
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Pulse diagnostics of batteries. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Chargers, batteries, galvanic cells During long-term storage and improper operation, large insoluble crystals of lead sulfate appear on the battery plates. Most modern chargers are made according to a simple scheme, which includes a transformer and a rectifier. Their use is designed to remove the working sulfitation from the surface of the battery plates, but they are not able to remove the old coarse-grained sulfitation. Lead sulfate crystals have high resistance, which prevents the passage of charging and discharging current. The voltage on the battery rises during charging, the charge current drops, and the abundant release of a mixture of oxygen and hydrogen can lead to an explosion. The developed pulse chargers [1-3] are capable of converting lead sulfate into amorphous lead during charging, followed by its deposition on the surface of plates cleaned from crystallization. Before charging and restoring the battery, it is necessary to diagnose its technical condition, first of all, to determine the internal resistance (degree of sulfitation). The simplest diagnostic device is a load plug, consisting of a low-resistance discharge resistor and a voltmeter. The discharge current, passing through the resistor, reduces the voltage on the battery. From the open-circuit voltage E and the load voltage U. knowing the discharge current Iр, determine the internal resistance of the battery RBH: Rvn=(EU)/Ir The complexity of diagnosing a battery is that additional devices and arithmetic calculations are required. Branded diagnostic devices with automatic detection of battery parameters (voltage under load, internal resistance, capacitance) are large due to the use of powerful discharge resistance and a relay circuit for connecting the load. The proposed electronic device allows you to make a direct reading of the internal resistance of the battery with the determination of the degree of sulfitation of the plates. Diagnostics of a battery with a pulsed discharge current makes it possible to reduce the dimensions of the device (almost by an order of magnitude), facilitate the thermal regime of discharge circuits, and speed up diagnostics from minutes to seconds. The rectangular shape of the discharge current is closest in shape to the starting current of car starter devices. The device does not have mains power, which allows you to measure the degree of battery sulfitation directly on the car. The electronic circuit of the device (Fig. 1) includes:
Device Features
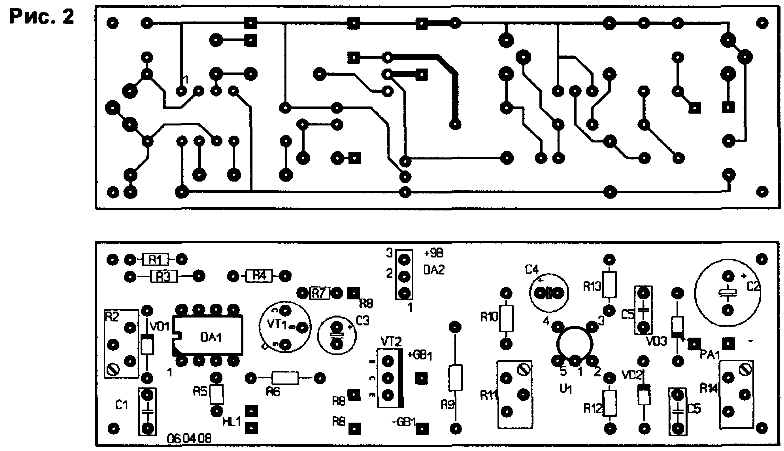
The generator operation mode is stabilized by negative feedback from the load of the key amplifier to the input 5 of the timer and by the external temperature compensation circuit with sensor R1. The power supply of the device is stabilized by an electronic stabilizer DA2. The generator of rectangular pulses on the DA1 timer allows, with a minimum number of additional radio components, to form rectangular pulses with a frequency and duty cycle that vary over a wide range. The microcircuit includes two comparators, the inputs of which are connected to pins 6 and 2 of DA1. with switching levels 2/3 Up and 1/3 Up respectively. The internal timer trigger allows you to change the state of the output (pin 3) DA1 depending on the voltage level on the charging capacitor C1. When power is applied, the capacitor C1 is charged to the level of 2/3 Up for a time depending on the ratings of R1 and C1. When this voltage is reached, the internal trigger switches, a low level appears at output 3, and the internal discharge transistor connected to pin 7 of DA1 turns on. Capacitor C1 is discharged through resistors R2 and R3, upon reaching a level of 1/3 Up, the trigger switches again, a high level appears at output 3, the internal transistor closes, and C1 begins to re-charge, i.e. the cycle is repeated. Resistor R2 sets the discharge time of capacitor C1. With an increase in resistance R2, the discharge time increases, and the power at the load R9 decreases. A thermistor R1 is installed in the charging circuit of capacitor C1. which at low temperature increases the charge time C1 and the duration of the current pulse in the discharge circuit of the battery. The frequency of the generator decreases, which leads to an increase in the voltage on the microammeter PA1. From output 3 DA1, rectangular pulses through the limiting resistor R6 are fed to the base of the power amplifier on the transistor VT2. The transistor VT2, opened by the next pulse, discharges the battery GB1 for a short time to the resistor R9. Input 5 DA1 is used to stabilize the discharge current of the load. When the voltage at the load R9 increases, it enters the base of the transistor VT8 through the setting resistor R7 and the limiting resistor R1. Reducing the voltage at input 5 DA1 with the open transistor VT1 allows you to automatically increase the frequency of the output pulses of the timer, which leads to a decrease in the voltage at the load. Thus, the current is stabilized. Capacitor C3 eliminates impulse noise based on VT1, resistor R4 limits the short circuit current at input 5 DA1 when VT1 is open. The pulse voltage from the battery GB1 through the resistor R10 and the coupling capacitor C4 is fed to the input of the amplifier on the optocoupler (optocoupler) VU1. Resistor R11 sets the DC amplification mode of the optocoupler. The load of the optoamplifier is the resistor R13, the signal from which, through the coupling capacitor C5, is fed to the rectifier with a doubling of the voltage on the diodes VD2, VD3. After straightening, it affects the readings of the PA1 microammeter. Resistor R14 sets the maximum readings of the device PA1. During working sulfitation, the internal resistance of the battery does not exceed the passport value, and the impulse voltage at the battery terminals is insignificant in amplitude. With coarse-grained sulfitation, when the internal resistance of the battery exceeds the operating resistance by tens of times. discharge current pulses create voltage pulses at the battery terminals, the amplitude of which depends linearly on the degree of sulfitation. With an increase in the amplitude of the pulses, the deviation of the microammeter needle increases, indicating an increase in sulfitation, a decrease in the battery capacity and its starting current. The readings of the microammeter correspond to the maximum sulfitation in percent. The main elements of the device are placed on a single-sided printed circuit board measuring 102x31 mm. the drawing of which is shown in Fig.2. The device is made in the BP-1 case. Regulator R8 (type Ab) and microammeter RA1 are installed on the front panel of the device.
Based on the value of the voltage under load, the resistor R14 sets the corresponding value of sulfitation as a percentage on the scale of the device RA1 with the middle position of the sliders of the resistors R2, R8 and R11. The readings of the device are corrected by the resistor R11 in accordance with the data given in the table.
The middle position of the resistor R8 slider (battery type) approximately corresponds to a battery capacity of 60 Ah. lower - 120 Ah, upper - 12 Ah. A possible discrepancy between the type of battery and the position of the R8 engine due to the scatter of the circuit elements is corrected by the resistor R2 (adjusts the duration of the pause between pulses), which corrects the value of the pulse discharge current of the battery. The reading of the battery sulfitation readings is performed after a short-term connection of the XT connector and the negative bus to the battery according to the PA1 device. Previously, the resistor R8 is set to the position corresponding to the type of battery being tested. The pulsating glow of the control LED HL1 indicates the correct polarity of the battery connection during testing and the correct operation of the rectangular pulse generator on DA1. Literature
Author: V.Konovalov, Irkutsk
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ CO2 emissions will save the Earth from the ice age ▪ LMP8100 Programmable Gain Amplifier
▪ section of the site Power supply. Article selection ▪ Article Planet Uranus. History and essence of scientific discovery ▪ article What is three times more dangerous than war? Detailed answer ▪ article Safety Rules (PB, RD, WFD). Directory ▪ article Vertical antenna for LF bands. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Comments on the article: Anatoly And where is the passport value of the internal resistance of the battery written?
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese

 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: