
|
|
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF RADIO ELECTRONICS AND ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING Sound in a vacuum. Lamp sound technology. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
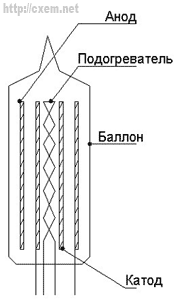
Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering / Tube Power Amplifiers Recently, the design of tube sound technology has become increasingly popular. In this article I will try to tell you what you need to know when starting work. 1. Anatomy The principle of operation of electronic lamps is based on the movement of charged particles (electrons) in an electrostatic field. Consider the device of a radio tube. The figure shows a diagram of the design of a simple lamp (diode) of indirect incandescence.
Actually, the lamp is a glass container in which a high vacuum (10-5 - 10-7 Torr) is created. In classical lamps, the shape of the electrodes is similar and are concentric "cylinders". The meaning of everything is that when the cathode is heated, the electrons are excited and leave it. The direct-heated cathode is simply a tungsten filament, as in an ordinary lighting lamp. Such cathodes are used in cases where there is no need to create a special regime on the cathode. Most lamps use an indirectly heated cathode. In this case, the filament is placed in a metal tube. At some distance from the cathode there is an anode - an electrode, which is the "end stop" of the electron flow. Additional electrodes are used to control the speed of electrons from the cathode to the anode. Grids are divided into 3 types. Control, screen and protective (anti-dinatron). The grid is a wire spiral wound on metal racks (traverses) sandwiched between two mica flanges. The same flanges hold the traverses of the anode and cathode. There are also lamps containing several electrode systems. Such lamps are called combined. Depending on the power of the lamp, its electrodes and body can be made of various materials, because. as the current passing through it increases, the dissipated power increases. 2. Morals It is quite clear that each type of lamp has its own original parameters and characteristics. First of all, let's find out the operating modes of the lamps. To create a normal electron flow, special electrostatic potentials are created in the interelectrode spaces of the lamp. These potentials are determined by the voltages acting on its electrodes. Consider the main operating modes:
2. Maximum permissible anode current (Ia max). The maximum permissible value of the current in the anode circuit. In essence, the current passing through the lamp, minus a small fraction "stretched out" by the potentials of the grids. 3. Heating voltage (Un). The typical voltage applied to the filament (heater) at which the cathode reaches the temperature required for thermionic emission, while at the same time the lamp maintains the declared durability parameters. 4. Heating current (In). The current drawn by the filament. There are also a number of characteristics due to the design of the lamps that affect the parameters of the assembly assembled on this lamp: 1. The slope of the characteristic (S). The ratio of the anode current increment to the voltage increment on the control grid. Those. we can determine how much the anode current will change when the control voltage changes by 1V. 2. Internal resistance of the lamp (Ri). The ratio of the anode voltage increment to the corresponding anode current increment. In some way, this can be compared with the current transfer coefficient of a transistor. with an increase in the control (positive) voltage, the anode current increases. Outwardly, this looks like a decrease in resistance. Naturally, the lamp does not have active resistance as such. It is determined by the interelectrode capacitances and is reactive in nature. 3. Static gain (µ). The ratio of the increment of the anode voltage to the increment of the control causing the same increment of the anode current. Those. in fact, it shows how many times more effective the increment of the control voltage by 1V is than the analogous increment of the anode voltage. 3. Names Some parameters and design features of lamps can be recognized by their marking: 1st element - a figure showing the rounded filament voltage The 2nd element is a letter indicating the type of lamp:
3rd element - a digit indicating the serial number of the type of device (i.e. the serial number of the development of the lamp in this series. For example, the 1st developed lamp from the series of 6-volt fingertip double triodes is 6N1P). 4th element - a letter characterizing the design of the lamp: A - in a glass case with a diameter of up to 8 mm.
4. Working conditions There is a preconceived notion that lamps are more demanding to install than semiconductor devices. Actually, the operating conditions of EVP are not much different from those required by semiconductor devices. Moreover, lamps are less demanding on thermal conditions than semiconductors. So the output stages of tube amplifiers with a power of up to 20W do not need forced cooling, unlike semiconductor ones. Most lamps are installed in a special kind of connectors - lamp sockets. Some lamps have terminals at the top of the bulb. Most often, these are the leads of the anode or screen grid, to which a relatively high voltage is applied. This is done to avoid breakdown between it and the leads of other electrodes. If the lamps become very hot during operation, it is advisable to spread them as far apart as possible. Recently, there has been a special trend in the construction of lamp technology. Lamps and transformers are placed on the top panel of the device, and the rest of the parts are mounted in the basement of the chassis. Such devices cool much better, and I think this approach is quite reasonable if there are no anode terminals in the upper part of the lamps that threaten the user with a high voltage shock. Lamps do not have to be strictly vertical. Any angle of inclination relative to the horizon is allowed, if there is no danger that the grids will heat up and sag, thereby creating an interelectrode short circuit. 5. Kicks and slaps The author will gladly accept questions and critical comments on the article. Based on the feedback, the possibility of writing a similar article on gas-discharge and electron-beam EWPs will be considered. Author: Pavel A. Ulitin, E-mail: Overlord7[bug]yandex.ru, ICQ #: 323-026-295; Publication: cxem.net
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024 Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024 Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
▪ Planet 9 times larger than Jupiter discovered ▪ Free Wi-Fi has become more important than sex and alcohol ▪ Features of the Lytro Camera for Mobile Phones ▪ Holodeck Design Lab by Nvidia ▪ Android smartphone becomes a listening device
▪ section of the site Normative documentation on labor protection. Article selection ▪ article Nails would be made of these people. Popular expression ▪ article For which film was the shortest film review written? Detailed answer ▪ article Electrician for switchgears. Job description ▪ article Electromine for rats. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
Comments on the article: Vladimir Great article! There is not enough comparison of lamps and transistors, regarding the difference in linearity from temperature and control currents / voltages.
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews www.diagram.com.ua |






 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article: