
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Power supply with electronic voltmeter, 220 / 0,3-30 volts 1 ampere. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
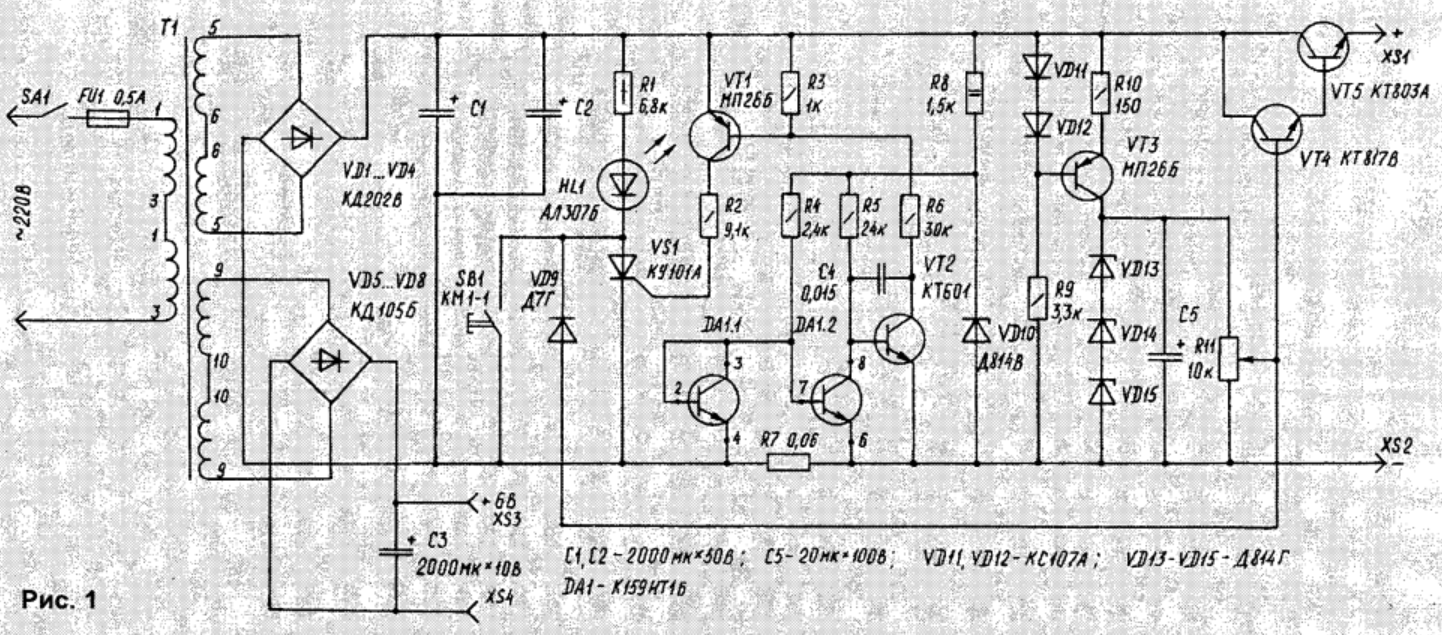
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies There is no need to prove that the mains power supply is the main unit in a radio amateur's home laboratory. The network power supply, the diagram of which is shown in Fig. 1, I believe, will satisfy the needs of many. The unit provides a stabilized output voltage, adjustable from 0,3 to 30 V at a load current of up to 1 A. The voltage stabilization factor is 30. The unit is equipped with effective electronic overload protection with overload indication. In addition, the stabilizer is equipped with an electronic output voltage voltmeter with voltage indication on seven-segment LED displays. Those who have worked with B5-43A or B5-44A power supplies know how convenient it is in practice. Let us dwell on the electrical circuit in more detail. The mains voltage, reduced by the transformer T1, is rectified by diodes VD1 ... VD4, connected in a bridge circuit. Capacitors C1. C2 smooth out the ripple of the rectified voltage. DC voltage is supplied to the input of a parametric stabilizer formed by transistors VT4.VT5 and zener diodes VD13...VD15. The voltage level at the output of the block is set by a variable resistor R11. To increase the stability of the output voltage during fluctuations in the mains voltage, the zener diodes are powered from a stable current source made on the transistor VT3, stabistors VD11, VD12 and resistors R9, R10. It is especially necessary to dwell on the device for protecting the power supply from overload. To trigger the protection of stabilizers, the fact is often used that the silicon transistor opens when the voltage between the base and the emitter exceeds 0,6 ... 0,65 V. In thyristor protection circuits, the thyristor is switched on when the voltage between the cathode and the control electrode exceeds 1.0 V [1, 2]. The main disadvantage of such circuits is the high voltage required to turn on the protection. For thyristor circuits, in addition, it is necessary to select a resistor for a specific type of thyristor. The indicated shortcomings are deprived of the scheme. considered in [3], which is taken as a basis. The protection device is made on the transistor assembly DA1.1, DA1.2, VT1, VT2, VS1, VD9. The threshold voltage for switching on the protection is the voltage drop across the resistor R7 from the flowing current. With the ratio R4/R5 = 1/10, the protection threshold is 60 mV. Unlike traditional circuits, the considered protection circuit has a pronounced thermal stability effect, since the resistor R7 is made of copper wire, and the power dissipation on the resistor is small. If a current less than the limit flows through the current sensor (R7), the voltage drop across it is less than 60 mV, and the DA1.2 assembly transistor is in saturation, the transistors VT1, VT2 are closed. No voltage is applied to the control electrode of the thyristor VS1. As soon as the current exceeds 1 A, the voltage drop across R7 becomes 60 mV, the transistor DA1.2 starts to close, and VT1, VT2 open. This turns on the thyristor VS1 and the LED HL1 lights up, indicating an overload. At the same time, the base VT4 through the diode VD9 and the thyristor VS1 is connected to the power source. Transistors VT4. VT5 are closed, and the voltage at the output of the stabilizer drops to 0,3 ... 0,5 V (depending on the position of the resistor R11 slider). After eliminating the cause of the overload, it is enough to briefly press the SB1 button to restore the power supply mode without disconnecting it from the network. This scheme provides protection against false positives. This is achieved by using the Miller effect in the cascade on the transistor VT2 using capacitor C4. The transistor assembly DA1 is powered by a parametric stabilizer on a VD10 zener diode. It should be noted that long-term operation of the power supply at an output voltage close to zero and maximum current is not recommended, since in this case the maximum power is dissipated on the VT5 transistor. In this case, its thermal breakdown is possible. Establishing a power source is reduced to setting the voltage at the cathode of the Zener diode VD13 not higher than 32 V. This is ensured by the selection of Zener diodes VD13 ... VD15 from the D814V, D814G series. The design used resistors of the type MYAT; electrolytic capacitors C1, C2 - type K50-20. C3 - type K50-6, capacitor C4 - any ceramic. Transistor VT5 can be replaced with KT819VM, VT2, VT3 - with transistors of the appropriate structure with a permissible collector-emitter voltage of at least 60 V. Thyristor VS1 can be replaced with any of this series. Toggle switch SA1 - type TP1-2. Resistance R7 is made from a piece of copper winding wire PEV-1 with a diameter of 0,31 mm and a length of 20 cm. The power transformer is of the TS 40-2 type. Transistor VT5 must be installed on a radiator with an area of 100 cm2. The electronic voltmeter is made on the basis of the microcircuit of the analog-to-digital converter KR572PV2 (Fig. 2). This chip works on the principle of double integration. It includes a clock generator. Its frequency is set by the elements C7, R9, and is chosen equal to 50 kHz. A voltage of 0 V is applied to the input of the reference voltage "+ u7bR" from the voltage divider R6, R4, R1 connected to a parametric stabilizer on two series-connected stabistors. The current through them is set by a stable current generator on a field-effect transistor VT1. The seven-segment indicator HG2 uses a comma. In this case, the maximum displayed voltage is 99,9 V. In order not to damage the microcircuit at such a high voltage, the measured voltage is applied to its input through the voltage divider R3. R2, R1 with division ratio 1:100. Establishing a voltmeter comes down to accurately setting the reference voltage using resistor R7 and setting the oscillator frequency using C7 or R9 with an accuracy of 1%. At the end of the adjustment process, it is necessary to apply voltage and to the input of the voltmeter. controlling it with an exemplary voltmeter, by selecting R3 to achieve the same readings of an electronic voltmeter with an exemplary one. Deviation of ratings R8, C3, C4, C6 from those specified in the diagram - no more than 5%. Resistors - type MYAT, S2-29; tuning resistor - type SP5-16VA; capacitors - type KM-3, KM-4, KM-5. To power an electronic voltmeter, a stabilized bipolar voltage of ±5 V is required. Therefore, a separate secondary winding of the transformer T1 (9-10) is used, to which a voltage converter is connected. The converter circuit with output voltage stabilization (Fig. 3) is borrowed from [4]. The changes affected only the key transistors. The converter is powered by a parametric stabilizer on VT1. The adjustment of the converter is reduced to the selection of R4 until a voltage of +5 V is obtained at the output. The circuit uses MNT-type resistors; ceramic capacitors such as KM-3, KM-4, KM-5; electrolytic - type K50-35. Transformer T1 is wound on a ferrite ring M1500NN1 K16x10x4,5. The primary winding contains 200 turns, and the secondary - 100 + 100 turns of PEV-1 wire with a diameter of 0,15. Inductors L1, L2 - type DM-0,2, 10 mH each. Literature:
Author: O. Belousov
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Sunswift 7 high-speed electric car ▪ Intel Core i9-10900K processor for gaming systems ▪ Huawei's first commercial 5G 3GPP chipset
▪ site section Infrared technology. Article selection ▪ article Scattered from Basseinaya Street. Popular expression ▪ article In what country was the national sign language invented by deaf children? Detailed answer ▪ Swiss article. Job description ▪ article Rectifier for three voltages. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: