
|
|
Reoplethysmograph on transistors. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
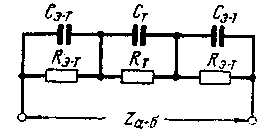
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Electronics in everyday life When assessing the state of the human cardiovascular system, modern medicine and biology widely use the technique of the so-called impedance reopletismography (registration of changes in the electrical conductivity of the human body). Rheoplethysmography is used in the study of both central and peripheral circulation. The advantage of this method is that the study itself practically does not change the state of the object under study. The electrical resistance between any parts of the human body is a complex volumetric resistance, a simplified equivalent circuit of which for alternating current is shown in Fig. one. Capacitance Se-t occurs between the surfaces of the electrodes and tissues adjacent to the inner side of the skin. The skin, especially the epithelium, has a very high resistivity and is the dielectric of Se-t capacitors. The tissues lying under the skin are conditionally accepted as homogeneous in structure. They are presented in the form of elements St and Rt. The capacitances of the Se-t capacitors depend on the dielectric properties of the skin, its condition (for example, on moisture) and the area of the applied electrodes.
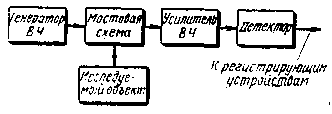
The value of the capacitance is determined by the value of the polarization effect, which decreases with increasing frequency. At frequencies above 80-100 kHz, the polarization phenomenon is practically not observed, and the capacitance of the capacitors St is small. Therefore, we can assume that the conductivity of the tissue in the region of these frequencies has only an active component. The absolute values of the resistance of living tissue are unstable, but depend on a number of reasons that are often difficult to take into account. As a result, they are of interest. not absolute values of resistance, but its relative changes from some initial level. At present, it can be considered proven that the electrical conductivity of living tissue is determined mainly by the degree of its blood supply. This is due to the fact that blood (mainly its plasma) has a very high electrical conductivity. Therefore, by the electrical conductivity of living tissue at high frequencies, one can judge the blood filling of individual organs or parts of the body. The research technique is called rheopletismography, and sometimes just rheography. The device described below, called a reoplethysmograph, is designed to study fast minor changes in the electrical conductivity of living tissue, reflecting pulse fluctuations in blood filling, as well as slow (from 0 Hz) changes in blood filling, for example, during breathing. Reoplethysmograph is a portable prefix on transistors to any cardiograph (when recording pulse oscillations of blood filling). From the output of this attachment, voltage can also be applied to the recorder (for example, H373). Operating frequency 150 kHz. The output voltage is at least 2 mV with a change in resistance of 50 ohms. by 0,1%. The frequency ranges of the output voltage taken from the output 1-4 are 0,2-150 Hz, and from the output 2-3 0-150 Hz. Schematic diagram The operating principle of the reoplethysmograph is illustrated by a block diagram (Fig. 2). The studied area of living tissue is connected to one of the arms of the bridge, powered by alternating current with a frequency of 150 kHz. The bridge is balanced in such a way that the RF voltage on its diagonal is minimal.
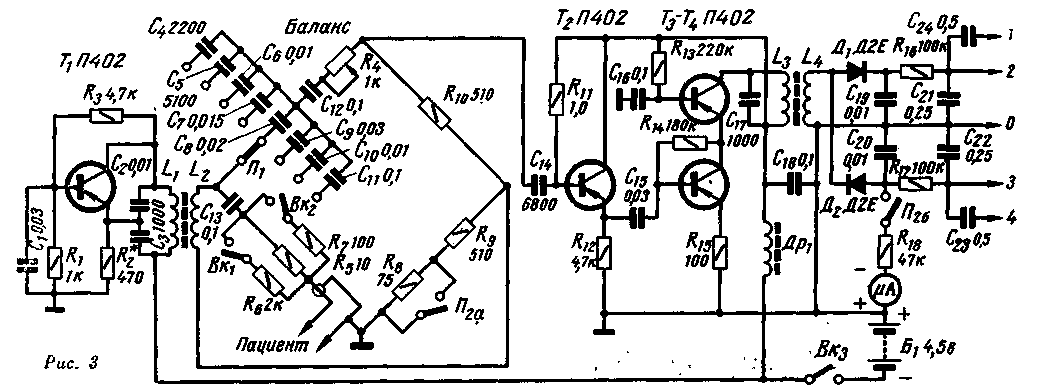
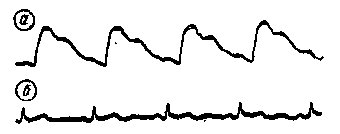
Changes in the conductivity of the object under study lead to modulation of the RF voltage at the output of the bridge according to the law of changes in the electrical conductivity of the object under study. The modulated RF voltage is amplified and detected. As a result of detection, a modulating LF voltage is released, which is fed to the recording device. The schematic diagram of the reopletismograph is shown in fig. 3. The RF generator is made on a transistor T1 according to a capacitive feedback circuit. The oscillating circuit is included in the collector circuit of the transistor, its resonant frequency is determined by the inductance of the coil L1 and the total capacitance of the capacitors C2 - C3. The depth of positive feedback depends on the ratio of the capacitances of the capacitors C2-C3 and the resistance of the resistor R2. The base of the transistor is grounded by alternating current (through capacitor C1). The generator, assembled according to this scheme, has a high frequency stability, the design of its loop coils is simple, and the adjustment does not cause difficulties, since it is not necessary to select the order in which the coil leads are turned on. From coil L1, high-frequency voltage is applied to the measuring bridge. In the left, lower according to the diagram, shoulder of the bridge, in series with the elements C13R5-R7, using a shielded cable, the object under study (conditionally indicated on the diagram "Patient") is connected. Using the potentiometer R4 ("Balance"), you can balance the bridge in terms of the active component, and with using capacitors C4-C11 - for the reactive component. In real conditions, both fast (pulse) fluctuations in electrical conductivity and slow ones, caused, for example, by breathing, are always observed. The amplitude of slow oscillations, as a rule, is much larger than the amplitude of pulse oscillations. If the bridge is finely balanced, slow changes in oscillation can lead to imbalance, which in turn will change the phase of the output voltage. Therefore, when balancing, switch P2 is set to a position where the resistor R8 is short-circuited, and the balance indicator (microammeter) is connected to the detector output. The research results can be obtained in numerical terms. For this purpose, a potentiometer is switched on in series with the "Patient" (and sometimes in parallel with it), by changing the resistance of which the sensitivity of the entire tract of the device is calibrated. Most often, the following calibration method is used: when the resistance in the "Patient" circuit changes by 0,05 ohm, the recording amplitude should be 1 cm. To eliminate the influence of the contact resistance of the contacts, the calibration scheme shown in Fig. 3 is used. A resistor R5 is connected in series with the "Patient", in parallel with which a resistor R1 is connected with a Vk6i switch, the resistance of which is 200 times greater than R5. At the same time, their total resistance is 0,05 ohm less than R5. When calibrating before recording slow oscillations, a resistor R5 is connected in parallel with R7. Then the total resistance of the circuit is reduced by 1 ohm. The voltage from the bridge is supplied to the emitter follower, assembled on the transistor T2, and then to a two-stage amplifier, made according to the cascode scheme. The amplifier load is the L3C17 circuit, tuned to a frequency of 150 kHz. The detector is made on semiconductor diodes D1 - D2. As a result of using a full-wave detector, the attachment has a symmetrical output. The time constants of the discharge circuits of the detector are chosen such that, after detection, signal components with frequencies up to 150 Hz are distinguished. From the side of lower frequencies, the time constant is determined by the capacitances of the transition capacitors C21 and C22 and the input impedance of the subsequent stages. With input impedances of 1 MΩ, the lower frequency cutoff is about 0,2 Hz at -3 dB. A microammeter is connected to the output of the detector, according to the minimum deviation of the arrow of which the bridge is balanced before starting the measurement. Construction and details The reoplethysmograph is made in a rectangular metal casing with external dimensions of 50X120X180 mm. All its parts, with the exception of power supplies, are mounted on circuit boards attached to the top cover, which is also a front panel. On the front panel there are: a microammeter, switches Vk1 - Vk3, switches P1, P2 and a connector for connecting the "Patient" cable. The connector for connecting the device to recording devices is located on the rear panel. All parts of the reoplethysmograph are mounted on two circuit boards. On one, placed in a screen made of tin, a generator is mounted, on the other - an amplifier, a detector and a measuring bridge. The device uses transistors with V in the range of 30-50. Loop coils are made on SB-2a type cores, wound with PEV 0,1 wire and contain: coil L1-200 turns, coil L2 - 80 turns, coil L3 - 200 turns and coil L4 - 100 turns. The inductor Dr1 is wound on an F-600 ferrite ring, the outer diameter of which is 12 mm, and contains 200 turns of PEV 0,1 wire. Resistor R4 must be wire-wound, and resistor R5 is made up of three connected in parallel with resistances of 27,27 and 91 ohms. As an indicator, you can use any microammeter, the sensitivity of which is 50-200 μA. Sample records obtained with the described rheoplethysmograph are shown in fig. four.
Authors: V. Bolshov, V. Smirnov; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Optical Neural Network Accelerator ▪ Nissan xStorage: domestic battery packs for households ▪ AMD discontinues 500MHz Athlon processors
▪ site section Power supply. Article selection ▪ article A mixture of French and Nizhny Novgorod. Popular expression ▪ What voyages did Henry the Navigator become famous for? Detailed answer ▪ article Real cardamom. Legends, cultivation, methods of application ▪ article Superstrong eggs. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: