
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Chinese clock - timer. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Clocks, timers, relays, load switches Often a radio amateur needs an electronic timer - a device that turns on or off an external load at a given point in time. Schemes of such devices have been published more than once in amateur radio publications. They differ from each other in the degree of complexity, functionality, constructive implementation. In the published article, the author proposes another, very simple design, made on the basis of cheap Chinese-made electronic watches. Most of the well-known timers are made either as an attachment to a serial electronic clock, or already contain an electronic clock (for example, based on the BIS K145IK1901). A common disadvantage of most known devices is a relatively large number of elements, the presence of a separate power source, and often also an additional housing, often quite large. All this complicates the task of manufacturing a timer. The peculiarity of the proposed design is that all the details of the timer are placed in the body of the basic electronic clock, and the necessary modifications to the design of the watch are minimal. In addition, the timer contains a small number of elements and consumes low current, which made it possible to refuse an additional power source (a clock battery is used). The timer performs the function of closing the external circuit at a predetermined time. Resetting is done manually. By changing the device settings, you can also get the functions of opening an external circuit and short-term closing or opening of an external circuit (for example, to give a signal to start some kind of automation). As a base clock, any electronic clock powered by a galvanic cell with a voltage of 1,5 V, having an alarm clock function and an electrodynamic sound indicator, can be used. In the described design, a Hong Kong-made pocket electronic watch with an alarm clock "TRAVEL CLOCK" was used. Schematic diagram of the timer is shown in fig. one.
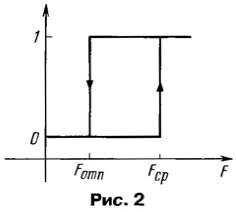
The added elements are depicted by a line of increased thickness. The device contains an input circuit R1C1, a DC amplifier on a transistor VT2 and an output key made on the relay K1. The timer provides the closure (or opening) of the external circuit when the clock alarm goes off. Galvanic isolation from the output circuit connected to connector X1 ensures high noise immunity of the device. The peculiarity of the timer is that it uses a special relay called a magnetic latching relay. It differs from the usual one in that its armature is able to remain both in the released and in the attracted state even in the absence of current in the winding. Therefore, the energy of the power supply is consumed only when the state of the relay changes, which greatly increases the efficiency of the device. The principle of operation of such a relay is as follows. The characteristic of any relay has a pronounced hysteresis. This means that the relay requires a greater magnetomotive force (MMF) to actuate than is sufficient to keep its armature attracted. Schematically, this characteristic is shown in Fig. 2.
Here, the value of the MMF of the winding F is plotted along the abscissa axis, and the points corresponding to the attracted (1) and released (0) state of the relay armature are conventionally shown on the ordinate axis. In a conventional relay, the actuation MMF Fav and release MMF Fotp is greater than zero and, therefore, when the winding is off, it can only be in the released state. In a relay with magnetic latching, in addition to the MMF of the winding, there is also an additional MMF created by a permanent magnet, and its value is greater than the release MMF, but less than the actuation MMF. Therefore, when the winding is off, the relay can be both in the released state of the armature, since the MMF of the magnet is insufficient for operation, and in the attracted state, since the MMF of the magnet is sufficient to keep the armature in the attracted state. To transfer the relay from one state to another, it is necessary to pass a short current pulse of one sign or another through its winding. In this case, the MMF of the winding is either added to the MMF of the magnet and the resulting MMF becomes sufficient to operate the relay, or is subtracted - in this case, the resulting MMF becomes less than the release MMF. The characteristic of the magnetic latching relay is shown in fig. 3.
The timer works like this. When the signal from the base clock is not applied, the transistor VT2 is closed, the current does not flow through the relay winding and it is in one of the stable states (for example, open, for clarity, the case when the timer is turned on will be considered). Capacitor C2 is charged through resistor R2 to the supply voltage. When the base clock alarm goes off, a series of rectangular pulses with a frequency of about 1 kHz begin to be sent to their sound indicator BA1. These pulses pass through the VD2R1C1 circuit and open the transistor VT2-As a result, the capacitor C2 is discharged to the winding of the relay K1, forming a current pulse. In this case, the relay is activated, its contacts K1.1 close and remain closed, since the armature is attracted by the magnetic flux of a permanent magnet. After the capacitor is discharged, the current through the winding drops to a value limited by the high resistance of the resistor R2, which achieves high efficiency of the entire device. To open the relay contacts (return to the initial state), an additional external permanent magnet is used, which is brought to the relay outside the watch case so that its MMF is subtracted from the total MMF of the relay, causing it to release. Diode VD1 prevents overvoltage in the winding of the sounder VA1. In the absence of a diode, device malfunctions are possible as a result of impulse overvoltage effects on the LSI clock. Diode VD3 performs a similar function. The following parts are used in the timer: ULM resistors, capacitors KM (C1), K53-14 (C2). They can be replaced by other small ones with suitable parameters. Capacitor C2 should have minimal leakage. The VD2 diode must be germanium, since the silicon diode may not open at a low signal amplitude (for example, with a partially discharged element), the rest of the diodes are any small-sized ones, for example, the KD503, KD509, KD521, KD522, D220 series. Transistor VT2, in addition to small dimensions, must have a small reverse collector current and, preferably, a low saturation voltage. Suitable, for example, transistors of the KT209, KT3107 series. These requirements are determined by minimizing the current consumption. The relay is self-made, based on the KEM-2A reed switch. The relay winding is wound on a thick paper frame and contains 1500 turns of PEV wire with a diameter of 0,1 mm. Winding length (distance between the cheeks of the frame) - 17 mm, inner diameter of the frame - 3 mm. The frame with the winding is put on the middle of the reed switch bulb. The winding resistance turned out to be about 70 ohms. A small-sized permanent magnet is used to create a constant bias. The installation of the timer is shown in the photograph (Fig. 4).
The relay is placed in the free space near the sound emitter and fixed with a compound (for example, paraffin). The remaining elements of the device are placed on top of the clock board. Hinged mounting, using rigid mounting wires. The fastening of the elements to the board and at the same time the electrical connection with the base clock is carried out using the terminals of the elements C2, R2 and VD2. The leads are passed through holes drilled in the board and soldered to the corresponding printed tracks on the reverse side. If the installation is not rigid enough, the elements can be additionally fixed with a compound. The location of the elements and holes in the board must be clarified in relation to the layout of the printed tracks on the board of a particular clock instance. To connect an external circuit, a small-sized plug connector is installed in the watch case, for example, a block MGK1-1. Its case is carefully ground down to a thickness of 5 mm and glued in the watch cover, having previously cut recesses for sockets in it. The connection to the terminals of the reed switch is carried out by a pair of flexible wires. An inseparable connection to an external circuit is also possible, without the use of a connector. An external permanent magnet used to reset the relay to its original state is desirable to be made, for example, in the form of a key fob, the design of which ensures that it is brought to the relay with the same pole. The design of the key fob is not given, as it depends on the size and shape of the magnet used. Setting the timer is reduced to the selection of the position of the permanent magnet. To do this, connect an ohmmeter-probe to the contacts of the reed switch and slowly bring the magnet to the reed switch. At the moment of closing the contacts, note the position of the magnet and slowly move the magnet away from the reed switch. Mark the position of the magnet at the moment of opening the contacts and then fix the magnet on the board between the two marks. Then check the operation of the relay as follows. With the battery installed, the outputs of the emitter and collector of the transistor VT2 are briefly closed, while the relay should work and remain in the attracted state. If operation does not occur, then it is necessary to swap the winding leads. The final check of the timer is carried out when the signal is given by the base clock. Some types of watches have a forced signaling mode, for example, for "TRAVEL CLOCK" watches, it is called up by simultaneously pressing the left and middle buttons, while all segments of the indicator light up and an audible signal sounds. In order for the timer to open, it is necessary to swap the outputs of the relay winding. Then, when the timer is triggered, the reed switch, previously closed by an external magnet, will open. To obtain the function of short-term contact closure, the magnet is installed so that its MMF is insufficient to keep the contacts closed (behind the second mark). In this case, relay K1 works like a normal polarized relay. The short-term opening function is obtained by placing a magnet in front of the first mark (so that its MMF is sufficient to trigger the reed switch) and swapping the winding leads. Since in the last two cases the relay has a higher tripping current, it is necessary to check the reliability of its operation at a reduced supply voltage and, if necessary, rewind the winding with a thicker wire (to reduce its resistance). If the time of the closed (open) state is not enough, a larger capacitor C2 should be used. The required time for the timer to operate is set in the usual way - by selecting the appropriate time on the clock alarm clock. Turning the timer on and off is done by turning on/off the alarm signal on the base clock. Due to the low current consumption of the timer (in standby mode, it is determined only by leaks), a separate power off is not provided. It is necessary to ensure that all other functions that give sound signals are turned off on the clock (for example, an alarm every hour), otherwise a false alarm will occur. Resetting the relay with an external magnet should be done after the clock stops beeping, otherwise, immediately after the reset, the timer will start again. The timer can be used, for example, as an alarm clock (when the volume of the standard sound emitter is not enough), while the relay contacts are connected to the external sound emitter circuit. It is also possible to use a two-winding doorbell, then the contacts are connected to its secondary (low-voltage) winding. Attention!!! The insulation of the relay is not designed for supplying mains voltage. If high voltage loads need to be controlled, an additional switch should be used. Author: D.Volkov, Shakhty, Rostov region
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Magnetic cooling system based on shape memory alloys ▪ Concrete will become stronger ▪ Tommy Hilfiger Jacket with Integrated Solar Panels ▪ Semi-rugged laptop Panasonic Toughbook CF-54
▪ section of the site Your stories. Article selection ▪ article Hygienic standards for the content of chemicals in water. Basics of safe life ▪ article Which playing coach managed to sell himself to a more famous club? Detailed answer ▪ Article Secretary. Job description ▪ Article Cold air. Focus Secret
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese



 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: