100-watt amplifier PA100GC. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering

Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Transistor power amplifiers
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
The UMZCH circuit is a parallel connection of two LM3886 operational amplifiers. Output power 2x100 W for a load of 4 ohms and 2x50 W for 8 ohms.
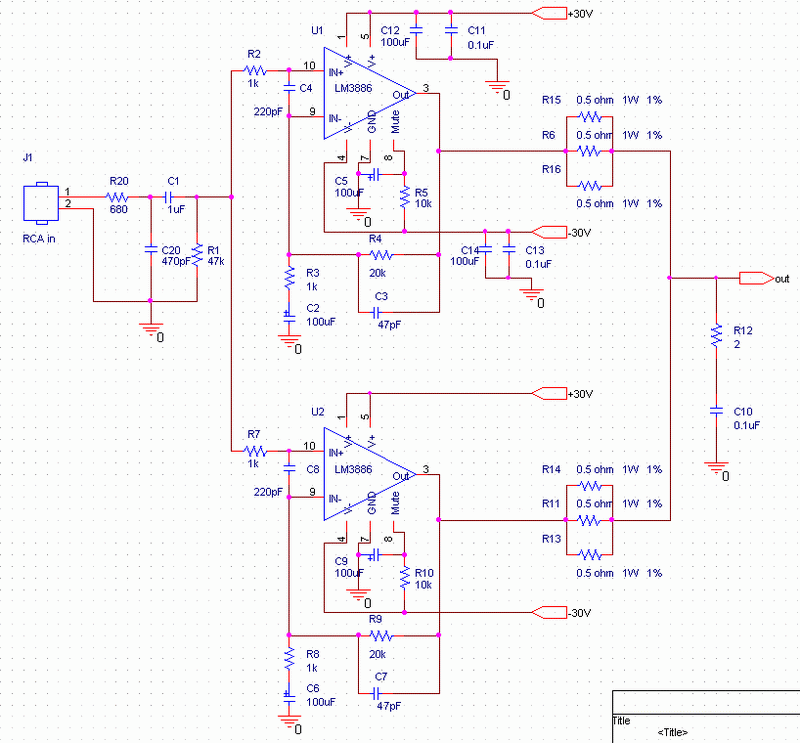
Rice. 1. Schematic diagram of the PA100GC amplifier (click to enlarge)
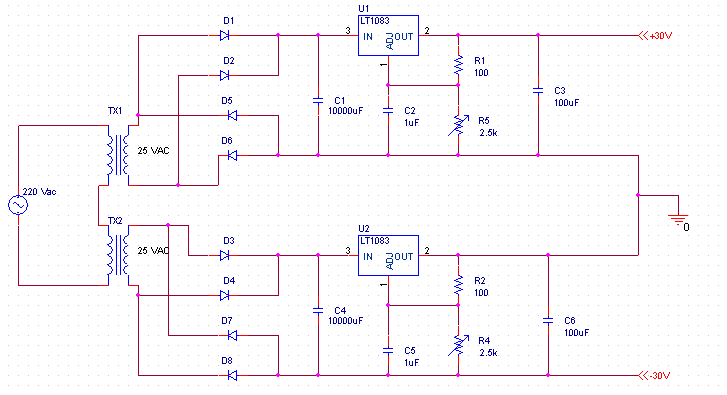
Rice. 2. Schematic diagram of the PSU (click to enlarge)

Rice. 3. PCB (top view)

Rice. 4. PCB (bottom view)

Rice. 5. Photo of the finished board


Rice. 6. The appearance of the amplifier
R20 and C20 are installed on the input connector. 0,1 uF capacitors are soldered directly to the microcircuit pins.
Transformer 500VA 2x25V.
Publication: cxem.net
 See other articles Section Transistor power amplifiers.
See other articles Section Transistor power amplifiers.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Seaweed makes clouds
01.08.2015
Clouds almost never dissipate over the Antarctic waters of the World Ocean, and the reason for this, as it turned out, is in phytoplankton - local microscopic algae literally make clouds, releasing aerosol particles into the atmosphere. Usually, when they talk about aerosols, they mean those that are obtained as a result of human activity (smoke from factory chimneys, etc.). Soot particles serve as a kind of "seeds" around which water vapor condenses - this is how drops are obtained that combine into a cloud.
But such condensation points can also have a completely natural origin: the smallest splashes of water containing organic substances and sea salt, or sulfates and ammonium salts as waste products of some living organisms. The fact that the sea and its inhabitants serve as a source of "natural aerosols" has long been talked about, but so far few people have tried to quantify the contribution of marine ecosystems to cloud formation. That's what Dennis Hartmann of the University of Washington, along with colleagues from the University of Leeds, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, and Los Alamos National Laboratory, tried to do.
The work used data from NASA satellites, which made it possible to estimate the density of clouds between 35° and 55° south latitude. The state of the clouds was compared with the concentration of chlorophyll a, which usually serves as a marker of biological activity in the seas and oceans. In an article in Science Advances, the authors write that the relationship between clouds and chlorophyll levels was unambiguous: the more photosynthetic pigment (that is, the more algae) there was, the cloudier the weather was.
Life in the ocean increased the amount of cloud water droplets by 60% annually; The effect was most noticeable in summer. Clouds that are low above the earth reflect sunlight, and the surface of the planet below them will cool. (The "lock-in" of heat and the greenhouse effect are caused by other, high-level clouds.) In summer, the level of solar radiation increases, and at the same time, as was said, the concentration of phytoplankton increases - according to the researchers, algal activity leads to the fact that the amount of reflected solar radiation increases by 10 watts per square meter. This is comparable to what happens in the northern hemisphere, with the exception that in the north an additional "cloud reflection" occurs due to industrial pollution of the atmosphere.
How can microscopic algae increase cloudiness? The first way: releasing gaseous dimethyl sulfide, which in the atmosphere turns into a sulfuric acid residue - sulfate, which, in turn, condenses water vapor very well. The second way: due to organic residues rising into the air on the surface of the smallest bubbles that have come off the water. Such bubbles with organic additives can also serve as condensation centers for cloud droplets. It is curious that from 35° to 45° south latitude clouds over the ocean are formed mainly due to dimethyl sulfide, and from 45° to 55° - due to phytoplankton organic matter.
Thus, the assumptions about the active climatic activity of marine ecosystems were confirmed - tiny algae can really make clouds. We tend to believe that only humans are powerful enough to make a big impact on the climate, but as we can see, the current state of affairs can be more complicated. (And not only because of phytoplankton - here we can also recall the work of employees of the University of Göttingen, published last year in Angewandte Chemie: it describes how ordinary conifers help form clouds with the help of substances contained in their resins.) By building climatic model, trying to assess our impact on the weather on the planet, we must also take into account the contribution of natural producers of cloud-forming aerosols.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ swivel socket
▪ Converting hydrogen to metal
▪ Highway with luminous markings
▪ LG Tone Free FP Wireless Headphones
▪ LCD monitors and TVs are getting cheaper
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the website Electrotechnical materials. Article selection
▪ article And in a word: he wanted a watermelon, / And that one wanted pickles. Popular expression
▪ article Why can the American gesture for the phrase I Love You be confused with a rocker goat? Detailed answer
▪ Amaranth article. Legends, cultivation, methods of application
▪ article Car radio watchman. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
▪ article Switching mains voltage converter. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese







 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: