
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Single-chip AC/DC converter with PFM. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Voltage converters, rectifiers, inverters The medium-power single-ended switching power supply (SMPS) presented in the article can be used to replace a conventional network adapter built on the basis of a linear power supply. Main Specifications
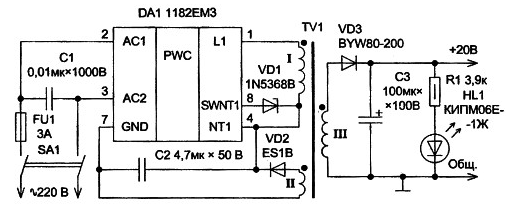
The schematic diagram of the power supply is shown in fig. one.
SMPS has galvanic isolation of input and output circuits. The main component of the SMPS is a specialized microcircuit of the brand 1182EMZ of the Bryansk company SPC "SIT". Reference information about the 1182EMZ chip can be found in the reference [1, p. 34, 35], which, in particular, says that this microcircuit has no analogues. The advantages of the microcircuit of this SMPS are in the presence of built-in protection against overloads in the load current and overheating of its semiconductor crystal. The microcircuit operates on the principle of pulse-frequency modulation (PFM) with a generation frequency range from 20 kHz to 70 kHz. The operating frequency range of the PFM can be varied by changing the inductance of the primary winding of the pulse voltage transformer TV1. The amplitude of the voltage pulses applied to the primary winding of the transformer TV1 depends on the voltage of the electrical breakdown of the zener diode VD1. Purpose and possible replacement of components The two-section component SA1 is a power switch, and FU1 is a fuse that protects the mains alternator from overload in the event of a failure of the DA1 chip. The high-voltage ceramic capacitor C1, which can be taken from the K15-5, K15-U2, KSO-10, KSO-11 or KSO-13 brands, suppresses the ripple generated by the converter, which consists of a DA1 chip and a TV1 pulse transformer. This capacitor must necessarily have the lowest possible parasitic parameters of inductance and resistance, and must also work reliably when an alternating voltage is applied to the plates. A half-wave rectifier, assembled on a VD2 diode and a capacitive filter on a capacitor C2, ensures the operation of the DA1 chip. Diode VD2 can be changed to devices of brands SF12, SF14, UF4002, US1D or KD212A, and capacitor C2 can be used brands K73-11, K73-20, K73-15, K73-16, K73-22 or K73P-2. The electrolytic capacitor C3 is designed to suppress ripple in the DC voltage applied to the load. This capacitor C3 can be taken of the type K50-6, K50-29, K50-31 or a similar imported capacitor, which has the smallest possible dimensions. Diode VD3 brand BYW80-200 rectifies the impulse voltage induced on the winding III of the voltage transformer TV1. It is necessary to provide thermal contact of this diode with the cooler of the DA1 chip, for which it may be necessary to use a gasket made of an electrically insulating material such as mica or beryllium ceramic. Diode VD3 must be high-frequency or pulsed; it is permissible to change it to the device 15ETH03, MUR820, KD213A, KD213B or KD213V. Chip DA1 should be mounted on a cooler brand HS113, HS118, HS134, HS184 or similar using thermal grease KPT-8. The microcircuit is enclosed in a metal-plastic case "Multiwatt-9" and has the following pin assignment: 1 - output is intended for connection of the primary winding of the transformer; 2 and 3 - conclusions for supplying alternating voltage of the mains; 4 - output is required to connect the primary winding of the transformer; 5, 6 and 9 - not involved; 7 - local common wire of the microcircuit; 8 - output for connecting a zener diode. The operating temperature of heating the semiconductor crystal of the microcircuit is in the range from -40°С to +150°С. The typical thermal resistance of the crystal-chip case is 4°C/W, and the thermal resistance of the crystal-to-environment reaches 50°C/W. The threshold for protection against overheating of the microchip crystal lies in the range from +135°С to +160°С. In addition, the microcircuit withstands a static potential with a voltage of up to 2 kV. Pulse voltage transformer TV1 is made on a ferrite core size SH12x15. Ferrite grade can be 2500NMS1, 2500NMS2 or 3000NMS. The length of the non-magnetic gap is selected to obtain a primary winding inductance of 2,5 mH (in this case, the conversion frequency will be about 30 kHz). Winding I is formed by 47 turns, winding by 11-14 turns, and winding III by 24 turns of PEV, PEL or PELSHO wire. The diameter of the wire with the insulation of winding I is 0,41 mm, windings 11-0,14 mm, and windings III - 0,89 mm. Although such large diameters of winding wires lead to increased losses due to skin effects, this can be tolerated or an equivalent section litz wire can be used. Each winding is isolated from one another with three layers of Mylar, lacquered or Teflon film. The fixed resistor R1 and the LED HL1 form a circuit for indicating the on state of the power supply, and also represent a small non-switchable load of a single-cycle converter. Resistor R1 can be used brands MLT, OMLT, S2-22, S2-23 or similar. The LED can be used brand KIPM05D-1Zh, KIPM05D1-1Zh, KIPM05E-1Zh, KIPM05E1-1Zh, KIPM06D-1Zh, KIPM07D-1Zh, KIPD35A-Zh or similar. Design When installing the SMPS, all connections should be made with as short conductors as possible. It is advisable to bend the paws 2 and 3 of the DA1 chip in opposite directions to prevent breakdown and short circuit. Setting and adjusting The power supply should start working immediately, without forging. However, it may be necessary to select the number of turns of the winding III of the transformer TV1 for a more accurate setting of the output voltage. If you hear a squeak or other extraneous sounds during the operation of the SMPS, then you should change the inductance of the primary winding of the pulse voltage transformer TV1, thereby adjusting the PFM frequency range. Literature
Author: E.Moskatov, Taganrog, moskatov.narod.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Satellite communications in the 300 GHz band ▪ Memory programmer BK PRECISION 848 ▪ Device permanently turned off ▪ ZL50233/4/5 - echo suppressor chip ▪ About the benefits of chocolate
▪ site section Welding equipment. Article selection ▪ article Top Ten Thousand. Popular expression ▪ Article How many galaxies are there? Detailed answer ▪ article coffee tree. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: