
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Another power supply for the Chizhevsky chandelier. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Electronics in medicine Most devices designed to produce high voltage that feeds the Chizhevsky Chandelier can be divided into transistor voltage inverters and trinistor (and sometimes thyristor, since they use varieties of this group: dinistors, trinistors, triacs) pulse converters. The disadvantage of the former is the need to lower and rectify the mains voltage, which increases both the cost and the dimensions of the device. Trinistor devices [1 - 3] are relatively simple, which is the main argument in their favor. As a rule, trinistor devices operate on the principle of a half-wave arrester (Fig. 1).
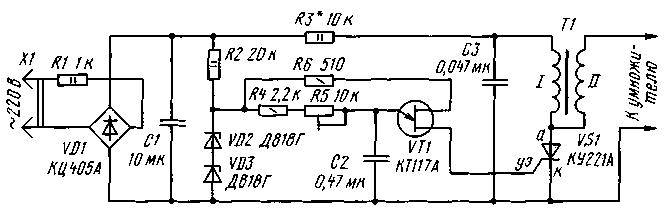
During one half-wave of the mains voltage, the storage capacitor C1 is charged, and during the other, it is discharged to the winding of the step-up transformer T1 through the trinistor VS1, which is turned on by the control system (CS). The differences sometimes come down only to the method of controlling the trinistor. The main disadvantage of such designs, according to the author, is the reduced frequency of the voltage multiplier supply, which can lead to an increase in the ripple at the output of the unit and a decrease in the efficiency of the "chandelier" [4]. In addition, sometimes it is possible to observe an increased noise level of the transformer, which is a consequence of the large amplitude of the current pulses. The author managed to avoid all this by developing a power supply, the circuit of which (without a high-voltage multiplier) is shown in Fig. 2. Let's take a look at his work. The mains voltage is rectified by the diode bridge VD1. The ripple of the rectified voltage is smoothed out by the capacitor C1, the charging current of the capacitor at the moment the device is connected to the network is limited by the resistor R1. Capacitor C3 is charged through resistor R3. At the same time, a pulse generator, made on a unijunction transistor VT1, comes into action. Its "trigger" capacitor is charged through resistors R4, R5 from a parametric stabilizer made on a ballast resistor R2 and zener diodes VD2, VD3. As soon as the voltage on the capacitor C2 reaches a certain value, the transistor "triggers" and an opening pulse arrives at the control transition of the trinistor (Fig. 3, b).
Capacitor C3 is discharged through the trinistor to the primary winding of the transformer (Fig. 3a). A high voltage pulse is formed on its secondary winding (Fig. 3c). The repetition rate of these pulses is determined by the frequency of the generator, which, in turn, depends on the parameters of the R4R5C2 chain. Trimmer resistor R5 can change the output voltage of the unit by about 1,5 times. In this case, the pulse frequency is regulated within 250 ... 1000 Hz. In addition, the output voltage changes when selecting the resistor R3 (in the range from 5 to 30 kOhm). The output voltage ripple does not exceed 5%, network interference is practically absent. = It is desirable to use paper capacitors (C1 and C3 - for a rated voltage of at least 400 V; the diode bridge should be designed for the same voltage). Instead of what is indicated on the diagram, a trinistor T10-50 or, in extreme cases, KU202N is suitable. Zener diodes VD2, VD3 - any others, with a total stabilization voltage of approximately 18 V. The high-voltage multiplier can be borrowed from [1-3]. The transformer is made on the basis of the line TVS-110P2 from black-and-white TVs, but in principle others will do [5]. All primary windings must be removed and 70 turns of PEL or PEV wire with a diameter of 0,5 ... 0,8 mm should be wound onto the vacated space. Step-up winding (II) should not be touched. Literature
Author: G. Glukhenky, Cheboksary; Publication: N. Bolshakov, rf.atnn.ru
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ 200MP ISOCELL HP1 image sensor ▪ The gadget is powered only by the heat of the human body ▪ Big Data Technologies for Healthcare
▪ section of the site Labor protection. Selection of articles ▪ bugle article. Popular expression ▪ article What elementary particles are named after the cry of ducks? Detailed answer ▪ Article Bricklayer. Job description ▪ Article Wonderful thread. Chemical experience
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: