance risk), when these circumstances were not (and should not have been) known to the insurer. However, the insurer may not demand recognition of the insurance contract as invalid if the circumstances that the policyholder has kept silent about have already disappeared; 2) if, as a result of fraud on the part of the insured, an overstated sum insured was indicated in the contract (including when the excess is the result of double insurance: insurance of the same object from two or more insurers). In addition, the insurer has the right to demand compensation for the losses caused to him by this in an amount exceeding the amount of the insurance premium received by him from the insured. Is an invalid (void) insurance contract in that part of the sum insured that exceeds the insured (actual) value under property or business risk insurance contracts, including if such excess was the result of double insurance. In such cases, the overpaid part of the insurance premium is not returned to the insured. 24. INSURANCE POLICY Insurance policy (insurance certificate, insurance certificate) is a written document of the established form, issued by the insurance company to the insured as evidence of the concluded insurance contract and containing its main conditions. The insurance policy must contain: - Title of the document; - name, legal address and bank details of the insurer; - surname, name, patronymic or name of the policyholder and his address; - indication of the object of insurance; - the amount of the sum insured; - indication of the insurance risk; - the amount of the insurance premium, the terms and procedure for its payment; - contract time; - the procedure for changing and terminating the contract: - other conditions as agreed by the parties, including additions to the insurance rules or exclusions from them; - signatures of the parties. The Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for the possibility for insurance companies to use a "bearer" policy, which can be issued by an insurer when concluding a property insurance contract in favor of a beneficiary whose name is not indicated in the policy (and contract). Insurance contracts in favor of a third party, which is not specified in the contract, are usually used for cargo insurance. Upon presentation by the insured or beneficiary of rights under such an insurance contract, it is necessary to present this policy to the insurer (Article 930 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation). In fact, air, train or bus tickets can also serve as insurance policies. In the event of an insured event en route, a passenger may apply to an insurance company that has entered into a passenger insurance contract with a passenger transportation company and, by presenting an appropriate ticket, be entitled to receive insurance compensation. The insurance premium is included in the ticket price. One of the types of policies that is directly defined in the Civil Code of the Russian Federation as an insurance contract is general policy (Article 941 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation), on the basis of which systematic insurance of different batches of homogeneous property (goods, cargo, etc.) can be carried out on similar conditions for a certain period by agreement between the insured and the insurer. With respect to each consignment of property falling under the scope of the general policy, the policyholder is obliged to inform the insurer of the information stipulated by such a policy within the period provided for by it, and if it is not provided for, immediately upon receipt thereof. The policyholder is not released from this obligation, even if by the time such information is received, the possibility of losses subject to compensation by the insurer has already passed. At the request of the insured, the insurance company is obliged to issue insurance policies for individual consignments of property that fall under the general policy. If the content of the insurance policy does not correspond to the general policy, the insurance policy shall prevail. 25. MAIN REQUIREMENTS FOR THE INSURER Insurers are legal entities established in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation to carry out insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance and have received a license to carry out insurance activities in accordance with the procedure established by law. The Insurance Law defines the following requirements for the insurer: 1) The main activity of an insurance company should be insurance business. At the same time, the legislation establishes some exemptions from the special legal capacity of insurers. Thus, an insurance organization has the right: a) to act as a guarantor in a bank guarantee; b) provide a loan to an insurant - an individual within the limits of the insurance reserve formed under a life insurance contract for a period of at least 5 years; 2) the business name of the subject of the insurance business - a legal entity must contain: a) an indication of the organizational and legal form; b) an indication of the type of activity of the insurance company using the words either "insurance" and (or) "reinsurance", or "mutual insurance", as well as derivatives of such words and phrases; c) a designation that individualizes the insurance company; 3) insurers must have a fully paid authorized capital, the amount of which must not be lower than the minimum amount of the authorized capital. The authorized capital of an insurance company must be formed at the expense of funds, which should maximally ensure the interests of the insured, insured persons, beneficiary, creditors of the insurance company; 4) the insurer must have a license (permission) to carry out insurance activities in the territory of the Russian Federation, obtained in the manner prescribed by law; 5) insurers are obliged to comply with the requirements of financial stability in terms of the formation of insurance reserves, the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover insurance reserves, reinsurance quotas, the standard ratio of the insurer's own funds and assumed obligations, the composition and structure of assets accepted to cover the insurer's own funds, as well as the issuance of bank guarantees: 6) the insurer may transfer the obligations assumed by it under insurance contracts (insurance portfolio) to one insurer or several insurers (replacement of the insurer) that have licenses to carry out those types of insurance for which the insurance portfolio is transferred and have sufficient own funds, i.e. corresponding to solvency requirements, taking into account newly assumed obligations; 7) the heads (including the sole executive body) of the subject of the insurance business - a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur who is the subject of the insurance business are required to have a higher economic or financial education, as well as work experience in the field of insurance business and (or) finance for at least two years; 8) the activity of insurers is not closed. Insurers are required to publish annual balance sheets and profit and loss accounts after audit confirmation of the accuracy of the information contained therein. 26. CONDITIONS FOR ENSURING THE FINANCIAL STABILITY OF INSURANCE COMPANIES Under financial stability An insurance organization is understood as the stability of its financial position, provided by a sufficient share of its own capital (net assets) as part of the sources of financing. An external manifestation of the financial stability of an insurance organization is its solvency, i.e. the ability of the insurer to fulfill obligations to pay the sum insured or insurance compensation to the insured or the insured person under insurance contracts. Own funds insurers include authorized capital, reserve capital, additional capital, retained earnings. A sufficient amount of authorized capital ensures the financial stability of the company at the time of its creation and for the initial period of activity, when the volume of insurance premiums is small. The next condition for ensuring financial stability is creation of insurance reserves and funds, which reflect the size of the obligations of the insurer for insurance payments that have not been fulfilled at the moment. Insurers form from the received insurance premiums the insurance reserves necessary for future insurance payments for personal insurance, property insurance and liability insurance. The insurance reserves include: 1) unearned premium reserve; 2) reserves for losses, including: a) reserve for reported but unsettled losses; b) a reserve for incurred but unreported losses; 3) stabilization reserve; 4) other insurance reserves. The next factor that ensures the financial stability of the insurer is compliance with the normative ratio between assets and liabilities assumed. The normative ratio between the assets of the insurer and the insurance liabilities assumed by it (the normative solvency margin) is understood as the amount within which the insurer, based on the specifics of the contracts concluded and the volume of insurance liabilities assumed, must have its own capital, free from any future liabilities, with the exception of the rights claims of the founders, reduced by the amount of intangible assets and receivables, the maturity of which has expired (the actual size of the solvency margin). Another important condition for ensuring the financial stability of insurance organizations is use of the reinsurance system. The transfer of part of the risks to reinsurance allows solving a number of important problems: stabilization of the results of the insurer's activities over a long period in the event of negative results for the entire insurance portfolio throughout the year: expanding the scale of activities (taking on a large number of risks) and increasing competitiveness; protection of own assets under adverse circumstances. However, at the same time, the insurance organization must evaluate the economic efficiency of this solution. 27. STATE REGISTRATION OF INSURANCE COMPANIES State registration of insurance organizations is carried out in two stages. First, the insurance company is registered as an entrepreneurial organization in the territory of a given country. Then it must be registered and entered in the Unified State Register of Insurers and Their Associations in the Insurance Supervision Bodies (in the Department of Insurance Supervision of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation), where licensing is carried out in parallel with registration. The following are submitted to the registration authority: documents: a) an application for state registration signed by the applicant in the form approved by the Government of the Russian Federation; b) a decision to establish a legal entity in the form of a protocol, agreement or other document. c) constituent documents of a legal entity: d) an extract from the register of foreign legal entities of the respective country of origin or other, equal in legal force, proof of the legal status of the foreign legal entity - founder; e) document confirming the payment of the state fee State registration of a legal entity. is carried out at the location of the permanent executive body indicated by the founders in the application for state registration, in the absence of such an executive body - at the location of another body or person entitled to act on behalf of the legal entity without a power of attorney. The decision on state registration, adopted by the registering body, is the basis for making the corresponding entry in the Unified State Register. The moment of state registration is the making by the registering body of an appropriate entry in the Unified State Register, which, no later than one working day from the moment of state registration, issues (sends) to the applicant a document confirming the fact of making an entry in the Unified State Register. The registering body within a period of not more than 5 working days from the date of state registration submits information on registration to state bodies determined by the Government of the Russian Federation. Denial of state registration legal entity is allowed in the following cases: - non-submission of documents required for state registration determined by federal law; - submission of documents to the wrong registration authority. 28. LICENSING OF ACTIVITIES OF INSURANCE ORGANIZATIONS A license to carry out insurance, reinsurance, mutual insurance, insurance brokerage activities is issued to subjects of the insurance business by the Federal Insurance Supervision Service (FSIS) under the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation. To obtain a license to carry out voluntary and (or) compulsory insurance, mutual insurance The license applicant submits the following documents to the FSIS: - an application for a license; - founding documents; - document on state registration as a legal entity; - minutes of the founders' meeting on approval of the constituent documents of the license applicant and approval for the position of the sole executive body, head (managers) of the collegiate executive body; - information on the composition of shareholders (participants) - documents confirming the payment of the authorized capital in full, etc.; License applicants who are subsidiaries in relation to foreign investors or have a share of foreign investors in their authorized capitals of more than 49% in addition to the above documents, submit the consent in writing of the relevant authority for supervision of the insurance activities of the country of residence for the participation of foreign investors in the authorized capital of insurance companies established in the territory of the Russian Federation, or notify the FSIS that there is no requirement for such permission to be available in the country of residence of foreign investors. The FSIS considers applications from legal entities and individual entrepreneurs for the issuance of licenses to them within a period not exceeding 60 days from the date of receipt of all documents necessary for obtaining a license. The FSIS is obliged to inform the license applicant about the decision within 5 working days from the date of the decision. by prescription is a written instruction from the FSIS and (or) the territorial body of insurance supervision, obliging the insurer to eliminate the identified violation within the prescribed period, i.e., in fact, this is an order for the insurer to eliminate the violations identified by the insurer within the prescribed period. Limitation validity of the insurer's license means a ban on the conclusion of insurance contracts for certain types of insurance, reinsurance contracts, as well as making changes that entail an increase in the obligations of the insurer. to the relevant agreements. Suspension the validity of the insurer's license means a ban on the conclusion of insurance contracts, reinsurance contracts, contracts for the provision of insurance broker services, as well as the introduction of changes that entail an increase in the obligations of the subject of the insurance business to the relevant contracts. 29. GROUNDS AND PROCEDURE FOR TERMINATION OF AN INSURER In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law "On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)", the subject of the insurance business - a legal entity may be liquidated on a voluntary basis by decision of its founders (participants) or by a body of a legal entity authorized to do so by constituent documents, and forcibly by court decision. In accordance with Art. 32.8 of the Insurance Law, the basis for terminating the insurance activity of an insurance business entity is a court decision, as well as a decision of the insurance supervisory authority to revoke a license, including one taken at the request of an insurance business entity. The decision to revoke a license is made by the insurance supervisory authority in the event of: 1) failure by the subject of the insurance business to eliminate violations of the insurance legislation within the prescribed period; 2) if the subject of the insurance business within 12 months from the date of receipt of the license has not started to carry out the activity provided for by the license or does not carry it out during the financial year; 3) in other cases provided for by federal law. License revocation entails the termination of the right of the subject of the insurance business to carry out insurance activities and its exclusion from the Unified State Register of Insurers and Associations of Insurers. From the date of entry into force of the decision of the insurance supervision body to revoke the license, the subject of the insurance business is not entitled to conclude insurance contracts, reinsurance contracts, contracts for the provision of insurance broker services, as well as to make changes that entail an increase in the obligations of the subject of the insurance business, in the relevant contracts. Within 6 months after the entry into force of the decision of the insurance supervisory body to revoke the license, the subject of the insurance business is obliged to: 1) make a decision to terminate insurance activities in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation; 2) fulfill the obligations arising from insurance (reinsurance) contracts, including making insurance payments for insured events that have occurred; 3) transfer obligations assumed under insurance contracts (insurance portfolio) and (or) terminate insurance contracts, reinsurance contracts, contracts for the provision of insurance broker services. Obligations under insurance contracts, under which the relations of the parties have not been settled, after three months from the date of entry into force of the decision of the insurance supervisory authority to revoke the license, are subject to transfer to another insurer. The transfer of obligations assumed under the specified contracts (insurance portfolio) is agreed with the insurance supervisory authority. Before the expiration of 6 months from the date of entry into force of the decision of the insurance supervision body to revoke the license, the subject of insurance business is obliged to submit to the insurance supervision body documents confirming the fulfillment of the relevant obligations. In case of non-receipt of documents within the established period, the insurance supervisory authority is obliged to apply to the court with a claim for the liquidation of the subject of the insurance business - a legal entity or for the termination by the subject of the insurance business - an individual of the activity as an individual entrepreneur. 30. BANKRUPTCY OF AN INSURANCE COMPANY When considering the bankruptcy case of an insurance company, the participation of the Federal Insurance Service in the arbitration process is mandatory. An application for declaring an insurance organization bankrupt may be filed with the arbitration court by the debtor, the bankruptcy creditor, or the authorized body. In the event that bankruptcy procedures are introduced against the debtor - an insurance company in the manner prescribed by the Insolvency Law, the debtor or the bankruptcy trustee is obliged, within 10 days from the date of the start of the monitoring or bankruptcy proceedings, to notify the Federal Service for Insurance of Insurance of the introduction of the relevant bankruptcy procedure against the debtor. Meanwhile, the bankruptcy procedures provided for by the Federal Law "On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)" apply to relations related to the insolvency of insurance companies, with some specific features: business) of the insurance company-debtor; 1) during bankruptcy proceedings, the property complex of an insurance company may be sold only with the consent of the buyer to take over insurance contracts, the validity of which has not expired and for which the insured event has not occurred on the date the insurance company was declared bankrupt; 2) the buyer of the property complex of an insurance company can only be an insurance company that has a license from the federal executive body for supervision of insurance activities to carry out the relevant type of insurance and has assets sufficient to fulfill obligations under insurance contracts assumed. If the arbitration court decides to declare the insurance company bankrupt and on the opening of bankruptcy proceedings creditors' claims are subject to satisfaction with the following features: a) the first two queues of creditors and extraordinary expenses are satisfied in the usual manner; b) the claims of creditors of the last, third priority are subject to satisfaction in the following order: 1) first of all, the claims of insured persons, beneficiaries under compulsory personal insurance contracts are satisfied; 2) in the second place - claims of beneficiaries, policyholders under other compulsory insurance contracts; 3) in the third place - the claims of insured persons, beneficiaries, policyholders under personal insurance contracts, including the requirements provided for in paragraph 2 of Art. 185 of the Federal Law "On Insolvency (Bankruptcy)"; 4) fourthly - claims of other creditors. Claims of creditors secured by a pledge of the debtor's property are satisfied at the expense of the value of the subject of pledge primarily to other creditors, with the exception of obligations to creditors of the first and second priority, the rights of claim on which arose before the conclusion of the corresponding pledge agreement. 31. ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE OF AN INSURANCE COMPANY Organizational structure of an insurance company - these are formal rules developed by its managers for the division of labor and distribution of job responsibilities among employees, determining the norm of management and lines of subordination, as well as for coordinating the tasks of the organization. Organizational structure is important because it allows employees to understand their place in the organization so that they can work together to achieve the goals of the company and get satisfaction from their contribution to its activities. The task of organizing insurance activities is to promote the implementation of the goals of the functioning of the insurance company through the division of labor, the creation of organizational structures (departments, offices, departments, branches, representative offices, etc.). On the other hand, the task of organizing insurance activities is to establish the work of the organizational structures of the insurance company in accordance with the goals and coordinate this work. Therefore, the organization of information support, the development of rules and procedures for the implementation of specific types of insurance activities are also becoming important. Thus, the organization of insurance activities aims to ensure the effective operation of the insurance company through the creation of a rational organizational structure and the establishment of its coordinated work. General requirements for the structure of an insurance company: optimality; - efficiency: - economy: - reliability. General principles for the formation of an organizational system (structure) for managing an insurance company provide for the creation of control centers on two main grounds - hierarchical and functional. Hierarchical construction of control centers insurance organization (vertical structure) provides for the allocation of different levels of management. Currently, the most common are two- or three-level management structures, where the first level is represented by the management apparatus of the insurance organization as a whole, and the subsequent ones are represented by the management services of its individual structural units and divisions. Functional construction of control centers insurance company (horizontal structure) is based on their division by management functions or activities. Within the framework of this system, the function carrier, i.e. the employee, receives instructions not from one, but from a number of higher employees, at the same time he informs not one person about his activities, but a certain number of employees who work in the same area. But within the framework of disciplinary responsibility, he submits to only one boss. 32. STRUCTURAL SUBDIVISIONS OF AN INSURANCE COMPANY Secretariat - a permanent body under the board of directors, the president and vice president of the insurance company to control the execution of their decisions. Under the secretariat public relations team, whose functional duties include informing the media, public organizations about the activities of the insurer, its charitable events, organizing press conferences, presentations, etc. Group of advisory consultants - a permanent advisory body under the management of the insurance company, consisting of permanently working and involved specialists to resolve the most important issues of the insurance company's activities. Executive directorates - functional departments for the main types of insurance activities. Usually, there are executive directorates (management departments) of personal, property insurance, reinsurance, after-sales service (marketing), management of the regional network; management (department) of personnel, legal department, accounting, etc. Department (department) of personal insurance carries out work related to the development, pricing and promotion to the market of all types of personal insurance. Office (department) of property insurance carries out similar activities in relation to covering property risks and civil liability risks. Department (Department) of Reinsurance and International Relations carries out work related to the transfer of part of the responsibility of the insurance company for insurance objects to other insurers. including foreign companies, with the organization of interaction with the latter. Financial and analytical department (department) carries out work on organizing the accounting of business operations of the insurer, maintaining its financial and statistical reporting, organizing interaction with the external audit service, extra-budgetary funds, tax authorities, deals with issues of current and long-term planning of the activities of the insurance company, issues of investment activities, etc. Management (department) of marketing deals with issues related to market research, the development of new insurance products, the pricing policy of the insurance company, the organization of the promotion of the company's insurance products to the market, as well as the organization, coordination and rationalization of the activities of the regional network of the insurance company, etc. Management (department) of personnel carries out work on the selection, certification, advanced training of personnel of the insurance company, rationalization of their number. Legal department provides legal support for the activities of the insurer related to filing claims, representing the interests of the insurer in court and arbitration, developing internal regulatory documents of the insurance company, etc. 33. ESSENCE OF ACTUARY CALCULATIONS Actuarial calculations - a system of statistical and economic-mathematical methods for calculating tariff rates and determining the financial relationship between the insurer and the insured. They make it possible to systematize mathematical and statistical regularities for long-term insurance operations, to select and justify the most effective scheme of financial relationships between the insurer and policyholders. On the basis of actuarial calculations, an insurance fund is formed and spent by types of long-term life insurance, tariff rates and volumes of reserve funds are determined in order to ensure the financial stability of insurance operations. In addition, time series of statistical data are established for short-term insurance, and tariffs, insurance reserves and income of the insurer are calculated on their basis. The main tasks of actuarial calculations: 1) the study and classification of risks according to certain characteristics (groups) within the insurance population; 2) calculation of the mathematical probability of the occurrence of an insured event, determination of the frequency and severity of the consequences of causing damage both in individual risk groups and in the whole insurance population; 3) mathematical justification of the necessary reserve funds of the insurer and the sources of their formation. Based on actuarial calculations, the share of participation of each insured in the creation of the insurance fund is determined, insurance premiums are recalculated when the terms of the life insurance contract change, and tariff rates are determined. which, with the help of long-term financial studies, are underestimated in advance by the amount of the income that will be received by the insurer from the use of the accumulated contributions of policyholders as investments. In actuarial calculations, indicators of insurance statistics are used, which is a systematic study of the most massive and typical insurance operations based on the use of methods for processing generalized final indicators of the insurance business. By insurance industry actuarial calculations are divided into calculations: 1) for personal insurance; 2) property insurance; 3) liability insurance; 4) for insurance of financial risks. By temporal actuarial calculations are divided into reporting and planned. Reporting actuarial calculations are made on already completed operations of the insurer and are focused on the activities of the insurer in the future period when carrying out this type of insurance. Planned ones are made when a new type of insurance is introduced, for which there are no reliable risk observations. In this case, the results of actuarial calculations are used for types of insurance of the same type or similar in content, which are already carried out by the insurance company. After a certain period (at least 3 years), the obtained statistical data on a certain risk are analyzed and appropriate adjustments are made to the planned actuarial calculations. On a hierarchical basis actuarial calculations are divided into federal (general for the entire territory of the Russian Federation), regional (for individual regions) and individual (for a specific insurance company). 34. CLASSIFICATION OF TYPES OF INSURANCE FROM THE POINT OF VIEW OF THE FEATURES OF CALCULATION OF NET RATES All types of insurance can be divided into two categories in terms of the specifics of calculating net rates: - life insurance; - risk types of insurance; In turn, among the risky types of insurance are: - mass risk types of insurance; - insurance of rare events and major risks. Life insurance is a set of types of personal insurance that provide for the obligations of the insurer for insurance payments in the following cases: 1) surviving of the insured until the end of the insurance period or the age specified in the insurance contract; 2) death of the insured: 3) as well as for the payment of a pension (annuity, annuity) in cases stipulated by the insurance contract. Features of the calculation of tariff rates for life insurance are that the formation of a reserve of contributions and the calculation of tariff rates are made using actuarial methods, based on mortality tables and rates of return on investments of temporarily free funds for life insurance. The net life insurance premium rate is calculated depending on the following factors: - the age and sex of the policyholder at the time of entry into force of the insurance contract or the insured person, if the insurance contract is concluded for the insurance of a third party: - type, size and term of payment of insurance coverage; - term and period of payment of insurance premiums: - validity period of the insurance contract; - the planned rate of return from investing life insurance reserves, adopted in the calculation. The long-term validity of life insurance contracts and the specifics of the insurance obligation for insurance payment determine the requirements for calculating insurance rates. At the same time, when calculating insurance rates under life insurance contracts, the following circumstances are taken into account: - an increase in the age of the insured during the term of the life insurance contract changes the probability of the occurrence of an insured event, while the probability of an insured event is determined on the basis of mortality tables; - the amounts of insurance payments payable upon the occurrence of an insured event are determined taking into account the interest income from investing the funds of insurance reserves (the amount of insurance premiums in the amount of the net insurance rate paid under the insurance contract). 35. RISK INSURANCE The types of insurance related to the types of insurance activities other than life insurance are considered risky: - not providing for the obligations of the insurer to pay the sum insured at the end of the term of the insurance contract; - not related to the accumulation of the sum insured during the term of the insurance contract. In these types of insurance, the principle of capitalization (accumulation) is not used and, therefore, when calculating net rates, methods of financial calculations (discounting, compound interest, etc.) are not used. This distinguishes risk types of insurance from life insurance. Risk types of insurance can be conditionally divided for mass types and insurance of rare events and major risks. Under mass types of insurance refers to the types of insurance that presumably cover a significant number of subjects of insurance and insurance risks, characterized by the homogeneity of the objects of insurance and a slight variation in the amount of sums insured. The presence of a large number of insured objects implies that there is a sufficient amount of statistical data on these risks. This data in relation to the insurance company can be both internal, i.e. based on the data of accounting contracts and accounting, and external, i.e. received from other organizations. On the basis of these data, the apparatus of mathematical statistics makes it possible to describe the entire set of risks using such numerical characteristics as average values and dispersion. At the same time, taking into account the homogeneity of the insured objects, it can be argued that the average values will accurately characterize the entire population as a whole. As a result, when calculating net rates for mass types of insurance, average indicators of the frequency of insured events, the amount of damage and the sums insured are widely used. К mass risk types of insurance include most types of property and civil liability insurance, as well as some types of personal insurance (accident insurance, medical expenses insurance, etc.). RџSЂRё insurance of rare events and major risks we are talking about risks characterized, on the one hand, by a low frequency of occurrence of insured events, and, on the other hand, by a large possible amount of damage. The number of objects that can be insured is very limited, and the spread of insurance amounts is significant. The most characteristic type of insurance that can be attributed to this category is insurance of industrial enterprises (primarily in case of fire). Insurance of rare events and major risks also includes aviation and space insurance. Another example of this category of insurance is natural disaster insurance. The frequency of occurrence of an insured event in a particular region is very low (no more than once every few years), and the possible damage is very significant. 36. CALCULATION OF INSURANCE RATES FOR RISK TYPES OF INSURANCE Insurance rates for risky types of insurance are calculated in accordance with the Methodology for calculating tariff rates. This technique is applied under the following conditions: 1) there are statistics or some other information on the type of insurance for which the calculations are made, which makes it possible to estimate the following values: q - the probability of an insured event occurring under one insurance contract; S - average sum insured under one insurance contract SB - average compensation under one insurance contract upon the occurrence of an insured event; 2) it is assumed that there will be no devastating events, when one event entails several insured events; 3) the calculation of tariffs is carried out with a predetermined number of contracts n, which are supposed to be concluded with insurers. If statistics are available, indicators are calculated as follows: q = M/N. where M is the number of insured events in N contracts; N - the total number of contracts concluded for a certain period of time in the past. 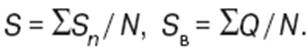
In accordance with this methodology, the net rate (7) includes the main part (7), which ensures the formation by the insurer of a fund of funds used for current insurance payments, the creation of insurance reserves, and the risk premium (7), due to which the insurer creates a part insurance reserve funds intended to cover a possible increase in insurance indemnity payments in certain unfavorable years compared to the average payments for the accepted tariff period. The main part of the net rate 70 corresponds to the average payments of the insurer, depending on the probability of occurrence of the insured event q, the average sum insured S and the average compensation SB. The risk premium is calculated by the formula: 
where n is the planned (actual) number of insurance contracts; a(y) is the guarantee coefficient, which means that the insurance company, with probability y, expects to ensure that the total amount of insurance indemnity payments exceeds the entire collected insurance premium by type of insurance. The value a(y) is taken for one level or another y according to a special table calculated on the basis of probability theory based on the assumption that the total amount of insurance claims paid is a normally distributed random variable. Gross rate 76 calculated by the formula: 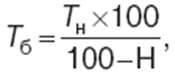
where H is the load in percent. 37. FACTORS AFFECTING THE COST OF INSURANCE SERVICES The price of the insurance service is expressed in the insurance premium (tariff, premium), which the insured pays to the insurer in accordance with the terms of the insurance contract. The amount of the insurance premium is set upon signing the insurance contract and, as a rule, remains unchanged during its validity period. The amount of the insurance premium must be sufficient to: 1) cover the expected claims during the insurance period; 2) create insurance reserves; 3) cover the costs of the insurer for doing business; 4) provide a certain amount of profit. The lower limit of the price is determined by the equality of receipts of payments from policyholders and payments of insurance compensation and sums insured under contracts, plus the costs of the insurance company. At such a price level, the insurance company does not receive a profit from insurance operations, so the provision of insurance services at such prices is unprofitable for the insurer. The upper limit of the price of an insurance service is determined primarily by: 1) the size of supply and demand for it; 2) the amount of bank interest on deposits. So, with a high demand for a certain insurance service, when there is a massive need for insurance coverage of certain risks, and the number of insurance companies providing such a service is small, insurers have the opportunity to maintain a high level of cost of this insurance service for some period. Insurance companies are forced to reduce this cost as the insurance market is saturated with offers of insurance services. The amount of bank interest has a significant impact on the formation of the price of insurance services. First of all, the trends in the dynamics of bank interest in comparison with the practice of insurance rates determine the client's decisions about which sources to seek funds from to cover possible losses in the event of a risk. It is likely that taking a loan from a bank or saving money in it for self-financing can be more profitable than insurance protection for risks. In addition, the funds received by the insurer in the form of insurance premiums and temporarily free until the payment of insurance indemnities are used by the insurance company for commercial purposes, that is, they are invested in securities, in real estate, and are provided on credit. Thus, the use of temporarily free funds by the insurer brings him additional income (investment income), part of which can be provided by the insured in the form of a certain percentage. The cost of insurance services provided by the insurer is also determined by the state of affairs of a particular insurance company, namely the size and structure of its insurance portfolio, management expenses, and income. It should be noted that the profitability of various types of insurance also depends on the phase of the life cycle in which a certain insurance service (insurance product) is located: introduction to the market, growth in demand, market saturation, decline in sales and profitability, ousting from the market. 38. INCOME OF THE INSURANCE COMPANY The income of an insurance company can be grouped according to their areas of activity, i.e., the income of an insurer includes the following types. Income of an insurance company from risks ceded to reinsurance are made up of commission, bonus, compensation by the reinsurer for the share of losses (insurance payments) on risks transferred to reinsurance. The reinsurer's commission is the part of the insurance premium retained by the reinsurer under the insurance contract, which falls on the share of liability assumed by the reinsurer. The amount of the commission is set by agreement of the parties in the reinsurance contract, usually up to 25% of the premium accrued to the reinsurer and is intended to cover the corresponding share of the costs of doing business. Bonus is the share of profit established by the reinsurance contract, received by the reinsurer from participation in risk reinsurance, which is paid by him to the reinsurer for the opportunity to receive additional income and conduct business under the insurance contract. Income of an insurance organization - reinsurer from risks accepted for reinsurance represent the sum of the insurance premium attributable to the share of liability for risks accepted for reinsurance under the reinsurance contract (minus the commission paid to the reinsurer), and the interest received accrued by the reinsurer on the depo (deposit) of premiums for risks accepted by the reinsurer for reinsurance. If there were no insured events, at the end of the reinsurance contract, the reinsurer transfers to the reinsurer the amount that was in the depot, together with the accrued interest on it for not using the funds in circulation. Income indirectly related to insurance activities includes: 1) commissions received by the insurer for the provision of services of an insurance agent, insurance broker, surveyor (accident commissioner) to other insurance companies; 2) the amounts received in the course of realization by the insurer, who paid the insurance indemnity, of the right of claim, which the insured has against the person responsible for the losses compensated by the insurance company in accordance with the insurance contract; 3) income received from the investment of insurance reserves and own funds: 4) savings on the conduct of business on compulsory health insurance; 5) income received from investing the funds of reserves for compulsory medical insurance, less the amounts used to cover the costs of paying for medical services and replenishment of the relevant reserves according to the standards established by the territorial fund of compulsory medical insurance. To income from non-insurance activities include: 1) profit from the sale of fixed assets, material assets and other assets; 2) income from the lease of property; 3) income from non-insurance activities not prohibited by law; 4) amounts received to pay off receivables written off in previous periods for losses; 5) written off accounts payable; 6) non-operating income. 39. EXPENSES OF THE INSURANCE COMPANY The expenses of the insurance company are grouped by line of business and include the following expenses: - related to direct insurance; - associated with the transfer of risks to reinsurance: - associated with the acceptance of risks into reinsurance: - for the conduct of business and non-operating losses, damages. Costs associated with direct insurance include: - insurance payments in the form of insurance compensation or insurance coverage; - amounts paid to the insured upon early termination of the insurance contract; - contributions to insurance reserves. Expenses of the insurance company related to the transfer of risk to reinsurance, include: - the insurance premium attributable to the share of the risk transferred to reinsurance to the reinsurer: - the amount of accrued interest on the depot of premiums on risks ceded to reinsurance; - the share of insurance reserves attributable to reinsurers. To the costs associated with the acceptance of risk into reinsurance, relate: - compensation to the reinsurer for losses on the risk accepted by the reinsurer for reinsurance; - commission and bonus paid by the reinsurer under the reinsurance contract to the reinsurer. Business expenses include costs included in the cost of insurance services on the basis of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation; commissions paid for the provision of services of an insurance agent, an insurance broker reimbursement by an insurance agent of travel expenses from the place of residence to the location of the insurer and back, as well as at the work site: payment for the provision of services related to insurance activities to enterprises, institutions, organizations or individual individuals persons, experts, emergency commissioners, collectors, banks, etc.; expenses for advertising, training and retraining of personnel, entertainment expenses within the limits of applicable norms and standards, calculated taking into account industry specifics; expenses for the production of insurance policies, strict reporting forms, receipts, etc.; payment for consulting, information services, as well as audit services provided in order to confirm the correctness of the annual accounting report; the costs of publishing the annual balance sheet and profit and loss account; expenses for the lease of fixed assets used to carry out insurance activities, including motor transport for the transportation of documents and material assets; non-operating losses, damages, such as legal costs, fines, penalties, forfeits, losses from the write-off of receivables, negative exchange differences. 40. LIFE INSURANCE Life insurance is a set of types of personal insurance that provide for the obligations of the insurer for insurance payments in the following cases: 1) the insured person survives until the end of the insurance period or the age specified in the insurance contract; 2) the death of the insured: 3) the obligation of the insurer to pay a pension (annuity, annuity) to the insured in cases provided for by the insurance contract (expiration of the contract, reaching a certain age by the insured, death of the breadwinner, permanent disability, current payments during the validity of the insurance contract, etc. .). The subject of insurance in life insurance is the life of the insured person, as well as income that guarantees a certain standard of living in the event of insured events. The subjects of life insurance are: 1) the insurer; 2) the policyholder; 3) insured; 4) a beneficiary appointed in the event of the death of the insured. Life insurance can be: 1) individual - insurance under a life contract for one person; 2) collective - insurance under a life contract for a group of persons or a team. Life insurance can be combined with accident insurance. This form of insurance is called "mixed life insurance" and has an additional goal - the protection of property interests in connection with harm to life, health, and ability to work as a result of an accident. Life insurance is carried out in accordance with the insurance rules developed by the insurer separately for each type of life insurance or for a number of related types related to life insurance, as well as in combination with accident insurance. Life insurance in the event of death is the acceptance by the insurer under the insurance contract of the obligation to pay the sum insured to the beneficiary in the event of the death of the insured person during the term of the contract. With this type of insurance, both individuals and legal entities can be insured, while there are age restrictions for individuals. Legal entities conclude mainly collective life insurance contracts in the event of the death of their employees. Individuals aged from 1 to 70 years old can be insured in this type of insurance, however, the insurance rules also provide for health restrictions. A life insurance contract in the event of death is concluded, as a rule, on the basis of a written application of the insured, however, this application may also be verbal, but in any case, the insured is obliged to inform the insurer of the basic information about the insured person, including the information that exists at the time of insurance or previous illnesses. If, after the conclusion of the life insurance contract, the insurer determines that he was given false information about the health status of the insured, the insurance company has the right to demand that this contract be declared invalid. 41. LIFETIME DEATH INSURANCE CONTRACT With life insurance, the contract is valid until the death of the insured, i.e., the validity period of the insurance contract is not established. Therefore, the sum insured will be paid without fail, but the moment of payment is unknown. In case of term insurance, the period of validity of the insurance contract is established, and if the death of the insured does not occur during this period, the insurance company does not make payments. Persons under the age of 65-70 can be insured under a life insurance contract. The basis for concluding a contract is a written application of the established form, signed by the insured. This application, among other things, contains questions regarding the state of health of the insured, which allows the insurer to assess the degree of risk accepted for insurance. The insurance company is interested in the presence of disability in the insured, cardiological, oncological, neurological and other diseases, facts of long-term and temporary disability, as well as hospitalizations over the past 3-5 years, etc. As a rule, invalids and seriously ill people are not accepted for insurance. Under insurance contracts concluded with a medical examination, the obligation of the insurer to make insurance payment, starting from the moment the contract comes into force. When concluding a contract without an examination, the insurance company during the first years of the insurance contract may impose certain restrictions, for example: during the first year, the sum insured can be paid only if the death of the insured occurred as a result of an accident or an acute infectious disease; if the cause of death is related to a disease hidden by the insured, then the insurance payment is not made. Upon conclusion of the contract, the insured is entitled to appoint one or more beneficiaries to receive the insurance payment. During the validity period of the contract, the policyholder, with the consent of the insured, has the right to change the order given by him earlier and appoint another person by submitting a written application about this. The sum insured is agreed upon between the insured and the insurance company in the process of concluding an insurance contract. The amount of insurance rates depends on the age (the older the person, the higher they are) and gender (rates for men are higher than for women) of the insured, his profession, health status, life habits (smoking, drinking alcohol, playing sports, etc.) , as well as the period of payment of the insurance premium. The insurance premium can be paid in a lump sum, but it is more common to pay it for each year in advance. At the request of the insured, an installment plan is provided: the insurance premium can be paid in advance for six months, a quarter, a month. The insured has the right to pay the premium during the entire period of the contract (for life, but usually up to the age of 80-85 years) or during the first 10 or 20 years - the most convenient period for fulfilling obligations under the contract. At the same time, the lowest tariffs are set for a lifetime payment, and the highest - for a 10-year settlement period. 42. TERM DEATH INSURANCE CONTRACT With term insurance, the insurance company pays the agreed amount in the event of the death of the insured during the term of the contract; if he lived to the end of the insurance period, no payments are due. Such contracts are concluded for a period of 1 to 20 years, but not more than for the period after which the insured person reaches the age of 65-70. The sum insured can be set in any amount. As with life insurance, when entering into a contract without a medical examination, the insurer usually limits its payment obligations in the initial period of insurance. Tariffs are differentiated depending on the duration of the insurance period, sex and age of the insured. There are several types of term insurance contracts in case of death. 1. Insurance with a constant sum insured. 2. Insurance with a constantly increasing sum insured. 3. Insurance with a constantly decreasing sum insured. 4. Insurance with the right to extend the contract. The insurer is liable under the contract; life insurance in case of death for any reason, except for events resulting from: - intentional infliction of bodily harm to oneself by the insured person; - criminal intent and actions of the beneficiary that resulted in the death of the insured; - Suicide or attempted suicide: - commission by the insured of illegal actions, deeds; - alcohol, narcotic or toxic intoxication or poisoning; - transfer by the insured person of driving a vehicle to a person who is in a state of alcoholic, narcotic or toxic intoxication, or to a person who does not have the right to drive this vehicle, etc. In the event of the death of the insured person during the validity period of the insurance contract, the insurer pays the sum insured to the beneficiary specified in the insurance policy, if he is not appointed, the sum insured is paid to the heirs of the deceased insured person. If the insured person survives until the expiration of the contract of temporary life insurance in case of death, the sum insured is not paid to anyone. If during the term of the life insurance contract an insured who is not an insured person dies and the payment of insurance premiums is terminated, the insured person is paid the amount of premiums paid by the insured minus the share attributable to cover the costs of the insurer for carrying out this type of insurance. 43. VOLUNTARY INSURANCE OF CITIZENS FROM ACCIDENTS Insurance companies may enter into contracts of voluntary individual accident insurance with capable individuals - insurers (insured). Such an agreement may be concluded in favor of third parties, provided that they are at least 15 years old. The policyholder has the right to appoint any person as the recipient of the sum insured (beneficiary) in the event of his death, but if such a person is not appointed, then he is the heir of the insured person. An accident insurance contract can be concluded for any period or for the period of performance by the insured of certain work, travel, etc. The premium is calculated on the basis of the sum insured, tariff rates and the term of insurance. Tariff rates may vary depending on the age, profession, state of health of the insured, as well as other factors affecting the degree of risk of an insured event. The sum insured is the amount of money within which the insurer is responsible for fulfilling its obligations under this insurance contract. The contract terminates in the event of: 1) expiration of the term of the contract; 2) fulfillment by the insurer of its obligations in full: 3) death of the insured; 4) at the request (initiative) of the insurer - in case of non-payment of the insurance premium by the insured; 5) at the request (initiative) of the insured - in case of violation by the insurer of the rules of insurance; 6) agreements of the parties; 7) liquidation of the insurer in accordance with the procedure established by the legislative acts of the Russian Federation; 8) liquidation of the insured - a legal entity, if the insured did not assume the obligations of the insured to pay insurance premiums (in the event that an insurance contract is concluded by an insurer - a legal entity in favor of a third party). Upon the occurrence of an insured event, the insurer is obliged to make an insurance payment to the insured (the insured or the beneficiary) in accordance with the terms of the contract. The following events that occurred during the period of validity of the insurance contract are recognized as insured events: 1) temporary loss of general working capacity by the insured person (the liability of the insurer begins from the 7th day of treatment); 2) permanent loss of general working capacity by the insured person; 3) death of the insured as a result of injury or other accidents. However, the listed events are not insured events if they occurred as a result of: 1) commission by the insured or the beneficiary of an intentional crime that caused the occurrence of the insured event; 2) driving the insured vehicle while under the influence of alcohol, drugs or toxic substances or transferring control to a person in such a state or to a person who does not have the right to drive this vehicle; 3) suicide, except for those cases when the insured person was brought to such a state by unlawful actions of third parties; 4) intentional infliction of bodily injury by the insured. 44. MANDATORY SOCIAL INSURANCE AGAINST WORKING ACCIDENTS AND OCCUPATIONAL DISEASES The procedure for conducting compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases is regulated by the Federal Law "On Compulsory Social Insurance against Industrial Accidents and Occupational Diseases". Accident at work is an event as a result of which the insured received an injury or other damage to health in the performance of his duties under an employment contract both on the territory of the insured and outside it, or while traveling to or returning from the place of work on the transport provided by the insured, and which entailed the need to transfer the insured to another job, temporary or permanent loss of his professional ability to work or his death. Occupational Illness - is a chronic or acute illness of the insured, which is the result of exposure to harmful production factors and has caused temporary or permanent loss of professional capacity for work. The insured is a legal entity of any organizational and legal form or an individual who employs persons subject to compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and industrial diseases. The insurer is the Social Insurance Fund of the Russian Federation. Compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases are subject to: 1) individuals performing work on the basis of an employment contract (contract) concluded with the insured; 2) individuals sentenced to deprivation of liberty and employed by the insured. The provision for compulsory social insurance against accidents at work and occupational diseases includes the following types of payments: 1) temporary disability benefits; 2) insurance payments: a one-time insurance payment to the insured person or persons entitled to receive such payment in the event of his death; monthly insurance payments to the insured or persons entitled to receive such payments in the event of his death; 3) payment of additional expenses related to damage to the health of the insured person, for his medical, social and professional rehabilitation, including expenses for additional medical care, including additional food and purchase of medicines; outside care for the insured, including those carried out by members of his family; health resort treatment, including payment for vacation for the entire period of treatment and travel to and from the place of treatment, the cost of the travel of the insured, and, if necessary, the cost of travel of the person accompanying him to the place of treatment and back, their accommodation and meals; prosthetics; 4) providing with special vehicles; 5) vocational training (retraining). 45. HEALTH INSURANCE OF CITIZENS Medical insurance is carried out in the form of an agreement concluded between the subjects of medical insurance. Subjects of health insurance are 1) a citizen; 2) the policyholder; 3) medical insurance organization; 4) medical institution. Each citizen in respect of whom a medical insurance contract has been concluded or who has concluded such an agreement independently receives an insurance medical policy. The insurance medical policy is valid throughout the territory of the Russian Federation, as well as in the territories of other states with which the Russian Federation has agreements on medical insurance of citizens. In the system of medical insurance, citizens of the Russian Federation have the right to: 1) compulsory and voluntary medical insurance; 2) choice of a medical insurance company; 3) the choice of a medical institution and a doctor in accordance with medical insurance contracts; 4) receiving medical care throughout the territory of the Russian Federation, including outside the permanent place of residence; 5) receipt of medical services corresponding in volume and quality to the terms of the contract, regardless of the amount of the actually paid insurance premium; 6) filing a claim against the insured, medical insurance organization, medical institution, including material compensation for damage caused through their fault, regardless of whether it is provided for in the health insurance contract or not: 7) refund of a part of insurance premiums for voluntary medical insurance, if it is determined by the terms of the contract. Medical institutions are responsible for the volume and quality of medical services provided and for the refusal to provide medical assistance to the insured party. In case of violation by the medical institution of the terms of the contract, the insurance medical organization has the right to partially or completely not reimburse the costs of providing medical services. The insurance organization bears legal and material liability to the insured person or the insured for failure to comply with the terms of the medical insurance contract. Liability is provided for by the terms of the medical insurance contract. Legal entities that are independent economic entities of any form of ownership provided for by law, possess the authorized capital necessary for health insurance and organize their activities in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation act as insurance medical organizations. Insurance medical organizations are not part of the healthcare system. The insurance rate of contributions for compulsory health insurance for enterprises, organizations, institutions, regardless of the form of ownership, is set as a percentage of the accrued wages for all reasons and is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation. Voluntary medical insurance is carried out at the expense of profits (revenues) of enterprises and personal funds of citizens by concluding an agreement. The amount of insurance premiums is established by agreement of the parties. 46. VOLUNTARY MEDICAL INSURANCE OF CITIZENS Voluntary health insurance is carried out on the basis of voluntary medical insurance programs and provides citizens with additional and other medical services in excess of those established by compulsory medical insurance programs. Voluntary health insurance can be collective and individual. Voluntary health insurance is an important addition to the system of public health and compulsory health insurance. The main purpose of voluntary medical insurance is to compensate insured citizens for financial expenses and losses associated with illness or injury that are not covered by state or compulsory insurance medicine. The insurers in case of voluntary medical insurance are individual citizens with legal capacity and/or enterprises representing the interests of citizens. Insurance medical organizations are legal entities that provide medical insurance and have a state permit (license) to engage in medical insurance. Medical institutions in the health insurance system are licensed medical and preventive institutions, research and medical institutes, as well as persons engaged in medical activities both individually and collectively. The object of voluntary medical insurance is the insured risk associated with the cost of medical care in the event of an insured event. 47. COMPULSORY HEALTH INSURANCE Compulsory health insurance is part of the state social insurance system. Compulsory medical insurance contract is an agreement according to which insured citizens have the right to receive medical services. Compulsory health insurance is regulated by the Law "On Health Insurance of Citizens in the Russian Federation" and is based on the following principles: 1) universality; 2) statehood; 3) non-commercial nature. The implementation of the state policy in the field of compulsory medical insurance is carried out by the Federal and territorial funds of compulsory medical insurance. The insurers in compulsory medical insurance are: 1) in case of insurance of the non-working population - the state represented by local executive authorities; 2) when insuring the working population - legal entities, regardless of the form of ownership and organizational and legal forms, concluding insurance contracts and paying insurance premiums. The compulsory health insurance contract is concluded between the insured - employer or public authority and the insurer on insurance of the working or non-working population, respectively. Insurers in this type of insurance are: 1) insurance medical organizations that have a state license for the right to conduct compulsory medical insurance; 2) medical institutions licensed to provide medical care and services in accordance with the territorial program of compulsory medical insurance. Persons insured under a compulsory medical insurance contract are individuals in whose favor an insurance contract is concluded, i.e. all citizens of the Russian Federation, as well as foreign citizens permanently residing in Russia. Insured citizens are required to have a compulsory medical insurance policy. The insured pays insurance premiums for compulsory medical insurance in the amount established by law to the territorial compulsory medical insurance fund Funds for non-working citizens are transferred by the territorial administration in accordance with their number and the established insurance premium for the non-working population. Control over the completeness and timeliness of paid insurance premiums is carried out by the tax authorities. The Territorial Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund transfers funds to an insurance medical organization, taking into account the number of insured citizens under insurance contracts concluded by the organization. An insurance medical organization pays bills to medical institutions for the medical care provided to insured citizens in accordance with the established price lists in the system of compulsory medical insurance of the corresponding territory. 48. RENTAL INSURANCE Annuity insurance is the acceptance by the insurer under the insurance contract of the obligation to make insurance payments to the insured or the insured person in a fixed amount and at a fixed frequency, provided that he survives to the term (age) stipulated by the contract and pays the insurance premium in full. Annuity insurance is also called annuity. The policyholders in case of annuity insurance may be able-bodied individuals who conclude annuity insurance contracts in their own favor or in favor of third parties - the insured, as well as legal entities. At the same time, individuals conclude individual annuity insurance contracts, and legal entities, as a rule, collective ones. Insured events in case of rent insurance are the survival of the insured person until the period specified by the insurance contract, by which the full payment of the insurance premium by the insured and the accumulation of the amount of money of the insurer necessary for insurance payments, as well as the survival of the periodical payments of insurance coverage in the form of annuity to the established deadlines. In the annuity insurance contract, the sum insured is the amount of insurance coverage payable by the insurer to the insured person at the intervals specified in the insurance contract. The amount of the insurance premium is determined by the amount insured and the level of the tariff rate for this type of insurance. The level of the insurance premium depends on: 1) the age and sex of the insured person; 2) time (years) from the moment of conclusion of the annuity insurance contract and making the first installment until the commencement of annuity insurance payments: 3) the procedure for insurance payments; 4) the duration of the period of time for the payment of annuity (the number of years specified in the agreement or for life); 5) method of payment of the insurance premium - at a time or in installments; 6) rates of return on investment by the insurer of insurance reserves. Due to the fact that under the annuity insurance contract an insurance reserve is accumulated, the insured may be granted the right to receive a loan within the limits of the actually formed reserve. At the same time, the term and procedure for repaying the loan by the insured are additionally established. With an immediate life annuity, the insurance premium is paid by the insured in a lump sum, and the obligations of the insurer for the insurance payment must be carried out immediately at the established frequency during the life of the insured person. A deferred life annuity involves the policyholder's obligation to pay the insurance premium in a lump sum or in installments within an agreed period and the obligation of the insurer to make insurance payments after the end of the waiting period between the end of the premium period and the start of annuity payments. With a time-based annuity, the insurer's obligations for insurance payment are established for a limited period, i.e., the payment of annuity to the insured person is made within the time specified by the contract. 49. PENSION INSURANCE Pension insurance is a type of insurance in which the insurer, under an insurance contract, assumes obligations to make insurance payments to the insured (insured person) in a fixed amount, as a rule, with a specified frequency, provided that he lives to the age stipulated by the contract and pays the insurance premium in full. With pension insurance, the main payments of insurance coverage are made when the insured person reaches the age of retirement, therefore, insurance payments in this type of insurance are called pensions. However, this condition is not mandatory, since the parties that have concluded the insurance contract can determine the age at which the payment of insurance coverage should begin. Insured events in case of pension insurance are the survival of the insured person to the age and period of commencement of insurance payments stipulated by the contract, as well as to the subsequent established periods for periodic payments of insurance coverage in the form of a pension. The insured may be capable citizens who have concluded an agreement in their own favor or in favor of another person, as well as legal entities. The maximum age of the insured person at the time of conclusion of the insurance contract for women is usually limited to 52-54 years, and for men - 57-59 years, i.e. 2-3 years before retirement age. The sum insured for pension insurance is set at the time of conclusion of the insurance contract in the amount of periodic payments. The amount of these payments is determined by the insured depending on his financial capacity to pay the insurance premium and is agreed with the insurance company. The amount of the insurance premium for pension insurance is established from tables calculated by the insurance company based on existing statistical data. Sometimes the insured himself indicates the amount of insurance premiums, taking into account his financial capabilities. The insurance premium under a pension insurance contract may be paid by the insured either in periodic payments or in a lump sum. With the installment form of premium payment, indexation of insurance premiums can be established. The amount of insurance coverage that the insured person will receive depends on: 1) the amount of insurance premiums paid; 2) the number of years that have elapsed from the moment of conclusion of the insurance contract until the start of pension payments: the longer the accumulation period, the greater the accumulated amount and the higher the amount of the pension received by the insured person, respectively; 3) the age of the insured person, since the older the insured person, the shorter the accumulation period and the higher the insurance premium that must be paid; 4) the gender of the insured person. As a rule, the amount of the insurance premium for women is 1,5 times higher than for men. However, there are pension insurance programs in which the amount of the insurance premium does not depend on gender. In these programs, the tariff tables are calculated from the combined mortality table. 50. COMPULSORY PERSONAL INSURANCE OF PASSENGERS (TOURISTS, EXCURSIONS) Compulsory personal insurance of passengers (tourists, sightseers) is carried out by concluding, in the manner and on the terms provided for by the legislation of the Russian Federation, agreements between the relevant transport, freight forwarding enterprises (carriers) and insurance companies licensed to carry out insurance operations for this type of compulsory insurance. The interests of a passenger (tourist, excursionist) at the conclusion of a compulsory insurance contract are represented by a transport organization. The objects of insurance are the property interests of the insured passengers (tourists, sightseers) that do not contradict the law and are related to their life and health. Compulsory personal insurance does not apply to passengers: 1) all types of international transport; 2) railway, sea, inland waterway and road transport of suburban communication; 3) sea and inland water transport of intracity communications and crossings; 4) road transport on urban routes. The size of the insurance rate for compulsory personal insurance of passengers (tourists, sightseers) of air, rail, sea, inland water and motor transport is established by insurers in agreement with the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation and approved by the federal executive body for supervision of insurance activities. The amount of the insurance premium is included in the cost of the travel document (voucher) and is charged from the passenger (tourist, excursionist) when selling the travel document. Passengers enjoying the right to travel free of charge in the Russian Federation are subject to compulsory personal insurance without paying an insurance premium. An insured event for this type of insurance is recognized as injury or death of a passenger as a result of an accident on the type of transport on which the insured was moving. The insurance amount for compulsory personal insurance of passengers (tourists, sightseers) is currently set at 120 minimum wages, established by law on the date of purchase of the travel document. Insurance payment for compulsory personal insurance of passengers (tourists, sightseers) is made to the insured person or his heirs no later than 10 days after the receipt by the insurer of the act drawn up by the carrier on the accident that occurred on the transport with the insured person, and other necessary documents provided for by the rules for this type of mandatory insurance. The carrier is obliged to draw up an act on each accident that occurred on the transport with the insured passenger (tourist, excursionist) and hand the first copy to the insured person to his representatives or heirs. At the written request of the insurer, the carrier is also obliged to send a copy of the accident report to the insurer within 10 days from the date of receipt of the request. 51. ESSENCE OF PROPERTY INSURANCE In the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, property insurance means the process of drawing up and executing contracts in which the insurer, for a certain premium, undertakes, upon the occurrence of an insured event, to compensate the insured or a third party in whose favor the insurance contract is concluded, losses caused to the insured property or other property interests of the insured. Property insurance is voluntary and mandatory. Mandatory - provided for insurance of property and property interests of agricultural enterprises (state, collective farm, rental, farm), leased enterprises, insurance of farm animals. Voluntary property insurance covers the property of business entities, public organizations, insurance of individual entrepreneurs, insurance of household property and means of transport owned by citizens. The volume of insurance liability - from fires, natural disasters, accidents and other insured events. Under a separate agreement, it is possible to insure property in case of theft, robbery, theft of means of transport. The term of insurance is usually 1 year, but if before the end of the next term the insured makes insurance payments again, the term of insurance can be extended. In case of property insurance, the object of insurance relations is property in various forms, as well as property interests. In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the following property interests can be insured under a property insurance contract: - risk of loss (destruction), shortage or damage to certain property; - the risk of liability for obligations arising from causing harm to life, health or property of other persons, and in cases provided for by law, also liability under contracts - the risk of civil liability; - the risk of losses from entrepreneurial activities due to violation of their obligations by counterparties of the entrepreneur or changes in the conditions of this activity due to circumstances beyond the control of the entrepreneur, including the risk of not receiving expected income - entrepreneurial risk. In accordance with the Law "On the Organization of Insurance Business in the Russian Federation", a property insurance contract may be concluded in relation to: - means of land transport, with the exception of railway transport means. - means of air transport; - means of water transport; - cargo; - agricultural crops, crops, perennial plantations, animals: - property of legal entities, except for vehicles; - property of citizens. The listed objects of insurance can be insured against risks such as fire, flood, earthquake, accident, explosion, hurricane, hail, etc. 52. FEATURES OF PROPERTY INSURANCE The property subject to insurance under a property insurance contract is understood as such objects of civil rights in respect of which: 1) there may be an interest in their preservation, i.e., which may be lost in whole or in part or be damaged as a result of a combination of circumstances; 2) the harm caused by them has a direct monetary value. Such objects include any property, as well as information. Of the intangible benefits, such objects include business reputation, which has a monetary value and is reflected in the balance sheet of organizations and enterprises. Property may be insured in favor of a third party (insured or beneficiary) who has an interest based on law, other legal act or contract in the preservation of this property. A contract concluded if the policyholder has no interest in preserving the insured property is invalid. Term of property insurance is established based on the interests of the insured, usually from 1 month to 1 year or more - with voluntary insurance. Sum insured - this is the amount within which the insurer bears insurance liability under the property insurance contract. The maximum sum insured is determined by the insurance value of the insurable interest at the time of the insured event. The classical concept of insurance is that the sum insured under the contract should not exceed the insurance value. Insurance value - the value at which the insured evaluates his property. It is determined by agreement between the insurer and the policyholder. The insured value of the property must not exceed its actual value at the time of conclusion of the insurance contract. The value of the insured property may change during the term of the contract. The amount of the insurance premium (the insurance fee that the owner of the property is obliged to pay) is determined by the insurance company, taking into account the amount of insurance liability for possible losses, depending on the industry of production or purpose of the property, the technology and equipment used, the type of construction. The insurance premium is calculated by the insurer for the entire period of insurance based on the sum insured under the insurance contract, its term and the amount of the insurance rate. A significant impact on the amount of the insurance premium is provided by the degree of risk, which is determined by: the type of buildings (structures), the category of building structures and materials, the type and quantity of stored or processed materials (raw materials), the intensity of production, the availability of fire extinguishing equipment and local fire extinguishing capabilities, the location of the object insurance, fire resistance of certain materials and other circumstances that have a significant impact on the likelihood of an insured event. When insuring property, insurance companies often offer their clients to install franchise, that is, they stipulate in advance that certain losses (as a rule, small ones) will not be reimbursed by the insurance company. At the same time, insurance premiums are also reduced. 53. INSURANCE OF PROPERTY AGAINST FIRE AND OTHER HAZARDS The objects of insurance can be: buildings, structures, construction in progress, transmission devices, power, working and other machines, equipment, inventory, products, raw materials, materials, goods, fuel, household property, exhibits and other property. The insurance contract can be concluded both for all property and for its part. Buildings and structures (including other property) located in a zone that is constantly threatened by collapses, landslides, floods and other natural disasters cannot be insured under voluntary insurance. The insured can be both the owner of the property and the owner under a lease or lease agreement. The property may be under the full economic control of the insured or in operational management, may be transferred to the insured for storage or disposal for any purpose (for processing, storage, sale, leasing, etc.) Insurance companies indemnify for losses that have arisen as a result of the direct impact of fire on the insured property, as well as the impact of side effects (smoke, heat, gas or air pressure). Indemnifies losses that may be inflicted on the insured property as a result of measures taken to extinguish a fire, for example, damage to property by water from fire installations, dismantling of a building or its parts during fire extinguishing to completely eliminate the source of ignition. However, fire insurance does not cover any damage to property caused by fire. Insurance companies, as a rule, do not compensate for losses resulting from the treatment of insured property by fire (other thermal impact) in accordance with the technological process; losses incurred not as a result of a fire, but from burning (for example, when storing raw materials, materials, products, etc. near sources of maintaining fire). Quite often, in the contract of insurance "against fire" is carried out property insurance against related risks, i.e., the insurance company also includes insurance protection against damage or loss of property due to such risks as: 1) natural disasters, namely: earthquake, volcanic eruption, underground fire, landslide, subsidence, hurricane, tornado, hail, rain, mudflow; 2) penetration of water from an adjacent room; 3) accidents of heating, water supply, sewerage and fire-fighting networks; 4) broken window panes, mirrors and shop windows; 5) unlawful actions of third parties; 6) interruption in production after a fire or loss of profit in this regard. Losses resulting from an earthquake are subject to compensation only if the insured proves that in the design, construction and operation of the insured buildings and structures in seismically hazardous areas, the seismological conditions of the area in which these buildings and structures are located were duly taken into account. The insurers shall not indemnify for losses incurred as a result of penetration of rain, snow, hail or dirt into the insured premises through unclosed windows, doors or other openings in buildings, unless these openings were caused by a storm, whirlwind, hurricane or tornado. 54. INSURANCE OF MOTOR VEHICLES Vehicle insurance is a type of insurance that provides for the obligations of the insurer for insurance payments in the amount of full or partial compensation for damage caused to the property interests of the insured associated with the possession, use, disposal of a motor vehicle due to damage or destruction (hijacking, theft) of a motor vehicle. This type of insurance is carried out on a voluntary basis. Motor vehicles subject to registration with the traffic police of the Russian Federation are accepted for insurance. Vehicle insurers can be Russian citizens, foreigners and stateless persons, as well as legal entities of any organizational and legal form. The vehicle may be owned by the insured or leased by the insured. Vehicle insurance, in which the insurer compensates for the damage caused to the policyholder in case of damage or destruction of only the vehicle itself, is called hull insurance. However, in the Russian practice of motor transport insurance, combined insurance is popular, when not only the vehicle is insured, but also the liability of its owner, as well as luggage and additional equipment. When insuring luggage, insurance cover does not cover antique and unique items, items made of precious metals, precious, semi-precious and ornamental stones, religious objects, collections, etc. In practice, there are various options for insurance of vehicles. They differ from each other in the number of risks in respect of which an insurance contract is concluded, and the volume of obligations of the insurer. Depending on the choice of insurance option, the contract may provide for full or partial compensation for damage caused as a result of damage, destruction, loss (hijacking) of the vehicle. However, regardless of the insurance option, according to Art. 964 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, losses incurred as a result of military operations, as well as maneuvers and other military events, civil war, popular unrest or radioactive contamination, etc., are not compensated. Vehicles can be insured up to their actual value (with a depreciation discount), including the value of the trailer; or for any smaller sum insured, if it is provided by the insurance contract. In the second case, insurance is carried out according to the principle of proportional liability, which provides for the payment of insurance compensation in such a percentage of the amount of damage that the sum insured is equal to the actual value of the vehicle. Additional equipment and items of luggage of the motor vehicle, at the request of the policyholder, may be insured together (in the total amount) with the means of transport or separately. 55. CARGO INSURANCE Cargo insurance is a set of types of insurance that provide for the obligations of the insurer for insurance payments in the amount of full or partial compensation for damage caused to the object of insurance, which in this case means the property interests of the person whose insurance contract is concluded, related to the possession, use, disposal of cargo , due to damage or destruction (loss) of cargo (goods, baggage or other cargo), regardless of the method of its transportation. Depending on the type of cargo being transported, insurers analyze the likelihood of the main risks that accompany the transportation of certain groups of cargo. When transporting bulk cargo (grain, sand, coal, gravel, etc.) the main risks are associated with the difference in weight when sending and receiving cargo (with the exception of the stipulated norms for the natural loss of cargo due to shrinkage, shaking, etc.). Industrial machinery and equipment. The main risks are caused by external impact on the cargo (damage during loading / unloading or transportation), as well as petty theft. The amount of damage caused to complete equipment can be very large, since even damage to one node will make it impossible to install the entire line. Automotive. A significant part of the risks is associated with minor damage to the paintwork and petty theft of components and assemblies. These risks are especially important when transporting expensive cars. Practice shows that the relationship between the insurer and the insured when calculating the amount of damage and using repair estimates for this purpose should be provided for by the contract. Food. In addition to risks such as theft and robbery, food products are also exposed to other hazards during transport, such as changes in temperature. Fruits, herbal products. To determine the degree of risk in the transportation of fruits, it is very important to study the GOSTs and the requirements of the sanitary authorities that allow these goods to be sold. Oil and oil products. The main risks for this group are underfilling when pumping from vehicles to terminals, and for oil products - pollution and dilution with water, which is practiced when transporting light oil products. Thus, in order to assess the degree of risk to which the goods are exposed, the insurer must first of all carefully study the requirements for the goods at the destination (i.e., the conditions for accepting the goods by the recipient under the contract or contract), and also pay due attention to statistical data. Analysis of statistical data, as well as the causes of losses, makes it possible to judge the degree of risk in a given transportation. Based on the analysis, the insurance company has the right to put forward requirements for the cargo insured, which he is obliged to fulfill in order to conclude an insurance contract, for example, change the packaging or route. After collecting information, analyzing it, assessing and determining the risk, the amount of the insurance premium, the policyholder and the insurer conclude an insurance contract. 56. GENERAL POLIS Systematic insurance of different batches of homogeneous property on similar conditions for a certain period may, by agreement of the insured with the insurer, be carried out on the basis of one insurance contract - a general policy. General policy - this is a kind of property insurance contract, it must comply with all the rules of this type of insurance. A distinctive feature of the general policy is that the terms of the insurance contract (on the insured cargo, the sum insured, the insurance premium) are agreed upon in it not in the form of a direct description of a specific cargo or an indication of specific amounts of money, but in the form of a description of the ways in which the relevant conditions are determined for each consignment on the basis of information provided by the insured to the insurer in respect of this consignment. Therefore, in respect of each consignment of cargo falling under the general policy, the insured is obliged to inform the insurer of the information stipulated by such a policy within the period provided for by it, and if it is not provided for, immediately upon receipt of the cargo. The list of such information is an essential condition of the general policy, and the parties are obliged to agree upon it when concluding the contract. Failure to comply with the obligation to provide information does not lead to the termination of insurance coverage, since the current general policy provides protection for all consignments that correspond to the description given in it. However, failure to fulfill this obligation by the insured may cause losses to the insurer. Therefore, the insured is not released from the obligation to provide information, even if by the time they are received, the threat of losses to be reimbursed by the insurer has already passed. The insurer, in turn, at the request of the insured, is obliged to issue insurance policies for individual lots of property that fall under the general policy. At the same time, the general policy is a contract, and the policies issued for a specific consignment of cargo are not contracts, but serve as confirmation of the existence of a general cargo insurance contract. Usually, the general policy stipulates: 1) cargo or types of cargo; 2) transportation routes, mode of transport (sometimes there are general policies, the insurance coverage of which applies to all cargoes of the insured throughout the world, the so-called Worldwide policies); 3) limit of the sum insured for one vehicle; 4) approximate delivery schedule; 5) the planned cargo turnover of the insured during the year. The general policy has a number of advantages: administrative costs for doing business are reduced. Simplify insurance premium payments. But its signing is possible only on condition that the insured has stable orders, established turnover and range of goods and can submit a delivery schedule or an approximate monthly volume of traffic. In most cases, the general policy is signed after the work of the insurer and the insured for some time on sole policies. 57. ESSENCE OF LIABILITY INSURANCE Liability insurance is different from other branches of insurance. In particular, it differs from personal insurance in that personal insurance is sum insurance, and liability insurance is damage insurance. And it differs from property insurance in that with property insurance a predetermined thing or property is insured for a predetermined amount, and with liability insurance, the object of protection is not predetermined property values, but well-being in general. Liability insurance is a branch of insurance where the object of insurance is liability to third parties (citizens and business entities) due to any action or inaction of the insured. Liability insurance provides for the possibility, in case of harm to health and property of third parties, by virtue of law or by a court decision, to make appropriate payments to compensate for the harm caused. The liability insurance block includes the following types of civil liability insurance: 1) motor vehicle owners: 2) owners of air transport means: 3) owners of water transport facilities; 4) owners of railway transport means: 5) organizations operating hazardous facilities: 6) for causing harm due to lack of goods, works, services; 7) for causing harm to third parties; 8) for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of obligations under the contract. Criminal liability cannot be an object of insurance. Civil liability is usually divided into contractual and non-contractual. The object of liability insurance is the property interests of policyholders (insured persons) associated with the need to compensate for damage caused by them to third parties in the course of their activities. At the same time, the liability of both the policyholder himself and other persons (insured persons) can be insured, which must be established in the insurance contract. Under the terms of the civil liability insurance contract, the insurer provides policyholders (insured persons) with insurance coverage in the event that they present claims to third parties (in accordance with the norms of civil law or by court decision) for compensation for damage caused by an insured event. A feature of this type of insurance is the procedure for determining the sum insured in the contract, which is called limit of liability. Unlike property insurance, in which the sum insured is usually determined by the insured value of the property or part of it, in liability insurance, the parties establish in the contract the maximum amount of compensation - the limit of the insured's liability assumed by the insurer, which may arise when the latter causes harm (losses) to third parties . When concluding a liability insurance contract, the amount of the sum insured is determined by the parties at their discretion and depends on the maximum possible volume (limit) of the policyholder's liability. 58. MANUFACTURER (SELLER) LIABILITY INSURANCE FOR PRODUCT QUALITY 1. Liability insurance of the commodity producer (manufacturer) for product quality. The insurance contract is concluded in case of property liability of the insured to consumers for the sale of products with defects. Insurance coverage covers insurance risks in the form of liability for: 1) property damage caused to the consumer: 2) harm caused to the life and health of the consumer; 3) moral damage. Insurance is carried out if: 1) the insured has a permit for the production of products issued in accordance with the law: 2) a certificate of conformity has been issued for goods subject to mandatory certification in accordance with the law; 3) clear and unambiguous requirements are established for product quality indicators that comply with the requirements of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Protection of Consumer Rights"; 4) the insured, at the request of the insurer, may submit documentary evidence of the compliance of the production conditions with the established requirements for product quality. 2. Seller's liability insurance for product quality. The property liability of the insured to consumers associated with the sale of defective products is accepted for insurance. Insurance coverage covers insurance risks arising from the seller's liability for harm caused to life, health or property of the consumer of products sold by the seller. Liability insurance of the insured to the consumer for product quality is carried out if: 1) for goods subject to mandatory certification, there is a certificate of conformity; 2) the policyholder has a permit for the sale of goods, issued in the prescribed manner; 3) the policyholder, at the request of the insurer, may submit documentary evidence of the fact of compliance with the conditions and rules of trade. In some cases, carried out contractor's liability insurance for the quality of work performed (services rendered). Insurers in this type of insurance are legal entities, as well as entrepreneurs who perform work (services) and who, in accordance with the law, are responsible to consumers for the quality of the services provided. Insurance protection covers the following insurance risks: 1) liability for property damage caused to consumers, including damage caused to natural objects in their possession; 2) liability for harm caused to the life and health of the consumer. Liability insurance of the insured to consumers for the quality of work is carried out if: 1) there are clear requirements for the nature and content of the work performed, subject to mandatory certification, there is a certificate of conformity issued in the prescribed manner; 2) the performer has a documented permission to perform work, drawn up in the prescribed manner in the form of a technical assignment of the contract, application. 59. PROFESSIONAL LIABILITY INSURANCE The object of professional liability insurance is the property interests of the insured person related to the obligation of the latter, in accordance with the procedure established by law, to compensate for damage caused to third parties in connection with the insured person's professional activities. Based on the rules of professional liability insurance, only the liability of a natural person engaged in notarial, medical or other activities on a professional basis as an individual entrepreneur can be insured. A legal entity cannot insure its professional liability. A legal entity has the right to insure its civil liability to third parties for harm caused by its employee in the performance of labor (official, official) duties. This type of insurance in accordance with the law refers to the insurance of other types of liability. The risk of liability for harm caused intentionally in the performance of professional duties is not covered by the terms of insurance. Unlike other types of insurance, in professional liability insurance, the occurrence of an insured event does not depend on external factors, but on the qualifications of a person performing a certain professional activity. With this type of insurance, the fact of the occurrence of an insured event is recognized after the entry into force of a court decision (general civil or arbitration), establishing the property liability of the insured for causing material damage to the client and the amount of damage. Each type of professional liability insurance has its own characteristics. This is due to the fact that some types of activities require a license, while others do not. In the implementation of certain types of activities, it is necessary to apply different standards and comply with the mandatory requirements established by law. The insurance contract shall enter into force upon payment by the insured of the entire amount of the insurance premium, unless otherwise provided by agreement of the parties. The insurance premium is established on the basis of insurance rates and depends on the insurance amount established by the contract, in addition, the amount of the insurance premium depends on: 1) the information submitted to the insurer contains information about the satisfaction of claims in accordance with the procedure established by law in connection with the performance of professional actions by a doctor (notary); 2) experience of medical activity; 3) qualifications of the insured. Insurance payment in accordance with the insurance contract is made to citizens in respect of whom, by a court decision, the liability of the insured person for the harm caused to them in the course of their professional activities has been established. The insurance payment may not exceed the amount of the property liability of the insured established by the court. In addition, the insurance payment for one or more insured events may not exceed the sum insured. 60. INSURANCE OF CIVIL LIABILITY OF OWNERS OF MOTOR VEHICLES Compulsory insurance contract of civil liability of vehicle owners - an insurance contract under which the insurer undertakes, for a fee (insurance premium) stipulated by the contract, upon the occurrence of an event (insurable event) provided for in the contract, to compensate the victims for the harm caused as a result of this event to their life, health or property (to carry out insurance payment) within the amount specified by the contract (sum insured). The compulsory insurance contract is concluded in the manner and on the terms provided for by the Federal Law "On Compulsory Insurance of Civil Liability of Vehicle Owners". The compulsory insurance contract is concluded in relation to the owner of the vehicle, persons. indicated by him in the compulsory insurance contract or in relation to an unlimited number of persons admitted by the owner to drive the vehicle in accordance with the terms of the compulsory insurance contract, as well as other persons using the vehicle legally. The object of compulsory insurance is property interests associated with the risk of civil liability of the owner of the vehicle for obligations arising from causing harm to the life, health or property of the victims when using the vehicle on the territory of the Russian Federation. The term of the contract of compulsory insurance is 1 year and is extended for the next year, if the insured not later than 2 months before the expiration of this contract has not notified the insurer of the refusal to renew it. The validity of the extended contract of compulsory insurance shall not be terminated in case of delay in payment by the insured of the insurance premium for the next year by no more than 30 days. The sum insured for civil liability insurance, within which the insurer, upon the occurrence of each insured event (regardless of their number during the term of the compulsory insurance contract), undertakes to compensate the injured for the harm caused, is: 1) in terms of compensation for harm caused to the life or health of each victim , no more than 160 thousand rubles. 2) in terms of compensation for damage caused to the property of several victims, no more than 160 thousand rubles. 3) in terms of compensation for damage caused to the property of one victim, no more than 120 thousand rubles. In turn, the size of the insurance premium is determined on the basis of insurance rates calculated by the insurer, which consist of base rates and coefficients. Insurance premiums under compulsory insurance contracts are calculated as the product of base rates and insurance rate coefficients. The base rates of insurance tariffs are set by the Government of the Russian Federation, depending on the technical characteristics, design features and purpose of vehicles, which significantly affect the likelihood of harm during their use and the potential amount of harm caused.
▪ Russian language and culture of speech. Crib ▪ Finance, money circulation and credit. Crib
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ site section Preamplifiers. Article selection ▪ article History of political and legal doctrines. Crib ▪ article Caches in cars.. Spy stuff ▪ UHF article for St. receiver. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 