 Free technical library
Free technical library
Siberian fly swatter. Tips for the home master

Directory / Builder, home master
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
Every warm season - from spring to autumn, throughout the entire foreseeable history of human existence, various harmful insects pester him, and the stronger, the closer to nature he is. And the most common of them, of course, are mosquitoes and flies. Man fought against them always and everywhere, but so far he has not been able to win a complete victory. But it is known that even one mosquito can keep you awake all night, and an annoying fly interferes with work so much that it can lead you out of balance. Therefore, a "weapon" against them (for example, an ordinary fly swatter) should always be ready and at hand.
However, commercially available fly swatters, even with a careful blow, flatten the insect so that only a wet place remains from it, but unfortunately it is poorly or not washed at all. So you have to wait until a fly or a mosquito sits on a place where you can kill an insect without undesirable consequences, and sometimes the hunt drags on for a long time.
So I had to invent my own fly swatter.
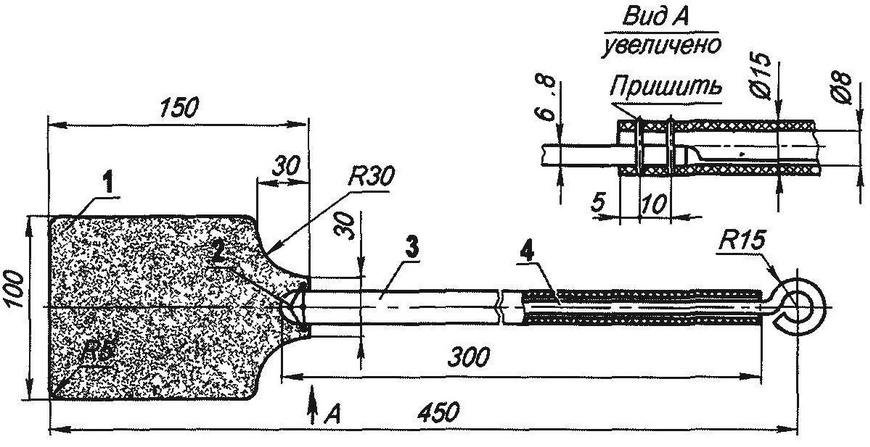
Siberian fly swatter (click to enlarge): 1 - striker (from the shaft of an old felt boot), 2 - seam (severe thread); 3 - handle shell (PVC tube); 4 - handle rod (aluminum wire Ø8)
The shape and design of the fly swatter is traditional: the striker is in the form of a spatula attached to a rather long, thin handle. But there are in this weapon against insects and "proprietary" features. The handle consists of a rod made of thick aluminum wire and a sheath put on it - a PVC tube. If necessary, the handle can also be bent to act as a "weapon" from around a corner or in a hard-to-reach (for a fly swatter with a straight handle) place.
The free end of the handle shaft is bent into a ring so that the fly swatter can be hung for storage on a hook or just a nail in the wall. But the main brand secret is in the material of the striker.
Probably, many people remember how in childhood they sometimes managed to catch soap bubbles with their hands, dressed in woolen mittens. This led to the idea to make a striker from a similar material, only denser and heavier.
And I picked up such material - a bootleg from an old Siberian felt boot. In the warmer regions of Russia, felt boots, even old ones, are more difficult to find. Then you can use a dense thick woolen insole for the striker.
To attach the striker to the handle, I cut a 20-mm groove in the shell the width of the striker, and at the end of the rod I ground a flat and drilled two diametrical holes perpendicular to it in the rod and the shell. Through these holes, the striker was sewn to the handle with harsh threads.
Having tested the weapon in action, I was convinced that it strikes insects (both flies and mosquitoes) on the spot and without traces - even on smooth glass, and without excessive noise-pop, characteristic of an ordinary fly swatter with a rubber or plastic "warhead".
Author: A.Matvejchuk
 We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
We recommend interesting articles Section Builder, home master:
▪ garden furniture
▪ To keep the bubble from falling
▪ How to heat the house with an ordinary kettle
 See other articles Section Builder, home master.
See other articles Section Builder, home master.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Nerve cells still regenerate
13.10.2018
The study of neurogenesis (the formation of new nerve cells - neurons) is a relatively new area of research. In recent years, scientists have proven that new neurons are formed throughout life in the brain of many mammals, but there is still no consensus in the scientific community on the issue of human neurogenesis.
New imaging techniques (such as confocal microscopy) have shown that, at least before puberty, new neurons form in the human hippocampus, a region of the brain involved in the formation of emotions and memory. But data on neurogenesis in adults is conflicting; More recently, a study was published stating that the formation of new cells in the adult brain does not occur, but scientists have proven the opposite. The new data could help develop drugs for neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's, scientists say.
Maura Boldrini, a neuroscientist at Columbia University, and her colleagues took tissue samples from the hippocampus of 28 healthy people who had died no more than a few hours before. The age of these people at the time of death ranged from 14 to 79 years. Scientists have established the rate at which new blood cells and neurons of the dentate fascia of the hippocampus, the part of the brain where neurogenesis occurs, were formed in the body of the deceased during life.
Boldrini and her colleagues found that the number of "mother" cells decreases with age, while "daughter" cells do not. Scientists found thousands of young, incompletely formed neurons in the dentate gyrus in all samples, regardless of the age of the people from whom the samples were taken. However, the older the person, the less cells in the dentate fascia that produce substances that are associated with the ability of the brain to rebuild existing neural connections and form new ones (neuroplasticity). "New neurons that appear in adulthood may form fewer connections with each other and other neurons, or migrate to other parts of the brain less frequently," the scientists conclude.
The loss of neuroplasticity may explain the emotional vulnerability that some people experience in adulthood, but new brain cells, including neurons, are still able to withstand the decline in cognitive skills, the authors of the new work say. Now scientists plan to find out at what rate young neurons are formed in people suffering from Alzheimer's disease and emotional problems.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Silver ink for printing conductors on flexible surfaces
▪ Strength sports are not suitable for children
▪ Visible and infrared image sensors in one chip
▪ Elastic Stopwatch
▪ Technique is controlled by thoughts
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ site section Infrared technology. Article selection
▪ article Cry (cry) in a vest. Popular expression
▪ article The wife of which Roman emperor kept a brothel and worked there herself as a prostitute? Detailed answer
▪ article Insulator. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article USB Module Ke-USB24A. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ Article Orange or Apple? Focus secret. Focus Secret
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 