 Free technical library
Free technical library
Automatic drain valve of the electric pump. Drawing, description

Directory / Tools and mechanisms for agriculture
 Comments on the article
Comments on the article
In the water supply systems of many country houses, submersible vibration electric pumps "Rucheyok", "Kid" and the like are used. They are convenient, compact, do not require maintenance, however, in winter, when the pump is turned off, the water is "locked" in their supply hose and, having no flow into the well, freezes.
The simplest solution to the problem is to make a drain hole at the bottom of the hose. However, if it is small, the water may have time to turn into ice, and if it is large, the working pressure becomes insufficient.
This problem can be solved by introducing an automatic drain valve into the electric pump hose. It consists of only four parts: a body and a cover with hose fittings, a rubber gasket between them and a cup-shaped piston valve.
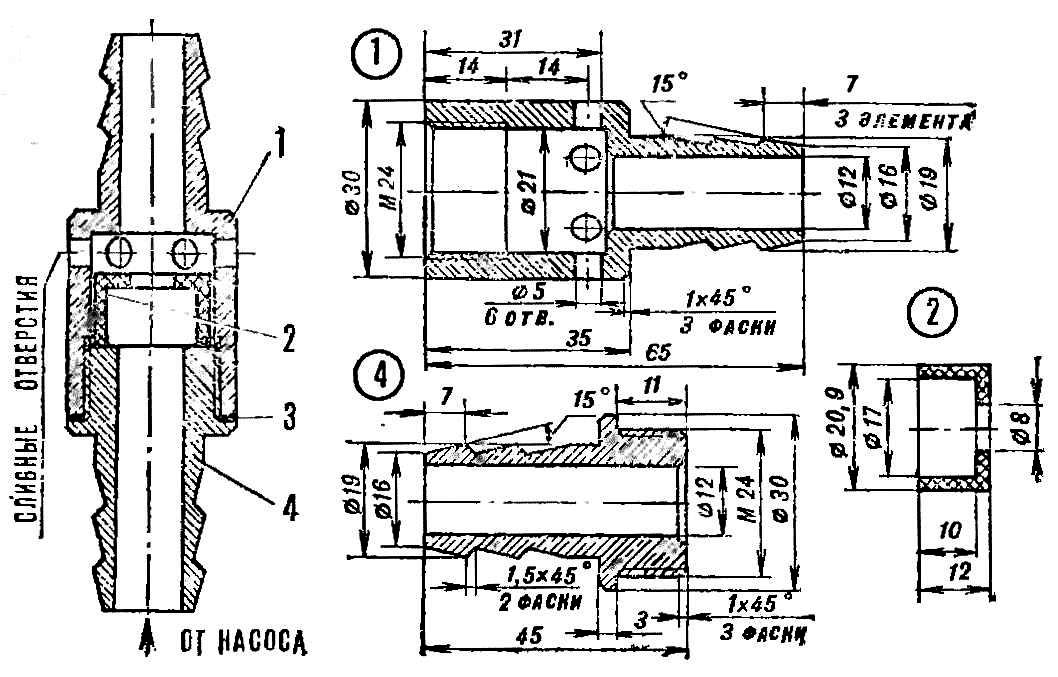
Automatic drain valve device (click to enlarge): 1 - valve body (brass, bronze), 2 - piston (textolite, fluoroplast, ebonite), 3 - gasket, 4 - body cover
During operation of the pump, the drain holes made in the housing are blocked by the cylindrical surface of the piston, since the flow of water keeps it in the upper position. When the unit is turned off, the piston under the action of its own weight falls, opens the drain holes and the water supply network is quickly emptied. So, with the dimensions indicated on the drawing, the discharge of the network with a length of about 25 m lasts no more than a minute, so even a 30-degree frost does not have time to bind water in the system.
The only condition for efficient operation is that the hose from the house to the pump must have a constant slope, without kinks and "pockets".
Author: V.Burtsev
 We recommend interesting articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture:
We recommend interesting articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture:
▪ Dirt cleaning machine for a well
▪ self-loading wheelbarrow
▪ light in the greenhouse
 See other articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture.
See other articles Section Tools and mechanisms for agriculture.
 Read and write useful comments on this article.
Read and write useful comments on this article.
<< Back
 Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Latest news of science and technology, new electronics:
Machine for thinning flowers in gardens
02.05.2024
In modern agriculture, technological progress is developing aimed at increasing the efficiency of plant care processes. The innovative Florix flower thinning machine was presented in Italy, designed to optimize the harvesting stage. This tool is equipped with mobile arms, allowing it to be easily adapted to the needs of the garden. The operator can adjust the speed of the thin wires by controlling them from the tractor cab using a joystick. This approach significantly increases the efficiency of the flower thinning process, providing the possibility of individual adjustment to the specific conditions of the garden, as well as the variety and type of fruit grown in it. After testing the Florix machine for two years on various types of fruit, the results were very encouraging. Farmers such as Filiberto Montanari, who has used a Florix machine for several years, have reported a significant reduction in the time and labor required to thin flowers.
... >>
Advanced Infrared Microscope
02.05.2024
Microscopes play an important role in scientific research, allowing scientists to delve into structures and processes invisible to the eye. However, various microscopy methods have their limitations, and among them was the limitation of resolution when using the infrared range. But the latest achievements of Japanese researchers from the University of Tokyo open up new prospects for studying the microworld. Scientists from the University of Tokyo have unveiled a new microscope that will revolutionize the capabilities of infrared microscopy. This advanced instrument allows you to see the internal structures of living bacteria with amazing clarity on the nanometer scale. Typically, mid-infrared microscopes are limited by low resolution, but the latest development from Japanese researchers overcomes these limitations. According to scientists, the developed microscope allows creating images with a resolution of up to 120 nanometers, which is 30 times higher than the resolution of traditional microscopes. ... >>
Air trap for insects
01.05.2024
Agriculture is one of the key sectors of the economy, and pest control is an integral part of this process. A team of scientists from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research-Central Potato Research Institute (ICAR-CPRI), Shimla, has come up with an innovative solution to this problem - a wind-powered insect air trap. This device addresses the shortcomings of traditional pest control methods by providing real-time insect population data. The trap is powered entirely by wind energy, making it an environmentally friendly solution that requires no power. Its unique design allows monitoring of both harmful and beneficial insects, providing a complete overview of the population in any agricultural area. “By assessing target pests at the right time, we can take necessary measures to control both pests and diseases,” says Kapil ... >>
 Random news from the Archive Random news from the Archive Absolutely unbreakable screen for gadgets
19.09.2016
Scientists at the University of Sussex in the UK have invented a shatterproof smartphone screen made not of glass, but of a thin layer of silver nanowire. The researchers promise that the touch conductivity of such a display will be better than that of a glass one.
According to the authors of the project, the material has no scaling restrictions, so it can also be used for touch screens of laptops and TVs. The production of such displays will cost five times less than conventional ones.
Under the layer of glass of a conventional screen are electrodes that are sensitive to finger touches. They are made from indium tin oxide, a rare and expensive material. Silver nanowire offers an alternative, much stronger electrode structure. It can be subdivided into extremely small pieces - pixels - making it suitable for display industries.
Alan Dalton, professor at the University of Sussex and one of the authors of the development, says that each pixel of a conventional display is divided into sub-pixels. Usually there are three of them - for red, green and blue. Approximately the same thickness as a subpixel is a silver nanowire, which makes it possible to make screens with high resolution and makes it possible to create a layer of wire so thin that it retains transparency. At the same time, the film remains so elastic and resistant to mechanical damage that the screen becomes impossible to break.
Alternatively, you can use a hybrid of a silver nanowire and graphene - a layer of carbon atoms connected via sp2 bonds into a hexagonal two-dimensional crystal lattice. Dalton argues that other alternative materials that have previously been proposed for the production of displays either cannot compete with indium tin oxide on technical performance or are too expensive.
The most difficult task was to calculate the smallest allowable subpixel size at which the nanowire and graphene retain their properties. This was done using a mathematical method that is used to describe phase changes (for example, freezing) in ultra-small spaces.
The scientists plan to commercialize the technology with Oxford-based M-Solv UK, which specializes in laser and inkjet micromachining. The company's technical department has already made a successful attempt to incorporate the new material into a multi-touch screen that is cheaper to produce than traditional materials. If the production of 1 sq. m layer of indium oxide and tin costs 40 pounds, then 1 square. m of silver nanowire with graphene costs eight pounds. Thus, the basis for an unbreakable screen can cost several times cheaper than for a regular one.
|
 Other interesting news:
Other interesting news:
▪ Man and chimpanzee: the differences are not so great
▪ Marvell IAP220 Single-Chip System for IoT and Wearable Electronics
▪ Charging electric vehicles on the move
▪ Baldness patch
▪ Boiled water is more harmful than filtered water
 News feed of science and technology, new electronics
News feed of science and technology, new electronics
 Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
Interesting materials of the Free Technical Library:
▪ section of the site Lecture notes, cheat sheets. Selection of articles
▪ article Coward does not play hockey. Popular expression
▪ article Why are there tides? Detailed answer
▪ article Working on a machine for creasing covers and sticking ribbons on the cover. Standard instruction on labor protection
▪ article Varnish for optical instruments. Simple recipes and tips
▪ article Six receivers on one transistor. Encyclopedia of radio electronics and electrical engineering
 Leave your comment on this article:
Leave your comment on this article:
 All languages of this page
All languages of this page
Home page | Library | Articles | Website map | Site Reviews

www.diagram.com.ua
2000-2024







 Arabic
Arabic Bengali
Bengali Chinese
Chinese English
English French
French German
German Hebrew
Hebrew Hindi
Hindi Italian
Italian Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Malay
Malay Polish
Polish Portuguese
Portuguese Spanish
Spanish Turkish
Turkish Ukrainian
Ukrainian Vietnamese
Vietnamese


 See other articles Section
See other articles Section 