
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Pedalless wah prefix. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
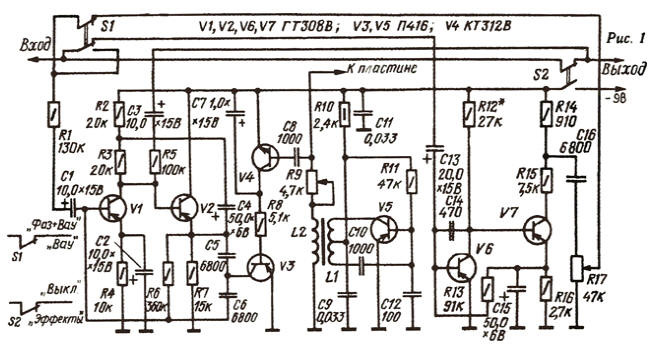
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Audio equipment "Electronic music", which came into fashion several decades ago, raised a wave of designing home-made set-top boxes to implement a variety of musical effects - "wow-wow", "phases", "leslie", etc. Descriptions of many options for amateur set-top boxes at one time were published in Radio magazine. Today's publication (it was placed in "Radio", 1977, No. 10, pp. 58, 59) we want to remind readers of one of these designs - pedalless "wow" prefix. The sound control for such consoles is usually a pedal mechanism with a foot platform. When a musician, while playing an instrument, presses his foot on the pedal platform, he rotates the variable resistor engine, while the prefix generates a control signal that affects the character of the instrument's sound accordingly. The “wow” prefix described in the article does not have a pedal as such. It is replaced by a metal plate lying on the floor, and the performer swings his leg over the plate, simulating pressing the pedal. The original operating principle used in the set-top box can be used in a number of other devices. In "wow" prefixes with pedal control, variable resistors or photoelectronic devices are usually used as a regulating element. The former have a short service life, while the latter are more difficult to manufacture and less reliable and economical due to the presence of an incandescent lamp, since in most cases the set-top boxes are powered by built-in batteries. Therefore, when developing the described design of the "wow" set-top box, the task was to increase the reliability of the device, simplify its control, and facilitate its manufacture. In this prefix, the regulating element is a capacitor, which is formed by a metal plate and the foot (or palm) of the performer. By changing the distance between the "plates" of the capacitor, its capacitance is changed, which leads to a change in the control voltage on the actuator - the transistor. Such control can also be used in other equipment where high reliability of the control element is required. In addition, the described prefix also contains a spectrum converter that implements the "phase" effect. The spectrum converter is assembled according to the amplifier-limiter circuit. The pedalless adapter (see the diagram in Fig. 1) is designed to be connected to an electric guitar with an electromagnetic pickup. "Wow" device provides a frequency tuning interval of 300...4000 Hz. The consumed current is about 5 mA.
The operation of the proposed "wow" attachment is based on the dependence of the collector-emitter resistance of the transistor on the bias voltage at its base. The high-frequency voltage from the generator on the transistor V5 is supplied to the base of the transistor V4 through a resistive-capacitive voltage divider, consisting of a variable capacitance plate-foot of the performer's foot. When the capacitance of this capacitor changes, the amplitude of the high-frequency signal based on transistor V4 changes. It opens, and the resistance of its collector-emitter section decreases, which causes an increase in the negative voltage at the base of transistor V3. This leads to a corresponding change in the collector-emitter resistance of transistor V3, and since it is part of an active RC bandpass filter, its frequency response also changes. The filter is assembled on transistors V1 and V2. Capacitor C7 prevents the RF signal from leaking into the active RC filter. The active filter has no features. Transistors V1 and V2 are selected with a low noise level and a large static current transfer coefficient, and the voltage at the collector of transistor V1 is selected small. Variable resistor R9 adjust the "wow" prefix just before the game. This adjustment is necessary to compensate for the capacitance between the floor and the plate, as well as differences in the sole thickness of the performer's shoes, and other factors. A feature of the operation of the described pedalless "wow" prefix is that, unlike pedal ones, it raises the highest sound frequency components when the performer's foot is in the upper position above the plate (at a distance of 3 ... 4 cm), and the lower ones - when the foot lies on plate (most pedal attachments work just the opposite). Both devices provide a linear characteristic if the foot is removed from the "pedal" (from the plate). This feature of a pedalless prefix, however, does not make it difficult to use: after the first rehearsal, the performer, as a rule, easily masters the technique of working with the prefix. The spectrum converter is assembled on transistors V6 and V7. Capacitor C14 in the feedback circuit serves to reduce the sensitivity of the device to high-frequency pickups. The output signal of the spectrum converter is taken from the divider R14R15C16R17 in the collector circuit of transistor V7. The use of an output voltage divider with appropriately selected element ratings reduces the tendency of the set-top box to self-excite due to the acoustic coupling between the loudspeakers of the final amplifier and the EMI pickups. Switches E1 and S2 select one or another mode of operation of the set-top box. When the power supply (S2) of the set-top box is turned off, its input is directly connected to the output. In the lower position of the contacts of switch S1, only the “wow” device works, and in the upper one, the attachment can ensure either the joint operation of both devices, or the “phase” device separately (in the latter case, the foot is removed from the plate). The prefix is powered by the built-in battery "Krona".
The prefix is mounted in a metal case with external dimensions of 110x90x30 mm (Fig. 2). The input and output of the attachment are made in the form of unified connectors SG-3, installed on one of the side walls of the case. A single-pole socket is provided for connecting the wah-device plate. The generator coils are wound on a K10x6x2 ring made of F600 ferrite. Coil L1 contains 8 turns (with a tap from the middle) of PELSHO 0,38 wire, and L2 - 26 turns of PELSHO 0,22 wire. Coil L2 is wound first. The variable resistor R9 must be non-wire, otherwise its own inductance will disrupt the "wow" device. Transistors GT308V can be replaced by P27A, P28, P416B, and KT312V - by KT315 with any letter index. The wow plate is made of one-sided foil-coated fiberglass. Its dimensions are 95x70x2 mm. A flexible unshielded conductor 1,5 ... 2,5 m long is soldered to the foil, ending in a single-pole plug. A sheet rubber plate 3-5 mm thick is glued over the foil. It is most convenient to set up a "wow" prefix using an oscilloscope. It is connected in parallel with the L2 coil and the waveform is observed - it must be sinusoidal. In this case, the base of the transistor V4 must be disconnected from the capacitor C8. The plate is also turned off. Signal amplitude - 3...5 V, frequency - about 3 MHz. If the amplitude is outside the specified limits, it is necessary to select the number of turns of the coil L2. Then the base circuit of the transistor V4 is restored, the switch S1 is set to the "Bay" position and the plate is connected. An audio signal with a frequency of 4 kHz and an amplitude of 100 mV is applied to the input, and the oscilloscope is connected to the output of the set-top box. The slider of the resistor R9 is set to the position corresponding to the maximum output voltage. The palm is brought closer to the control plate, while the amplitude should, gradually decreasing, reach a minimum when there is a gap of 3 ... 4 cm between the palm and the plate. generator. The establishment of the spectrum converter is reduced to the selection of the resistor R12 in such a way that the signal clipping is symmetrical and starts at its minimum amplitude at the input. To do this, a signal with a frequency of 13 kHz is fed to the input of the spectrum converter (to the upper, according to the scheme, plate of the capacitor C1). Sometimes you have to clarify the resistance of the resistor R13. It should be noted that the reason for the appearance of an unpleasant tone of sound is most likely a noticeable asymmetry in signal clipping. Author: A. Elez, Rovno
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Computer mouse will prevent stress ▪ Biometric authentication for PC ▪ Logitech G CLOUD Gaming Handheld Console
▪ section of the site Application of microcircuits. Article selection ▪ article Tidy up your planet every morning. Popular expression ▪ How is mass distributed in the solar system? Detailed answer ▪ article Gobi Desert. Nature miracle ▪ article Antennas HF. Directory ▪ article That's the vase! Focus secret. Focus secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: