
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Acoustic short circuit in a loudspeaker and its overcoming. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Speakers Is it possible to have a different acoustic design of the loudspeaker besides the now widely used phase inverter or closed box, as well as more expensive variants of horn and labyrinth loudspeakers? This article describes a method for broadening the bandwidth of effectively reproduced low frequencies in open-type enclosures and provides practical loudspeaker designs. In a loudspeaker, when the cone of an electrodynamic head cone oscillates, its front and rear surfaces set the air in motion, creating alternately its compression and rarefaction. Thus, when the pressure increases on one side of the diffuser, on the other hand, on the contrary, it decreases. At low frequencies, if the dynamic head has no acoustic design (in free space), due to the diffraction of sound waves, an acoustic short circuit occurs and the resulting sound pressure in the surrounding space is greatly weakened. To eliminate this harmful phenomenon, the dynamic head is placed in an acoustic screen, which eliminates the compensating effect of antiphase compression-discharge oscillations. The main designs of such screens and their features are described in [1-3]. Let us briefly recall these well-known variants. A shield whose dimensions must be sufficiently large and at least commensurate with the acoustic wavelength at the lowest reproducible frequency. At lower frequencies (tens of hertz), the dimensions of the shield are large - several meters, which is unacceptable for practical designs. A box with an open back wall is a "folded" shield. Such an acoustic design of the loudspeaker was widely used in the 30-60s of the last century, when the requirements for the band of reproducible sound vibrations were small. A box with a labyrinth, the length of which is equal to half the wavelength at low frequencies [1], is unreasonably complex in design and manufacturing technology and, therefore, is practically not common. A horn, which is a divergent waveguide, is also used to increase sound output. At low frequencies, the dimensions of the horn are too large. Closed box, usually filled with sound-absorbing material to prevent standing and other waves. In this case, the acoustic energy emitted by the rear surface of the diffuser is dissipated inside the box. A closed box with a phase inverter is now one of the most popular types of acoustic design, proposed back in 1930. A phase inverter is a pipe or hole made in a box. The phase inverter operates in a very narrow frequency band, and with a sufficiently wide range of low-frequency signals, transient processes are delayed in the form of "coloring" the sounds of the bass register. As a result, musical instruments of different timbres sound very similar, i.e., the phase inverter actually distorts the real sound. As in the previous version, about half of the acoustic power is lost in the box. The absence of other effective acoustic design forces the developers of acoustic systems (AS) to use this technical solution [2, 3]. Overcoming the acoustic short circuit in the speaker while creating a simple and energy-efficient acoustic design of loudspeakers, operating in a wide band of sound frequencies with virtually no sound loss, is currently an important and unresolved problem [2, 4]. The technical solutions described in the article, which exclude acoustic short circuits, make it possible to use the sounded room to increase the efficiency of the AU at low frequencies. At the same time, the requirements for the design of acoustic design are reduced due to the exclusion of standing waves in the box, since the sound energy of the back radiation of the head leaves the box into space, voicing it. In these designs, the influence of the elasticity of the air limited by the volume of the box is reduced or completely disappears, and the increase in the resonant frequency of the loudspeaker. Sound energy in solid materials propagates in the form of a stream, and the propagation orthogonal with respect to the radiation axis is much smaller (up to -30 dB) than along the radiation axis [5]. In the air environment, the principles of vector addition of vibrational velocity also operate, regardless of the frequency and phase of the summed streams of sound vibrations. It is also known from the theory of oscillations [6] that two harmonic oscillations having the same frequency and an arbitrary phase between themselves and propagating mutually perpendicularly do not interact with each other. In the near zone of the emitters, the ratios of the vibrational velocity and propagation velocity, as well as the wavelength a and the diameter of the emitter d (radiation holes), turn out to be important. Separation of the sound streams of direct and reverse radiation of the head and their conversion into streams orthogonal relative to each other makes it possible to eliminate the acoustic short circuit of the emitter. By constructive measures - with the help of a "waveguide" - it is possible to turn the sound flow created by the rear surface of the loudspeaker diffuser by 90 degrees, as shown in Fig. 1 (vector B). In the vicinity of the point O, the oscillatory velocities of the tangential flow from the waveguide and the flow of the frontal radiation of the head (vector A) are added. If the flows and vibrational velocities are equal, when calculating the resultant R, we obtain a total acoustic pressure 1,41 times greater than each of the components.
Thus, in the space near the emitter, the acoustic pressure p increases by 3 dB. The acoustic power given off by the speakers in the room [7] will double, therefore, to obtain the same sound power for such a speaker, an UMZCH of half the power will be required: Ra = p2V/Tc 10-5, W (at Rr = 3 m), where V is the volume of the room; Тс - average time of optimal reverberation; Rr - boom radius. As can be seen from the formula, the value of the acoustic power Ra noticeably increases if the well-known design solutions for the acoustic design of the speakers are abandoned. Given the effect of the sound absorbing material that is typically stuffed into the closed box of a loudspeaker to absorb the energy radiated from the back of the cone, the real benefit can be even greater. Following the stated principle of acoustic short circuit exclusion, the author developed acoustic design constructions, one of the variants of which is shown in Fig. 2.
In a case with a blank back wall 1, the lower part of the front panel 2 ("broken deck") is inclined at an angle to the vertical, forming with the upper part of the front panel a "waveguide" for sound waves generated from the back of the loudspeaker head. When calculating the design, it is important to fulfill the condition that the cross-sectional area of the waveguide, through which the sound flux from the box propagates, is not less than the area of the rear surface of the diffuser. Otherwise, the reproduction of the lowest frequencies will be weakened due to the residual elasticity of the air in the box. The measurements carried out in the anechoic chamber of the Acoustic Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences confirmed the considered assumptions, which allows us to make the recommendations presented in this article. The sound coming out of the waveguide is depleted in the high frequency region, and it sounds more velvety to the ear than the sound of the frontal stream. This does not at all impair the musicality of the sound due to a different direction of the expanded flow: the room also participates in the formation of the sound image, making it voluminous. Even if the room contains a lot of sound absorbers, such as carpets and upholstered furniture, the naturalness of the sound and its spaciousness are not lost. On the basis of the proposed method, the author developed and manufactured a stereo speaker system "Tsunami". Each of the loudspeakers of the system uses a low-frequency 15-inch head L-3712 (from Germany), which has a maximum power of 100 W, and two high-frequency heads 6GDV-4. The sound range is divided into two bands - 20...5000 Hz and 5000...25000 Hz. The measured efficiency in the LF mode was found to be 110 dB/VBt-m with excellent sound reproduction quality. With the help of this speaker, with an average electrical power of 5 W, a hall with 600 people was sounded for each channel. The results of experimental studies of samples of loudspeakers and acoustic systems were presented by the author in a report at the Nizhny Novgorod Acoustic Session [7]. On fig. 3 shows another loudspeaker design and a vector diagram of the propagation of sound streams A, B and R.
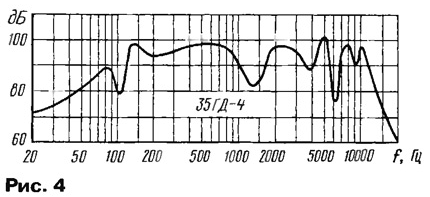
Sound stream A is frontal, stream B is rear. The vector R is the resultant of the addition of the vectors A and B. In this figure, the following designations of the elements: 1 - sound head; 2 - body; 3 - waveguide for the output of sound energy of the rear radiation; 4 - output hole of the waveguide; 5 - waveguide wall; 6 - front wall of the waveguide. Such a loudspeaker provides a more diffuse distribution of sound in space. High-frequency heads are also installed on the front wall of the loudspeaker. Analysis of the vector diagrams shown in fig. 1 and 3 shows that the proposed method for eliminating acoustic closure between streams A and B makes it possible to overcome this harmful phenomenon in sound systems with a simultaneous energy and quality gain. Experimental work was carried out with 4A-32 heads in a large closed room using a GZ-33 sound generator, a VZ-33 voltmeter, a 43-32 frequency meter, and a 00017 precision noise meter with an MKD-type condenser microphone. To obtain comparative parameters, a conventional speaker with a 4A-32 head was also investigated; a serial loudspeaker 35GD-4 in a closed case was taken as a prototype. Its measured frequency response is shown in fig. 4.
In the frequency range 80 ... 12000 Hz, the average characteristic sensitivity is about 94 dB / VBt-m with unevenness up to 26 dB. Sound-absorbing material is placed in the case. The sound of this speaker is not of high quality. On fig. Figure 5a shows the results of measuring the frequency response of the Tsunami loudspeaker (its design is similar to that shown in Fig. 1) with the same 4A-32 head. The average efficiency of the front radiation increased to 98 dB/VBt-m in the frequency range 40...20000 Hz, the frequency response unevenness decreased to 9 dB, the reproducible frequency band expanded. The gain in electro-acoustic efficiency of the prototype and AS "Tsunami" turned out to be 6,4 times!
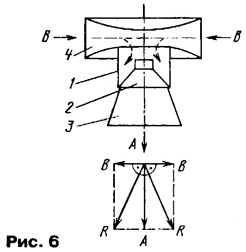
On fig. 5,6 shows the frequency response of the loudspeaker along vector B, from which it follows that the radiated frequency band is 50..J6000 Hz with an efficiency of 96 dB / W-m and unevenness in the band of 12 dB. In AS 35GD-4 and similar ones, the energy of the rear radiation of the head is converted into heat. AS made by the author by analogy with the design in fig. 2 using housings from tube TVs "Rubin", "Electron" and others showed excellent results. Heads 4A-32, 6GD-2, etc. were used, capable of reproducing low frequencies well. The author did not use heads with a heavy moving system due to their low efficiency and insufficiently wide operating frequency band. The manufacture of the proposed speakers, devoid of acoustic short circuit, is available at home and is of interest when disposing of obsolete equipment. The proposed method for eliminating acoustic short circuits in a loudspeaker makes it possible to significantly improve horn loudspeakers as well. On fig. 6 shows a simplified design of a horn loudspeaker 1, made on the basis of a conventional (diffuser) electrodynamic head 2. Direct sound emission occurs through the horn 3, and the return radiation from the head through a symmetrical waveguide 4. A vector diagram of the sound radiation fluxes in the horizontal plane is given in the same place.
The AS designs presented in the article, built on the basis of the stated provisions, are only a small part of the possible variety of options. Literature
Author: V. Nosov, Moscow
Artificial leather for touch emulation
15.04.2024 Petgugu Global cat litter
15.04.2024 The attractiveness of caring men
14.04.2024
▪ Dell Latitude 13 Education Series Laptops ▪ Cafe visitors are served by robots ▪ NearLink wireless technology ▪ New router for communication networks DS33Z41
▪ section of the website job descriptions. Article selection ▪ article To be either Caesar or nothing. Popular expression ▪ article Countries, peoples, languages. Big encyclopedia for children and adults ▪ article Features of the regulation of women's labor ▪ article Intercom. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering ▪ article Wax crayon. Focus Secret
Comments on the article: Eugene There is and was about forty years ago a simpler solution without "philosophizing from the evil one. Used to set up the first column: ZG, oscilloscope, ML. 19, ears of musicians. And the possibility of altering the volume of the column. the optimal bass response was also found. The so-called "spectacular" heads were used, located on the side walls of the cinema hall. They were equipped with large-format cinemas. They were ordered from the factory. And the solution was very simple. Swing the speaker cones without air resistance from behind. A rear hole was made in the speaker box, the area of \u1540b\u15bwhich was selected according to the characteristic, according to the "curve", naturally. Then this product could be repeated. The owners of the speakers still have it, which were then made. And, note. For playback, amplifiers assembled according to scheme of the Hungarian control acoustic units. mounting systems in radio centers. Decent recording studios. Tube amplifiers. Lamps for output stages of the type - 150. It was difficult to get. But these tetrodes are durable and if you do not overload them with anode voltage, they can work for a very long time. The amplifier circuit for the control unit is very good. The average output is 6 watts. I don’t remember the measurements now. But this power is quite acceptable for a room of 5 cubic meters. With three stripes. HF. MF and LF I have already forgotten the characteristics, but the frequency of the amplifier with a normal output was very wide. Overtones were not cut off. With conventional speakers, filters were used that cut off high frequencies and mids. This was a slightly worse solution. However...! By the way! Absolutely unique sound, reproduction of AF by an amplifier on double triodes of the 6H7-, 17H-XNUMX type. transformerless circuit. It was made for eight-hundred-ohm speakers manufactured by RRR, Latvia. Unfortunately, the second one failed. Hands did not reach. And in stereo they would be very good. But you can do it on autotrans. Peak output up to XNUMX watts. In vain are forgotten panel emitters. Produced here, in the USSR. It was a very good reproduction. Even MOTOROLLA tried to copy them from us. Yes, something went wrong. Although they, the striped ones, had excellent playback units. For a small room and a decent speaker, amplifiers based on double powerful triodes were quite ... One such amplifier also still works. At that time, we, who experimented with high quality sound reproduction, were considered eccentrics. Plays and plays. Sings and sings. Then suddenly realized the high quality of the sound! Former exhibitor and diploma winner of the XNUMXth radio exhibition.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese




 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: