Chokeless voltage converter, 10-15/15-27 volts 3,5 amps. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The circuit of a chokeless pulse voltage converter is shown in fig. 4.69.
The circuit provides a voltage conversion of 12 V, a voltage of 15 ... 27 V at a load current of up to 3 ... 3,5 A. The oscillograms shown in fig. 4.70, explain the operation of the converter. The generator on DD1.1, DD1.2 forms a meander with a frequency of about 20 kHz. If the key transistors VT1, VT2 were opened by anti-phase signals from the outputs of the trigger DD2, a through current would flow through the transistors at the moment of switching, and a short circuit of the power source would occur. To eliminate this phenomenon, negative polarity pulses (see Fig. 4.70) are formed so that transient processes in transistors occur alternately and do not coincide in time.
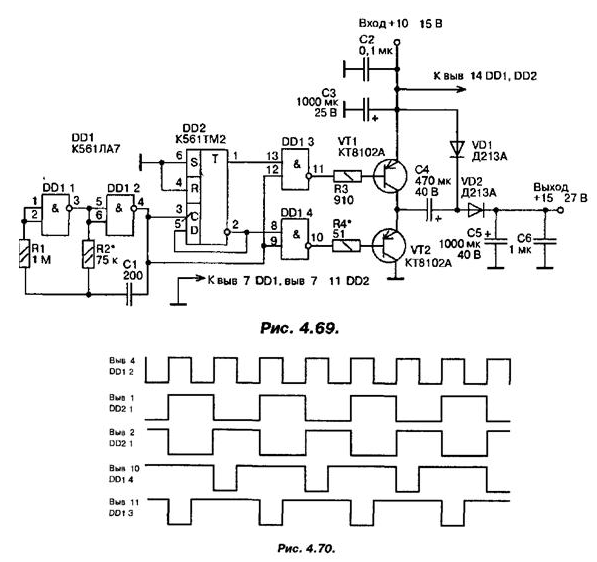
At the moment of opening VT2, C4 is charged through the diode VD1 to the supply voltage. After VT1 opens, C4 will be connected in series with the power circuit. In this case, VD1 will prevent C4 from interacting with the power supply in a parallel circuit, and C5 will be charged through the VD2 diode by the power supply voltage added to the voltage on the charged capacitance C4. The output voltage of the converter depends to some extent on the input voltage and load current.
The operability of the circuit is maintained when the supply voltage is reduced to +5...6 V (after doubling this voltage becomes equal to +10...+ 12 V, which allows the converter to be used also to power twelve-volt equipment from small-sized batteries).
Author: Semyan A.P.
 See other articles Section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters.
See other articles Section Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive History of African Dust
31.07.2021
The research group, headed by an honorary professor of the School of Marine and Atmospheric Sciences. Rosenstiel at the University of Miami (UM) by Joseph Prospero, chronicles the transport of African dust, including three independent "first" discoveries of African dust in the Caribbean in the 1950s and 1960s.
Each year, mineral-rich dust from the Sahara desert in North Africa is lifted into the atmosphere by winds and carried on a 5000-mile journey across the North Atlantic to the Americas. African dust contains iron, phosphorus and other important nutrients that are essential for life in marine and terrestrial ecosystems, including the Amazon basin. Wind-blown mineral dust also plays an important role in climate by modulating solar radiation and cloud properties.
The researchers also discuss the discovery in the 1970s and 1980s of a link between dust transport and the African climate after increased dust transport to the Caribbean due to the onset of severe drought in the Sahel. Much of today's dust research is focused on North Africa, as it is the largest and most persistent source of dust on Earth.
Today, Prospero, nicknamed the "Father of Dust," uses a system of ground stations and satellites to study the effect of global transport from the Sahara on atmospheric composition over the Caribbean Sea.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Glass recognizes the image
▪ 5" plastic-based flexible AMOLED display
▪ From rhubarb - not only compote
▪ The ozone hole must disappear
▪ Eco-friendly thorium nuclear reactor
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Electricity for beginners. Article selection
▪ article Politics from a position of strength. Popular expression
▪ article Do other planets have their own satellites? Detailed answer
▪ Electrician article. Job description
▪ article Microcontroller security device. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Active splitter of TV signals. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: