
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING The power supply unit of the radio with switching Network-battery. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
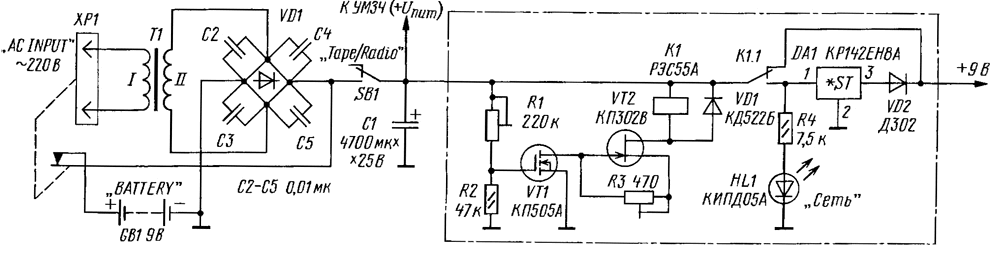
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Power Supplies The author improved the portable radio power supply described earlier in the journal ("Radio", 2002, No. 11, pp. 12, 13), introducing automatic switching of the power supply and battery. It should be borne in mind that powering up the power supply with such a refinement is advisable only for equipment with a sufficient margin in terms of the power of the acoustic system. As you know, the currently popular portable audio equipment in offline mode is usually powered by a built-in battery with a voltage of 7,5 ... allow its increase to 9 ... 12 V [14]. Using this feature of microcircuits, it is often possible to more than double the musical (peak) output power by just altering the network power supply unit [18]. The instantaneous power headroom created improves the dynamic performance of the amplifier. In the power supply of the radio [2] with an unstabilized supply voltage increased for the UMZCH, the stabilizer is provided only to power the low-power cascades of the device. The transition from mains to battery power was carried out by a push-button switch. The main disadvantage of the device is connected with this switch: if the button is accidentally switched to the "Battery" position during mains operation, an increased voltage is supplied to the preliminary stages of the radio tape recorder, which can lead to failure of the universal amplifier and receiver. This disadvantage is completely eliminated in the device, the circuit of which is shown in the figure. Here, instead of a manual "Network-Battery" switch, automatic electronic switching is introduced, which excludes the supply of increased voltage to the preliminary cascades of the radio. In "Battery" mode, the switch does not consume current; in the "Network" mode, its current consumption does not exceed 20 mA. The transition to the "Network" mode occurs at a voltage of 11,5 V, and the transition to the "Battery" mode occurs at 11 V. The switch is built into the radio's power supply. The input part is highlighted in the scheme by a dash-dotted line. It is a sensitive and economical voltage relay, as well as an integrated voltage regulator DA1. The unstabilized voltage across the capacitor C1 monitors the field effect transistor VT1. A current limiter for relay K2 is assembled on transistor VT1. The HL1 LED indicates switching to the "Network" mode. When operating on battery power, when the voltage across the capacitor C1, even with fresh batteries, does not exceed 10 V, the transistor VT1 is closed - the positive voltage at its gate, set by the divider R1R2, is below the threshold. Relay K1 is de-energized, its contact K 1.1 is in the upper position according to the diagram. Stabilizer DA1 is disabled at the input by contact K1.1, and at the output - by a decoupling diode VD2, which prevents the battery from discharging through the output impedance of the stabilizer. In this state, the device practically does not consume current, which is especially important in battery mode. When the network cable is connected to the AC INPUT connector, the battery is turned off by the additional contact of the connector, and the voltage increases to the UMZCH power level. Increasing the voltage at the gate of the transistor VT1 will open it. A current limited by transistor VT1 will flow through the winding of relay K2, but sufficient to operate the relay. Contacts K1.1 will include the DA1 stabilizer in the power circuit. Now the supply voltage of the preliminary stages will be limited to the required level (9 V) and additionally stabilized. UMZCH is powered by increased voltage from a power supply unit, modified according to the recommendations in [2]. At the same time, the HL1 LED will light up, indicating the "Network" mode. Disconnecting the mains cable connector switches to battery mode. The RES55 relay for an operating voltage of 12 V (passport 4.569.602) operates at a voltage of 7...8 V and a current of 10...12 mA. Without a current limiter through the relay winding, at a maximum supply voltage of UMZCH of 16 V, its value would reach 35 mA, which is undesirable. It is also impossible to use a relay for a response voltage close to the maximum - this voltage is not stabilized and fluctuates during operation of the UMZCH. The use of a current stabilizer on a field-effect transistor VT2 limits the current consumption of the relay to a level exceeding the actuation current by 2 ... 3 mA. This is sufficient for reliable switching and economical operation in conditions of supply voltage instability. The high steepness of the field-effect transistor VT1 provided a small difference in the switching levels of modes - about 0,5 V. The diode avoids the use of another relay switching contact. The direct voltage drop across the VD2 diode (D302 - germanium) does not exceed 0,3 V and, when using a silicon diode (KD212A and similar), can be compensated by selecting the DA1 chip. But with a germanium diode and without selection, the accuracy of setting the output voltage is sufficient and is 8,7 ± 0,27 V. The manufacture of the device should begin with the refinement of the existing power supply. Typical transformer T1 in the radio, as a rule, is low-power; it is better to replace it with a toroidal one, designed for the effective voltage of the secondary winding, 1,2 .. 1,3 times less than the allowable supply voltage of a particular UMZCH microcircuit. Some recommendations for choosing a ring magnetic circuit for a transformer are given in [2]. The consumed current of the UMZCH after the alteration increases, therefore, the capacitance of the filter capacitor should be increased to 4700 microfarads (by 25 V). The increased filter capacitance also contributes to increased peak power, and the voltage margin ensures reliable operation of the capacitor. The input part of the device is assembled on a separate board of the appropriate size next to the main PSU. In this device, transistors KP305B, KP305V can also be used, and in position VT2 - KP302B or KP302G (when selected by the initial drain current - at least 15 mA - and KP303E). Relay K1 can be replaced with a similar small one with a minimum trip current and a trip voltage of not more than 10 V. The HL1 LED can be replaced with another one, but it must have sufficient brightness at a current of 1 ... 2 mA. For operational reliability, the DA1 chip and the UMZCH chip should be installed on small heat sinks. Establishing the device is reduced to setting the voltage threshold for the "Network-Battery" switch with a trimmer resistor R1; the current through the relay winding is set by resistor R3. Before setting the sliders of resistors R1, R3 should be moved to the top and left according to the position scheme, respectively. Then, with the help of LATR, the voltage on the primary winding of the transformer T1 is gradually increased, controlling the constant voltage on the capacitor C1. At a level of 11,5V, transistor VT1 is opened and relay K1 is activated. The process is visually noticeable by the glow of the HL1 LED. The current in the relay winding is controlled by a milliammeter and limited to about 15 mA by adjusting the resistor R3. After that, the primary voltage is gradually reduced and the device is turned off: the release of the relay K1, visible by the extinction of the HL1 LED, should occur at a voltage of 11 ... 11,2 V on the capacitor C1. This completes the setup. An electronically switched power supply can be used in various models of wearable equipment. Reliability and ease of use are guaranteed by the absence of manual switches, and the increase in power depends on the allowable supply voltage and the maximum output power of the UMZCH. Literature
Author: A.Pakhomov, Zernograd, Rostov region
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Silicon Labs BGM111 Blue Gecko Module ▪ Cell division recreated outside the cell ▪ Axiomtek AIE100-903-FL-NX Compact System ▪ Reservoir bombarded with balloons
▪ section of the site Big encyclopedia for children and adults. Selection of articles ▪ Article Magic word. Popular expression ▪ article Why Jews couldn't buy Tamagotchi? Detailed answer ▪ article Sandarac tree. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: